+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Phosphorylated human NKCC1 in complex with bumetanide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Additional Map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Phosphorylation / sodium potassium chloride cotransporter / outward-open / bumetanide / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of cell volume / positive regulation of aspartate secretion / transepithelial ammonium transport / regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion / cell body membrane / metal ion transmembrane transporter activity / inorganic anion import across plasma membrane / inorganic cation import across plasma membrane / chloride:monoatomic cation symporter activity / sodium:potassium:chloride symporter activity ...positive regulation of cell volume / positive regulation of aspartate secretion / transepithelial ammonium transport / regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion / cell body membrane / metal ion transmembrane transporter activity / inorganic anion import across plasma membrane / inorganic cation import across plasma membrane / chloride:monoatomic cation symporter activity / sodium:potassium:chloride symporter activity / Cation-coupled Chloride cotransporters / potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity / transepithelial chloride transport / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / negative regulation of vascular wound healing / ammonium transmembrane transport / sodium ion homeostasis / ammonium channel activity / chloride ion homeostasis / cell projection membrane / cellular response to chemokine / T cell chemotaxis / potassium ion homeostasis / intracellular sodium ion homeostasis / sodium ion import across plasma membrane / cell volume homeostasis / cellular response to potassium ion / hyperosmotic response / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / lateral plasma membrane / transport across blood-brain barrier / monoatomic ion transport / sodium ion transmembrane transport / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / basal plasma membrane / chloride transmembrane transport / cell periphery / cell projection / Hsp90 protein binding / extracellular vesicle / protein-folding chaperone binding / cell body / basolateral plasma membrane / neuron projection / apical plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / protein kinase binding / extracellular exosome / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao YX / Cao EH | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2025 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis for human NKCC1 inhibition by loop diuretic drugs. Authors: Yongxiang Zhao / Pietro Vidossich / Biff Forbush / Junfeng Ma / Jesse Rinehart / Marco De Vivo / Erhu Cao /    Abstract: Na-K-Cl cotransporters functions as an anion importers, regulating trans-epithelial chloride secretion, cell volume, and renal salt reabsorption. Loop diuretics, including furosemide, bumetanide, and ...Na-K-Cl cotransporters functions as an anion importers, regulating trans-epithelial chloride secretion, cell volume, and renal salt reabsorption. Loop diuretics, including furosemide, bumetanide, and torsemide, antagonize both NKCC1 and NKCC2, and are first-line medicines for the treatment of edema and hypertension. NKCC1 activation by the molecular crowding sensing WNK kinases is critical if cells are to combat shrinkage during hypertonic stress; however, how phosphorylation accelerates NKCC1 ion transport remains unclear. Here, we present co-structures of phospho-activated NKCC1 bound with furosemide, bumetanide, or torsemide showing that furosemide and bumetanide utilize a carboxyl group to coordinate and co-occlude a K, whereas torsemide encroaches and expels the K from the site. We also found that an amino-terminal segment of NKCC1, once phosphorylated, interacts with the carboxyl-terminal domain, and together, they engage with intracellular ion exit and appear to be poised to facilitate rapid ion translocation. Together, these findings enhance our understanding of NKCC-mediated epithelial ion transport and the molecular mechanisms of its inhibition by loop diuretics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45084.map.gz emd_45084.map.gz | 94.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45084-v30.xml emd-45084-v30.xml emd-45084.xml emd-45084.xml | 21.2 KB 21.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_45084.png emd_45084.png | 48.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45084.cif.gz emd-45084.