+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
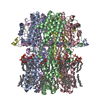
| タイトル | BEST2 + GABA open state | |||||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | sharp_map | |||||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | calcium-activated chloride channel / GABA-bound anion channel / channel-activator complex / membrane protein | |||||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報intracellularly ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / ligand-gated monoatomic anion channel activity / bicarbonate channel activity / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / chloride channel activity / membrane depolarization / chloride channel complex / Stimuli-sensing channels / sensory perception of smell / basolateral plasma membrane ...intracellularly ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / ligand-gated monoatomic anion channel activity / bicarbonate channel activity / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / chloride channel activity / membrane depolarization / chloride channel complex / Stimuli-sensing channels / sensory perception of smell / basolateral plasma membrane / cilium / metal ion binding / plasma membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.31 Å | |||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Owji AP / Kittredge AK / Zhang Y / Yang T | |||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 4件 米国, 4件
| |||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2024タイトル: Neurotransmitter-bound bestrophin channel structures reveal small molecule drug targeting sites for disease treatment. 著者: Aaron P Owji / Jingyun Dong / Alec Kittredge / Jiali Wang / Yu Zhang / Tingting Yang /  要旨: Best1 and Best2 are two members of the bestrophin family of anion channels critically involved in the prevention of retinal degeneration and maintenance of intraocular pressure, respectively. Here, ...Best1 and Best2 are two members of the bestrophin family of anion channels critically involved in the prevention of retinal degeneration and maintenance of intraocular pressure, respectively. Here, we solved glutamate- and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-bound Best2 structures, which delineate an intracellular glutamate binding site and an extracellular GABA binding site on Best2, respectively, identified extracellular GABA as a permeable activator of Best2, and elucidated the co-regulation of Best2 by glutamate, GABA and glutamine synthetase in vivo. We further identified multiple small molecules as activators of the bestrophin channels. Extensive analyses were carried out for a potent activator, 4-aminobenzoic acid (PABA): PABA-bound Best1 and Best2 structures are solved and illustrate the same binding site as in GABA-bound Best2; PABA treatment rescues the functional deficiency of patient-derived Best1 mutations. Together, our results demonstrate the mechanism and potential of multiple small molecule candidates as clinically applicable drugs for bestrophin-associated diseases/conditions. | |||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_47306.map.gz emd_47306.map.gz | 230.4 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-47306-v30.xml emd-47306-v30.xml emd-47306.xml emd-47306.xml | 19.7 KB 19.7 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_47306.png emd_47306.png | 142.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47306.cif.gz emd-47306.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_47306_additional_1.map.gz emd_47306_additional_1.map.gz emd_47306_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47306_half_map_1.map.gz emd_47306_half_map_2.map.gz emd_47306_half_map_2.map.gz | 122.9 MB 226.8 MB 226.8 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47306 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47306 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47306 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47306 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_47306_validation.pdf.gz emd_47306_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_47306_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47306_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_47306_validation.xml.gz emd_47306_validation.xml.gz | 15.8 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_47306_validation.cif.gz emd_47306_validation.cif.gz | 18.7 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47306 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47306 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47306 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47306 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ | 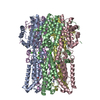 9dyjMC 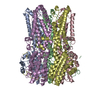 9dyhC  9dyiC 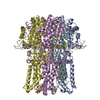 9dykC  9dylC  9dymC  9dynC  9dyoC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_47306.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_47306.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 244.1 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | sharp_map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-追加マップ: full map
| ファイル | emd_47306_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | full_map | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: halfB
| ファイル | emd_47306_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | halfB | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: halfA
| ファイル | emd_47306_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | halfA | ||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : BEST2 + GABA open state
| 全体 | 名称: BEST2 + GABA open state |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: BEST2 + GABA open state
| 超分子 | 名称: BEST2 + GABA open state / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 286 KDa |
-分子 #1: Bestrophin-2a
| 分子 | 名称: Bestrophin-2a / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 5 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 57.188637 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MTVTYTARVA NARFGGFSQL LLLWRGSIYK LLWRELLCFL GFYMALSAAY RFVLTEGQKR YFEKLVIYCD QYASLIPVSF VLGFYVTLV VNRWWSQYLC MPLPDALMCV VAGTVHGRDD RGRLYRRTLM RYAGLSAVLI LRSVSTAVFK RFPTIDHVVE A GFMTREER ...文字列: MTVTYTARVA NARFGGFSQL LLLWRGSIYK LLWRELLCFL GFYMALSAAY RFVLTEGQKR YFEKLVIYCD QYASLIPVSF VLGFYVTLV VNRWWSQYLC MPLPDALMCV VAGTVHGRDD RGRLYRRTLM RYAGLSAVLI LRSVSTAVFK RFPTIDHVVE A GFMTREER KKFENLNSSY NKYWVPCVWF SNLAAQARRE GRIRDNSALK LLLEELNVFR GKCGMLFHYD WISVPLVYTQ VV TIALYSY FLACLIGRQF LDPAQGYKDH DLDLCVPIFT LLQFFFYAGW LKVAEQLINP FGEDDDDFET NFLIDRNFQV SML AVDEMY DDLAVLEKDL YWDAAEARAP YTAATVFQLR QPSFQGSTFD ITLAKEDMQF QRLDGLDGPM GEAPGDFLQR LLPA GAGMV AGGPLGRRLS FLLRKNSCVS EASTGASCSC AVVPEGAAPE CSCGDPLLDP GLPEPEAPPP AGPEPLTLIP GPVEP FSIV TMPGPRGPAP PWLPSPIGEE EENLA UniProtKB: Bestrophin-2a |
-分子 #2: CALCIUM ION
| 分子 | 名称: CALCIUM ION / タイプ: ligand / ID: 2 / コピー数: 5 / 式: CA |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 40.078 Da |
-分子 #3: GAMMA-AMINO-BUTANOIC ACID
| 分子 | 名称: GAMMA-AMINO-BUTANOIC ACID / タイプ: ligand / ID: 3 / コピー数: 5 / 式: ABU |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 103.12 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ABU: |
-分子 #4: CHLORIDE ION
| 分子 | 名称: CHLORIDE ION / タイプ: ligand / ID: 4 / コピー数: 1 / 式: CL |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 35.453 Da |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.8 構成要素:
| ||||||||||||
| グリッド | モデル: UltrAuFoil R0./1 / 材質: GOLD | ||||||||||||
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 283 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / 実像数: 1130 / 平均電子線量: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | C2レンズ絞り径: 100.0 µm / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.5 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.8 µm / 倍率(公称値): 105000 |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 初期モデル | モデルのタイプ: OTHER / 詳細: ab initio reconstruction |
|---|---|
| 最終 再構成 | 想定した対称性 - 点群: C5 (5回回転対称) / 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 2.31 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 使用した粒子像数: 103839 |
| 初期 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| 最終 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)