[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-48074: Cryo-EM structure of Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex b... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
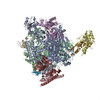
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to an apo RECQL5 helicase (RECQL5 IRI Module focused-classified) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | cryo-EM structure of the Stalled Human RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to the apo RECQL5 Helicase (RECQL5 IRI Module focused classified) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | translocation / Human RNA polymerase II / RECQL5 helicase / IRI Module / TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSFERASE-DNA-RNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmitotic DNA-templated DNA replication / microfibril binding / chromosome separation / cellular response to camptothecin / four-way junction helicase activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / transcription preinitiation complex / FGFR2 alternative splicing / MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis ...mitotic DNA-templated DNA replication / microfibril binding / chromosome separation / cellular response to camptothecin / four-way junction helicase activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / transcription preinitiation complex / FGFR2 alternative splicing / MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / Signaling by FGFR2 IIIa TM / DNA 3'-5' helicase / DNA metabolic process / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / RNA polymerase II complex binding / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / RNA polymerase II, core complex / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / DNA helicase activity / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / positive regulation of RNA splicing / replication fork / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / promoter-specific chromatin binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / DNA-templated transcription termination / helicase activity / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / kinase binding / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / mitotic cell cycle / chromosome / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exoribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA replication / hydrolase activity / cell division / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA repair / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Florez Ariza A / Lue N / Nogales E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation | Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Title: Structural insights into transcriptional regulation by the helicase RECQL5. Authors: Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza / Nicholas Z Lue / Patricia Grob / Benjamin Kaeser / Jie Fang / Susanne A Kassube / Eva Nogales /  Abstract: Transcription and its regulation pose a major challenge for genome stability. The helicase RECQL5 has been proposed as an important factor to help safeguard the genome, and is the only member of the ...Transcription and its regulation pose a major challenge for genome stability. The helicase RECQL5 has been proposed as an important factor to help safeguard the genome, and is the only member of the human RecQ helicase family that directly binds to RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) and affects its progression. RECQL5 mitigates transcription stress and genome instability in cells, yet the molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon is unclear. Here, we employ cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the structures of stalled Pol II elongation complexes (ECs) bound to RECQL5. Our structures reveal the molecular interactions stabilizing RECQL5 binding to the Pol II EC and highlight its role as a transcriptional roadblock. Additionally, we find that RECQL5 can modulate the Pol II translocation state. In its nucleotide-free state, RECQL5 mechanically twists the downstream DNA in the EC, and upon nucleotide binding, it undergoes a conformational change that allosterically induces Pol II towards a post-translocation state. We propose this mechanism may help restart Pol II elongation and therefore contribute to reduction of transcription stress. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_48074.map.gz emd_48074.map.gz | 105.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-48074-v30.xml emd-48074-v30.xml emd-48074.xml emd-48074.xml | 25.2 KB 25.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_48074_fsc.xml emd_48074_fsc.xml | 11.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_48074.png emd_48074.png | 88.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_48074_msk_1.map emd_48074_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-48074.cif.gz emd-48074.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_48074_additional_1.map.gz emd_48074_additional_1.map.gz emd_48074_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48074_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48074_half_map_2.map.gz emd_48074_half_map_2.map.gz | 115.9 MB 98.2 MB 98.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48074 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48074 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48074 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48074 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9ei2MC  9ehzC  9ei1C  9ei3C  9ei4C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_48074.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_48074.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | cryo-EM structure of the Stalled Human RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to the apo RECQL5 Helicase (RECQL5 IRI Module focused classified) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_48074_msk_1.map emd_48074_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Unsharpened cryo-EM density map
| File | emd_48074_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened cryo-EM density map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 1
| File | emd_48074_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-map 2
| File | emd_48074_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Stalled Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to an ap...
| Entire | Name: Stalled Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to an apo RECQL5 helicase (RECQL5 IRI Module-focused classified) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Stalled Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to an ap...
