[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8664: Nucleotide-driven Triple-state Remodeling of the AAA-ATPase Chann... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8664 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Nucleotide-driven Triple-state Remodeling of the AAA-ATPase Channel in the Activated Human 26S Proteasome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Activated Human 26S Proteasome | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | 26S proteasome / ATP-dependent protease / AAA-ATPase / peptide-unfolding channel / 20S core particle / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor binding / nuclear proteasome complex / host-mediated perturbation of viral transcription / positive regulation of inclusion body assembly / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Omega peptidases / proteasome accessory complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / meiosis I / proteasome regulatory particle / cytosolic proteasome complex ...thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor binding / nuclear proteasome complex / host-mediated perturbation of viral transcription / positive regulation of inclusion body assembly / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Omega peptidases / proteasome accessory complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / meiosis I / proteasome regulatory particle / cytosolic proteasome complex / positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome-activating activity / proteasome regulatory particle, lid subcomplex / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / metal-dependent deubiquitinase activity / negative regulation of programmed cell death / protein K63-linked deubiquitination / Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) / Proteasome assembly / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / proteasome core complex / Somitogenesis / K63-linked deubiquitinase activity / proteasome binding / transcription factor binding / regulation of protein catabolic process / myofibril / proteasome storage granule / general transcription initiation factor binding / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / blastocyst development / protein deubiquitination / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / immune system process / NF-kappaB binding / proteasome endopeptidase complex / endopeptidase activator activity / proteasome core complex, beta-subunit complex / proteasome assembly / threonine-type endopeptidase activity / proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / enzyme regulator activity / inclusion body / ERAD pathway / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome complex / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / TBP-class protein binding / sarcomere / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / stem cell differentiation / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Degradation of DVL / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / lipopolysaccharide binding / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / Degradation of AXIN / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / P-body / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / G2/M Checkpoints / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / Regulation of RUNX3 expression and activity / Hedgehog 'on' state / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / response to virus / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Metalloprotease DUBs / FCERI mediated NF-kB activation / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhu Y / Wang WL | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: Structural mechanism for nucleotide-driven remodeling of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase in the activated human 26S proteasome. Authors: Yanan Zhu / Wei Li Wang / Daqi Yu / Qi Ouyang / Ying Lu / Youdong Mao /   Abstract: The proteasome is a sophisticated ATP-dependent molecular machine responsible for protein degradation in all known eukaryotic cells. It remains elusive how conformational changes of the AAA-ATPase ...The proteasome is a sophisticated ATP-dependent molecular machine responsible for protein degradation in all known eukaryotic cells. It remains elusive how conformational changes of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase in the regulatory particle (RP) control the gating of the substrate-translocation channel leading to the proteolytic chamber of the core particle (CP). Here we report three alternative states of the ATP-γ-S-bound human proteasome, in which the CP gates are asymmetrically open, visualized by cryo-EM at near-atomic resolutions. At least four nucleotides are bound to the AAA-ATPase ring in these open-gate states. Variation in nucleotide binding gives rise to an axial movement of the pore loops narrowing the substrate-translation channel, which exhibit remarkable structural transitions between the spiral-staircase and saddle-shaped-circle topologies. Gate opening in the CP is thus regulated by nucleotide-driven conformational changes of the AAA-ATPase unfoldase. These findings demonstrate an elegant mechanism of allosteric coordination among sub-machines within the human proteasome holoenzyme. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8664.map.gz emd_8664.map.gz | 612.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8664-v30.xml emd-8664-v30.xml emd-8664.xml emd-8664.xml | 57.9 KB 57.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8664.png emd_8664.png | 174.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8664.cif.gz emd-8664.cif.gz | 13.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_8664_additional_1.map.gz emd_8664_additional_1.map.gz emd_8664_additional_2.map.gz emd_8664_additional_2.map.gz | 591 MB 613.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8664 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8664 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8664 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8664 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_8664_validation.pdf.gz emd_8664_validation.pdf.gz | 706.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_8664_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_8664_full_validation.pdf.gz | 705.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_8664_validation.xml.gz emd_8664_validation.xml.gz | 6.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_8664_validation.cif.gz emd_8664_validation.cif.gz | 8.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8664 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8664 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8664 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8664 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5vfqMC  8662C  8663C  8665C  8666C 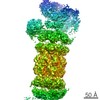 8667C 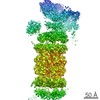 8668C  5vfoC  5vfpC  5vfrC  5vfsC  5vftC  5vfuC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10090 (Title: Nucleotide-Driven Triple-State Remodeling of the AAA-ATPase Channel in the Activated Human 26S Proteasome EMPIAR-10090 (Title: Nucleotide-Driven Triple-State Remodeling of the AAA-ATPase Channel in the Activated Human 26S ProteasomeData size: 2.8 TB Data #1: Motion-corrected single frame micrographs of ATP-gS-bound human proteasome [micrographs - single frame] Data #2: Single-particle stacks of classified conformations [picked particles - multiframe - processed]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8664.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8664.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Activated Human 26S Proteasome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.75 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
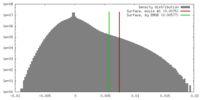
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Activated Human 26S Proteasome, additional map #1
| File | emd_8664_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Activated Human 26S Proteasome, additional map #1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
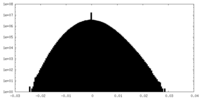
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Activated Human 26S Proteasome, additional map #2
| File | emd_8664_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Activated Human 26S Proteasome, additional map #2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 26S proteasome bound to ATP-gammaS
+Supramolecule #1: 26S proteasome bound to ATP-gammaS
+Macromolecule #1: Proteasome subunit alpha type-6
+Macromolecule #2: Proteasome subunit alpha type-2
+Macromolecule #3: Proteasome subunit alpha type-4
+Macromolecule #4: Proteasome subunit alpha type-7
+Macromolecule #5: Proteasome subunit alpha type-5
+Macromolecule #6: Proteasome subunit alpha type-1
+Macromolecule #7: Proteasome subunit alpha type-3
+Macromolecule #8: Proteasome subunit beta type-6
+Macromolecule #9: Proteasome subunit beta type-7
+Macromolecule #10: Proteasome subunit beta type-3
+Macromolecule #11: Proteasome subunit beta type-2
+Macromolecule #12: Proteasome subunit beta type-5
+Macromolecule #13: Proteasome subunit beta type-1
+Macromolecule #14: Proteasome subunit beta type-4
+Macromolecule #15: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 1
+Macromolecule #16: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 3
+Macromolecule #17: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 12
+Macromolecule #18: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 11
+Macromolecule #19: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 6
+Macromolecule #20: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 7
+Macromolecule #21: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 13
+Macromolecule #22: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 4
+Macromolecule #23: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14
+Macromolecule #24: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 8
+Macromolecule #25: Sem1
+Macromolecule #26: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 7
+Macromolecule #27: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4
+Macromolecule #28: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 8
+Macromolecule #29: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B
+Macromolecule #30: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 10B
+Macromolecule #31: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A
+Macromolecule #32: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2
+Macromolecule #33: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #34: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.3) / Number images used: 66246 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.3) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.3) |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Overall B value: 70 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5vfq: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)