+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
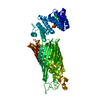
| Title | E. coli cellulose synthase BcsAG3B6 complex - Consensus map | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Low resolution consensus map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) / catalytic BcsA-B / c-di-GMP binding protein / membrane proteins / TRANSFERASE | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.67 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Verma P / Zimmer J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Insights into phosphoethanolamine cellulose synthesis and secretion across the Gram-negative cell envelope. Authors: Preeti Verma / Ruoya Ho / Schuyler A Chambers / Lynette Cegelski / Jochen Zimmer /  Abstract: Phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) cellulose is a naturally occurring modified cellulose produced by several Enterobacteriaceae. The minimal components of the E. coli cellulose synthase complex include the ...Phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) cellulose is a naturally occurring modified cellulose produced by several Enterobacteriaceae. The minimal components of the E. coli cellulose synthase complex include the catalytically active BcsA enzyme, a hexameric semicircle of the periplasmic BcsB protein, and the outer membrane (OM)-integrated BcsC subunit containing periplasmic tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR). Additional subunits include BcsG, a membrane-anchored periplasmic pEtN transferase associated with BcsA, and BcsZ, a periplasmic cellulase of unknown biological function. While cellulose synthesis and translocation by BcsA are well described, little is known about its pEtN modification and translocation across the cell envelope. We show that the N-terminal cytosolic domain of BcsA positions three BcsG copies near the nascent cellulose polymer. Further, the semicircle's terminal BcsB subunit tethers the N-terminus of a single BcsC protein in a trans-envelope secretion system. BcsC's TPR motifs bind a putative cello-oligosaccharide near the entrance to its OM pore. Additionally, we show that only the hydrolytic activity of BcsZ but not the subunit itself is necessary for cellulose secretion, suggesting a secretion mechanism based on enzymatic removal of translocation incompetent cellulose. Lastly, protein engineering introduces cellulose pEtN modification in orthogonal cellulose biosynthetic systems. These findings advance our understanding of pEtN cellulose modification and secretion. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44793.map.gz emd_44793.map.gz | 167.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44793-v30.xml emd-44793-v30.xml emd-44793.xml emd-44793.xml | 17.7 KB 17.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44793_fsc.xml emd_44793_fsc.xml | 12 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44793.png emd_44793.png | 129.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44793.cif.gz emd-44793.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44793_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44793_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44793_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44793_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.3 MB 165.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44793 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44793 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44793 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44793 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44793.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44793.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Low resolution consensus map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_44793_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_44793_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Bacterial cellulose synthase BcsA-BcsG3-BcsB6 complex