| Supramolecule | Name: Stalled Human RNA polymerase II Elongation Complex bound to an apo RECQL5 helicase (RECQL5 IRI Module-focused classified) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 490 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 217.420047 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MHGGGPPSGD SACPLRTIKR VQFGVLSPDE LKRMSVTEGG IKYPETTEGG RPKLGGLMDP RQGVIERTGR CQTCAGNMTE CPGHFGHIE LAKPVFHVGF LVKTMKVLRC VCFFCSKLLV DSNNPKIKDI LAKSKGQPKK RLTHVYDLCK GKNICEGGEE M DNKFGVEQ ...String: MHGGGPPSGD SACPLRTIKR VQFGVLSPDE LKRMSVTEGG IKYPETTEGG RPKLGGLMDP RQGVIERTGR CQTCAGNMTE CPGHFGHIE LAKPVFHVGF LVKTMKVLRC VCFFCSKLLV DSNNPKIKDI LAKSKGQPKK RLTHVYDLCK GKNICEGGEE M DNKFGVEQ PEGDEDLTKE KGHGGCGRYQ PRIRRSGLEL YAEWKHVNED SQEKKILLSP ERVHEIFKRI SDEECFVLGM EP RYARPEW MIVTVLPVPP LSVRPAVVMQ GSARNQDDLT HKLADIVKIN NQLRRNEQNG AAAHVIAEDV KLLQFHVATM VDN ELPGLP RAMQKSGRPL KSLKQRLKGK EGRVRGNLMG KRVDFSARTV ITPDPNLSID QVGVPRSIAA NMTFAEIVTP FNID RLQEL VRRGNSQYPG AKYIIRDNGD RIDLRFHPKP SDLHLQTGYK VERHMCDGDI VIFNRQPTLH KMSMMGHRVR ILPWS TFRL NLSVTTPYNA DFDGDEMNLH LPQSLETRAE IQELAMVPRM IVTPQSNRPV MGIVQDTLTA VRKFTKRDVF LERGEV MNL LMFLSTWDGK VPQPAILKPR PLWTGKQIFS LIIPGHINCI RTHSTHPDDE DSGPYKHISP GDTKVVVENG ELIMGIL CK KSLGTSAGSL VHISYLEMGH DITRLFYSNI QTVINNWLLI EGHTIGIGDS IADSKTYQDI QNTIKKAKQD VIEVIEKA H NNELEPTPGN TLRQTFENQV NRILNDARDK TGSSAQKSLS EYNNFKSMVV SGAKGSKINI SQVIAVVGQQ NVEGKRIPF GFKHRTLPHF IKDDYGPESR GFVENSYLAG LTPTEFFFHA MGGREGLIDT AVKTAETGYI QRRLIKSMES VMVKYDATVR NSINQVVQL RYGEDGLAGE SVEFQNLATL KPSNKAFEKK FRFDYTNERA LRRTLQEDLV KDVLSNAHIQ NELEREFERM R EDREVLRV IFPTGDSKVV LPCNLLRMIW NAQKIFHINP RLPSDLHPIK VVEGVKELSK KLVIVNGDDP LSRQAQENAT LL FNIHLRS TLCSRRMAEE FRLSGEAFDW LLGEIESKFN QAIAHPGEMV GALAAQSLGE PATQMTLNTF HYAGVSAKNV TLG VPRLKE LINISKKPKT PSLTVFLLGQ SARDAERAKD ILCRLEHTTL RKVTANTAIY YDPNPQSTVV AEDQEWVNVY YEMP DFDVA RISPWLLRVE LDRKHMTDRK LTMEQIAEKI NAGFGDDLNC IFNDDNAEKL VLRIRIMNSD ENKMQEEEEV VDKMD DDVF LRCIESNMLT DMTLQGIEQI SKVYMHLPQT DNKKKIIITE DGEFKALQEW ILETDGVSLM RVLSEKDVDP VRTTSN DIV EIFTVLGIEA VRKALERELY HVISFDGSYV NYRHLALLCD TMTCRGHLMA ITRHGVNRQD TGPLMKCSFE ETVDVLM EA AAHGESDPMK GVSENIMLGQ LAPAGTGCFD LLLDAEKCKY GMEIPTNIPG LGAAGPTGMF FGSAPSPMGG ISPAMTPW N QGATPAYGAW SPSVGSGMTP