+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8525 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
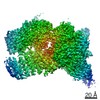
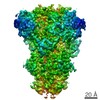
| Title | MalFGK2 ATP-BMOE | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | MalFGK2-ATPBMOE | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationABC-type maltose transporter / ABC-type maltose transporter activity / negative regulation of maltose transport / enzyme IIA-maltose transporter complex / negative regulation of transmembrane transport / maltose transport complex / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex ...ABC-type maltose transporter / ABC-type maltose transporter activity / negative regulation of maltose transport / enzyme IIA-maltose transporter complex / negative regulation of transmembrane transport / maltose transport complex / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA damage response / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 18.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fabre L / Bao H / Innes J / Duong F / Rouiller I | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2017 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2017Title: Negative Stain Single-particle EM of the Maltose Transporter in Nanodiscs Reveals Asymmetric Closure of MalK and Catalytic Roles of ATP, MalE, and Maltose. Authors: Lucien Fabre / Huan Bao / James Innes / Franck Duong / Isabelle Rouiller /  Abstract: The MalE-MalFGK complex is one of the best characterized members of the large and ubiquitous family of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. It is composed of a membrane-spanning heterodimer, ...The MalE-MalFGK complex is one of the best characterized members of the large and ubiquitous family of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. It is composed of a membrane-spanning heterodimer, MalF-MalG; a homodimeric ATPase, MalK; and a periplasmic maltose receptor, MalE. Opening and closure of MalK is coupled to conformational changes in MalF-MalG and the alternate exposition of the substrate-binding site to either side of the membrane. To further define this alternate access mechanism and the impact of ATP, MalE, and maltose on the conformation of the transporter during the transport cycle, we have reconstituted MalFGK in nanodiscs and analyzed its conformations under 10 different biochemical conditions using negative stain single-particle EM. EM map results (at 15-25 Å resolution) indicate that binding of ATP to MalK promotes an asymmetric, semi-closed conformation in accordance with the low ATPase activity of MalFGK In the presence of MalE, the MalK dimer becomes fully closed, gaining the ability to hydrolyze ATP. In the presence of ADP or maltose, MalE·MalFGK remains essentially in a semi-closed symmetric conformation, indicating that release of these ligands is required for the return to the initial state. Taken together, this structural information provides a rationale for the stimulation of MalK ATPase activity by MalE as well as by maltose. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8525.map.gz emd_8525.map.gz | 4.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8525-v30.xml emd-8525-v30.xml emd-8525.xml emd-8525.xml | 11.8 KB 11.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8525.png emd_8525.png | 72.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8525 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8525 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8525 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8525 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8524C  8526C  8527C  8529C  8530C  8531C  8533C  8534C  8535C  8536C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8525.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8525.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | MalFGK2-ATPBMOE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.23 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Maltose transMalKS83Cporter MalFGK2
| Entire | Name: Maltose transMalKS83Cporter MalFGK2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Maltose transMalKS83Cporter MalFGK2
| Supramolecule | Name: Maltose transMalKS83Cporter MalFGK2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 Details: MalFGK2 (MalKS83C) reconstituted in Nanodiscs, with ATP and BMOE |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Recombinant plasmid: pBAD22-FGK |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.05 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Formate / Details: Freshly prepared 1.5% uranyl formate (pH 5) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | MalKS83C reconstituted in nanodiscs at a molar ratio MalFGK2:MSP1D1:lipid (DOPC)of 1:3:60. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 134010 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