| Entire | Name: Bacterial cellulose synthase BcsA-BcsG3-BcsB6 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Bacterial cellulose synthase BcsA-BcsG3-BcsB6 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Bacterial cellulose synthase BcsA-BcsG3-BcsB6 complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Proteins: 1. Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit A (BcsA) 2. Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit B (BcsB) 3. Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit G (BcsG) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit A (BcsA)
| Macromolecule | Name: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit A (BcsA) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: mgsiltrwll ippvnarlig ryrdyrrhga safsatlgcf wmilawifip lehprwqrir aehknlyph inasrprpld pvryliqtcw lligasrket pkprrrafsg lqnirgryhq w mnelperv shktqhldek kelghlsaga rrlilgiivt fslilalicv ...String: mgsiltrwll ippvnarlig ryrdyrrhga safsatlgcf wmilawifip lehprwqrir aehknlyph inasrprpld pvryliqtcw lligasrket pkprrrafsg lqnirgryhq w mnelperv shktqhldek kelghlsaga rrlilgiivt fslilalicv tqpfnplaqf if lmllwgv alivrrmpgr fsalmlivls ltvscryiww rytstlnwdd pvslvcglil lfa etyawi vlvlgyfqvv wplnrqpvpl pkdmslwpsv difvptyned lnvvkntiya slgi dwpkd klniwilddg greefrqfaq nvgvkyiart thehakagni nnalkyakge fvsif dcdh vptrsflqmt mgwflkekql ammqtphhff spdpfernlg rfrktpnegt lfyglv qdg ndmwdatffc gscavirrkp ldeiggiave tvtedahtsl rlhrrgytsa ymripqa ag lateslsahi gqrirwargm vqifrldnpl tgkglkfaqr lcyvnamfhf lsgiprli f ltaplaflll hayiiyapal mialfvlphm ihasltnski qgkyrhsfws eiyetvlaw yiapptlval inphkgkfnv takgglveee yvdwvisrpy iflvllnlvg vavgiwryfy gpptemltv vvsmvwvfyn livlggavav sveskqvrrs hrvemtmpaa iaredghlfs c tvqdfsdg glgikingqa qilegqkvnl llkrgqqeyv fptqvarvmg nevglklmpl tt qqhidfv qctfaradtw alwqdsyped kpleslldil klgfrgyrhl aefapssvkg ifr vltslv swvvsfiprr persetaqps dqalaqqHHH HHHLEHHHHH H |
-Macromolecule #2: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit B (BcsB)
| Macromolecule | Name: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit B (BcsB) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: AWSHPQFEKt patqplinae pavaaqteqn pqvgq vmpg vqgadapvva qngpsrdvkl tfaqiapppg smvlrginpn gsiefgmrsd evvtka mln leytpspsll pvqsqlkvyl ndelmgvlpv tkeqlgkktl aqmpinplfi sdfnrvr le fvghyqdvce ...String: AWSHPQFEKt patqplinae pavaaqteqn pqvgq vmpg vqgadapvva qngpsrdvkl tfaqiapppg smvlrginpn gsiefgmrsd evvtka mln leytpspsll pvqsqlkvyl ndelmgvlpv tkeqlgkktl aqmpinplfi sdfnrvr le fvghyqdvce kpasttlwld vgrssgldlt yqtlnvkndl shfpvpffdp sdnrtntl p mvfagapdvg lqqasaivas wfgsrsgwrg qnfpvlynql pdrnaivfat ndkrpdflr dhpavkapvi eminhpqnpy vkllvvfgrd dkdllqaakg iaqgnilfrg esvvvnevkp llprkpyda pnwvrtdrpv tfgelktyee qlqssglepa ainvslnlpp dlylmrstgi d mdinyryt mppvkdssrm dislnnqflq sfnlsskqea nrlllripvl qglldgktdv si palklga tnqlrfdfey mnpmpggsvd ncitfqpvqn hvvigddsti dfskyyhfip mpd lrafan agfpfsrmad lsqtitvmpk apneaqmetl lntvgfigaq tgfpainltv tddg stiqg kdadimiigg ipdklkddkq idllvqates wvktpmrqtp fpgivpdesd raaet rstl tssgamaavi gfqspyndqr svialladsp rgyemlndav ndsgkratmf gsvavi res ginslrvgdv yyvghlpwfe rvwyalanhp illavlaais villawvlwr llriisr rr lnpdne |
-Macromolecule #3: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit G (BcsG)
| Macromolecule | Name: Bacterial cellulose synthase subunit G (BcsG) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MTQFTQNTAM PSSLWQYWRG LSGWNFYFLV KFGLLWAGYL NFHPLLNLVF AAFLLMPLPR YSLHRLRHW IALPIGFALF WHDTWLPGPE SIMSQGSQVA GFSTDYLIDL VTRFINWQMI G AIFVLLVA WLFLSQWIRI TVFVVAILLW LNVLTLAGPS FSLWPAGQPT ...String: MTQFTQNTAM PSSLWQYWRG LSGWNFYFLV KFGLLWAGYL NFHPLLNLVF AAFLLMPLPR YSLHRLRHW IALPIGFALF WHDTWLPGPE SIMSQGSQVA GFSTDYLIDL VTRFINWQMI G AIFVLLVA WLFLSQWIRI TVFVVAILLW LNVLTLAGPS FSLWPAGQPT TTVTTTGGNA AA TVAATGG APVVGDMPAQ TAPPTTANLN AWLNNFYNAE AKRKSTFPSS LPADAQPFEL LVI NICSLS WSDIEAAGLM SHPLWSHFDI EFKNFNSATS YSGPAAIRLL RASCGQTSHT NLYQ PANND CYLFDNLSKL GFTQHLMMGH NGQFGGFLKE VRENGGMQSE LMDQTNLPVI LLGFD GSPV YDDTAVLNRW LDVTEKDKNS RSATFYNTLP LHDGNHYPGV SKTADYKARA QKFFDE LDA FFTELEKSGR KVMVVVVPEH GGALKGDRMQ VSGLRDIPSP SITDVPVGVK FFGMKAP HQ GAPIVIEQPS SFLAISDLVV RVLDGKIFTE DNVDWKKLTS GLPQTAPVSE NSNAVVIQ Y QDKPYVRLNG GDWVPYPQDY KDDDDK |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 51.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






































