[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8256: Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8256 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
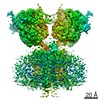
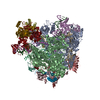
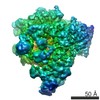
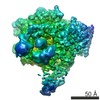
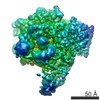
| Title | Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex elucidated by single particle cryo-electron microscopy | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of the complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Tetrameric / ionotropic / glutamate receptors / GluA2 - TARP gamma2 complex / fully occupied / antagonist-bound state / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPresynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / channel regulator activity / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / channel regulator activity / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization / nervous system process / protein targeting to membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine cytoplasm / cellular response to amine stimulus / dendritic spine head / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / perisynaptic space / Activation of AMPA receptors / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / neuromuscular junction development / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / response to lithium ion / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / transmission of nerve impulse / AMPA glutamate receptor clustering / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / cellular response to glycine / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / regulation of receptor recycling / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / membrane depolarization / conditioned place preference / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / response to fungicide / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / glutamate-gated receptor activity / cytoskeletal protein binding / extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / dendrite membrane / excitatory synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / synaptic membrane / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / PDZ domain binding / calcium channel regulator activity / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / regulation of membrane potential / protein tetramerization / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / establishment of protein localization / response to calcium ion / cerebral cortex development / postsynaptic density membrane / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / long-term synaptic potentiation / synaptic vesicle membrane / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / presynapse / growth cone / presynaptic membrane / scaffold protein binding / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / perikaryon / postsynaptic membrane / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / axon / external side of plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / synapse / dendrite / protein kinase binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao Y / Chen S | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2016 Journal: Nature / Year: 2016Title: Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor-TARP complex elucidated by cryo-EM. Abstract: Fast excitatory neurotransmission in the mammalian central nervous system is largely carried out by AMPA-sensitive ionotropic glutamate receptors. Localized within the postsynaptic density of ...Fast excitatory neurotransmission in the mammalian central nervous system is largely carried out by AMPA-sensitive ionotropic glutamate receptors. Localized within the postsynaptic density of glutamatergic spines, AMPA receptors are composed of heterotetrameric receptor assemblies associated with auxiliary subunits, the most common of which are transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins (TARPs). The association of TARPs with AMPA receptors modulates receptor trafficking and the kinetics of receptor gating and pharmacology. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the homomeric rat GluA2 AMPA receptor saturated with TARP γ2 subunits, which shows how the TARPs are arranged with four-fold symmetry around the ion channel domain and make extensive interactions with the M1, M2 and M4 transmembrane helices. Poised like partially opened ‘hands’ underneath the two-fold symmetric ligand-binding domain (LBD) 'clamshells', one pair of TARPs is juxtaposed near the LBD dimer interface, whereas the other pair is near the LBD dimer-dimer interface. The extracellular ‘domains’ of TARP are positioned to not only modulate LBD clamshell closure, but also affect conformational rearrangements of the LBD layer associated with receptor activation and desensitization, while the TARP transmembrane domains buttress the ion channel pore. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8256.map.gz emd_8256.map.gz | 96.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8256-v30.xml emd-8256-v30.xml emd-8256.xml emd-8256.xml | 12.5 KB 12.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8256.png emd_8256.png | 123.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8256.cif.gz emd-8256.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8256 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8256 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5kk2MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8256.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8256.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of the complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.35 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex
| Entire | Name: Fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor - TARP complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 99.530391 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GVSSNSIQIG GLFPRGADQE YSAFRVGMVQ FSTSEFRLTP HIDNLEVANS FAVTNAFCSQ FSRGVYAIF GFYDKKSVNT ITSFCGTLHV SFITPSFPTD GTHPFVIQMR PDLKGALLSL IEYYQWDKFA YLYDSDRGLS T LQAVLDSA ...String: MQKIMHISVL LSPVLWGLIF GVSSNSIQIG GLFPRGADQE YSAFRVGMVQ FSTSEFRLTP HIDNLEVANS FAVTNAFCSQ FSRGVYAIF GFYDKKSVNT ITSFCGTLHV SFITPSFPTD GTHPFVIQMR PDLKGALLSL IEYYQWDKFA YLYDSDRGLS T LQAVLDSA AEKKWQVTAI NVGNINNDKK DETYRSLFQD LELKKERRVI LDCERDKVND IVDQVITIGK HVKGYHYIIA NL GFTDGDL LKIQFGGANV SGFQIVDYDD SLVSKFIERW STLEEKEYPG AHTATIKYTS ALTYDAVQVM TEAFRNLRKQ RIE ISRRGN AGDCLANPAV PWGQGVEIER ALKQVQVEGL SGNIKFDQNG KRINYTINIM ELKTNGPRKI GYWSEVDKMV VTLT ELPSG NDTSGLENKT VVVTTILESP YVMMKKNHEM LEGNERYEGY CVDLAAEIAK HCGFKYKLTI VGDGKYGARD ADTKI WNGM VGELVYGKAD IAIAPLTITL VREEVIDFSK PFMSLGISIM IKKPQKSKPG VFSFLDPLAY EIWMCIVFAY IGVSVV LFL VSRFSPYEWH TEEFEDGRET QSSESTNEFG IFNSLWFSLG AFMRQGCDIS PRSLSGRIVG GVWWFFTLII ISSYTAN LA AFLTVERMVS PIESAEDLSK QTEIAYGTLD SGSTKEFFRR SKIAVFDKMW TYMRSAEPSV FVRTTAEGVA RVRKSKGK Y AYLLESTMNE YIEQRKPCDT MKVGGNLDSK GYGIATPKGS SLGNAVNLAV LKLNEQGLLD KLKNKWWYDK GECGSGGGD SKEKTSALSL SNVAGVFYIL VGGLGLAMLV ALIEFCYKSR AEAKRMKVAK NPQNINPSSS QNSQNFATDY KDDDDKEGYN VYGIESVKI UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.938746 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGLFDRGVQM LLTTVGAFAA FSLMTIAVGT DYWLYSRGVC KTKSVSENET SKKNEEVMTH SGLWRTCCLE GNFKGLCKQI DHFPEDADY EADTAEYFLR AVRASSIFPI LSVILLFMGG LCIAASEFYK TRHNIILSAG IFFVSAGLSN IIGIIVYISA N AGDPSKSD ...String: MGLFDRGVQM LLTTVGAFAA FSLMTIAVGT DYWLYSRGVC KTKSVSENET SKKNEEVMTH SGLWRTCCLE GNFKGLCKQI DHFPEDADY EADTAEYFLR AVRASSIFPI LSVILLFMGG LCIAASEFYK TRHNIILSAG IFFVSAGLSN IIGIIVYISA N AGDPSKSD SKKNSYSYGW SFYFGALSFI IAEMVGVLAV HMFIDRHKQL RATARATDYL QASAITRIPS YRYRYQRRSR SS SRSTEPS HSRDASPVGV KGFNTLPSTE ISMYTLSRDP LKAATTPTAT YNSDRDNSFL QVHNCIQKDS KDSLHANTAN RRT TPV UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-2 subunit |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 55.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5kk2: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)