GAAGFSPSAA SDASGFSPGY SPAWSPTPGS PGSPGPSSPY IPSPGGAMSP SYSPTSPAY EPRSPGGYTP QSPSYSPTSP SYSPTSPSYS PTSPNYSPTS PSYSPTSPSY SPTSPSYSPT SPSYSPTSPS YSPTSPSYSP TSPSYSPTS PSYSPTSPSY SPTSPSYSPT SPSYSPTSPS YSPTSPSYSP TSPSYSPTSP SYSPTSPNYS PTSPNYTPTS P SYSPTSPS YSPTSPNYTP TSPNYSPTSP SYSPTSPSYS PTSPSYSPSS PRYTPQSPTY TPSSPSYSPS SPSYSPASPK YT PTSPSYS PSSPEYTPTS PKYSPTSPKY SPTSPKYSPT SPTYSPTTPK YSPTSPTYSP TSPVYTPTSP KYSPTSPTYS PTS PKYSPT SPTYSPTSPK GSTYSPTSPG YSPTSPTYSL TSPAISPDDS DEEN UniProtKB: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP-dependent DNA helicase Q5
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-dependent DNA helicase Q5 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: DNA 3'-5' helicase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 109.024859 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSSHHTTFPF DPERRVRSTL KKVFGFDSFK TPLQESATMA VVKGNKDVFV CMPTGAGKSL CYQLPALLAK GITIVVSPLI ALIQDQVDH LLTLKVRVSS LNSKLSAQER KELLADLERE KPQTKILYIT PEMAASSSFQ PTLNSLVSRH LLSYLVVDEA H CVSQWGHD ...String: MSSHHTTFPF DPERRVRSTL KKVFGFDSFK TPLQESATMA VVKGNKDVFV CMPTGAGKSL CYQLPALLAK GITIVVSPLI ALIQDQVDH LLTLKVRVSS LNSKLSAQER KELLADLERE KPQTKILYIT PEMAASSSFQ PTLNSLVSRH LLSYLVVDEA H CVSQWGHD FRPDYLRLGA LRSRLGHAPC VALTATATPQ VQEDVFAALH LKKPVAIFKT PCFRANLFYD VQFKELISDP YG NLKDFCL KALGQEADKG LSGCGIVYCR TREACEQLAI ELSCRGVNAK AYHAGLKASE RTLVQNDWME EKVPVIVATI SFG MGVDKA NVRFVAHWNI AKSMAGYYQE SGRAGRDGKP SWCRLYYSRN DRDQVSFLIR KEVAKLQEKR GNKASDKATI MAFD ALVTF CEELGCRHAA IAKYFGDALP ACAKGCDHCQ NPTAVRRRLE ALERSSSWSK TCIGPSQGNG FDPELYEGGR KGYGD FSRY DEGSGGSGDE GRDEAHKREW NLFYQKQMQL RKGKDPKIEE FVPPDENCPL KEASSRRIPR LTVKAREHCL RLLEEA LSS NRQSTRTADE ADLRAKAVEL EHETFRNAKV ANLYKASVLK KVADIHRASK DGQPYDMGGS AKSCSAQAEP PEPNEYD IP PASHVYSLKP KRVGAGFPKG SCPFQTATEL METTRIREQA PQPERGGEHE PPSRPCGLLD EDGSEPLPGP RGEVPGGS A HYGGPSPEKK AKSSSGGSSL AKGRASKKQQ LLATAAHKDS QSIARFFCRR VESPALLASA PEAEGACPSC EGVQGPPMA PEKYTGEEDG AGGHSPAPPQ TEECLRERPS TCPPRDQGTP EVQPTPAKDT WKGKRPRSQQ ENPESQPQKR PRPSAKPSVV AEVKGSVSA SEQGTLNPTA QDPFQLSAPG VSLKEAANVV VKCLTPFYKE GKFASKELFK GFARHLSHLL TQKTSPGRSV K EEAQNLIR HFFHGRARCE SEADWHGLCG PQR UniProtKB: ATP-dependent DNA helicase Q5 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)