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45084_additional_1.map.gz emd_45084_additional_1.map.gz emd_45084_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45084_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45084_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45084_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.2 MB 95.5 MB 95.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45084 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45084 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45084 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45084 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_45084_validation.pdf.gz emd_45084_validation.pdf.gz | 874.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_45084_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_45084_full_validation.pdf.gz | 874.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_45084_validation.xml.gz emd_45084_validation.xml.gz | 13.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_45084_validation.cif.gz emd_45084_validation.cif.gz | 16 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45084 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45084 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45084 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-45084 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9c0hMC  9c0eC  9c0gC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45084.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45084.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Additional Map | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Phosphorylated human NKCC1 in complex with bumetanide
| Entire | Name: Phosphorylated human NKCC1 in complex with bumetanide |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Phosphorylated human NKCC1 in complex with bumetanide
| Supramolecule | Name: Phosphorylated human NKCC1 in complex with bumetanide / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Solute carrier family 12 member 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Solute carrier family 12 member 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 131.743391 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MEPRPTAPSS GAPGLAGVGE TPSAAALAAA RVELPGTAVP SVPEDAAPAS RDGGGVRDEG PAAAGDGLGR PLGPTPSQSR FQVDLVSEN AGRAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAGA GAGAKQTPAD GEASGESEPA KGSEEAKGRF RVNFVDPAAS SSAEDSLSDA A GVGVDGPN ...String: MEPRPTAPSS GAPGLAGVGE TPSAAALAAA RVELPGTAVP SVPEDAAPAS RDGGGVRDEG PAAAGDGLGR PLGPTPSQSR FQVDLVSEN AGRAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAGA GAGAKQTPAD GEASGESEPA KGSEEAKGRF RVNFVDPAAS SSAEDSLSDA A GVGVDGPN VSFQNGGDTV LSEGSSLHSG GGGGSGHHQH YYYDTHTNTY YLR(TPO)FGHN(TPO)M DAVPRIDHYR HTAA QLGEK LLRPSLAELH DELEKEPFED GFANGEESTP TRDAVVTYTA ESKGVVKFGW IKGVLVRCML NIWGVMLFIR LSWIV GQAG IGLSVLVIMM ATVVTTITGL STSAIATNGF VRGGGAYYLI SRSLGPEFGG AIGLIFAFAN AVAVAMYVVG FAETVV ELL KEHSILMIDE INDIRIIGAI TVVILLGISV AGMEWEAKAQ IVLLVILLLA IGDFVIGTFI PLESKKPKGF FGYKSEI FN ENFGPDFREE ETFFSVFAIF FPAATGILAG ANISGDLADP QSAIPKGTLL AILITTLVYV GIAVSVGSCV VRDATGNV N DTIVTELTNC TSAACKLNFD FSSCESSPCS YGLMNNFQVM SMVSGFTPLI SAGIFSATLS SALASLVSAP KIFQALCKD NIYPAFQMFA KGYGKNNEPL RGYILTFLIA LGFILIAELN VIAPIISNFF LASYALINFS VFHASLAKSP GWRPAFKYYN MWISLLGAI LCCIVMFVIN WWAALLTYVI VLGLYIYVTY KKPDVNWGSS TQALTYLNAL QHSIRLSGVE DHVKNFRPQC L VMTGAPNS RPALLHLVHD FTKNVGLMIC GHVHMGPRRQ AMKEMSIDQA KYQRWLIKNK MKAFYAPVHA DDLREGAQYL MQ AAGLGRM KPNTLVLGFK KDWLQADMRD VDMYINLFHD AFDIQYGVVV IRLKEGLDIS HLQGQEELLS SQEKSPGTKD VVV SVEYSK KSDLDTSKPL SEKPITHKVE EEDGKTATQP LLKKESKGPI VPLNVADQKL LEASTQFQKK QGKNTIDVWW LFDD GGLTL LIPYLLTTKK KWKDCKIRVF IGGKINRIDH DRRAMATLLS KFRIDFSDIM VLGDINTKPK KENIIAFEEI IEPYR LHED DKEQDIADKM KEDEPWRITD NELELYKTKT YRQIRLNELL KEHSSTANII VMSLPVARKG AVSSALYMAW LEALSK DLP PILLVRGNHQ SVLTFYS UniProtKB: Solute carrier family 12 member 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: CHLORIDE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CHLORIDE ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.453 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: 3-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid
| Macromolecule | Name: 3-(butylamino)-4-phenoxy-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 82U |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 364.416 Da |
| Chemical component information | 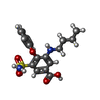 ChemComp-82U: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





