+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Human liver-type glutaminase, bound with inhibitor Compound 968 | ||||||||||||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | |||||||||||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | Metabolic / Cancer / HYDROLASE | ||||||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.69 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Feng S / Aplin C / Nguyen T-TT / Milano SK / Cerione RA | ||||||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 5件 米国, 5件
| ||||||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2024タイトル: Filament formation drives catalysis by glutaminase enzymes important in cancer progression. 著者: Shi Feng / Cody Aplin / Thuy-Tien T Nguyen / Shawn K Milano / Richard A Cerione /  要旨: The glutaminase enzymes GAC and GLS2 catalyze the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate, satisfying the 'glutamine addiction' of cancer cells. They are the targets of anti-cancer drugs; however, their ...The glutaminase enzymes GAC and GLS2 catalyze the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate, satisfying the 'glutamine addiction' of cancer cells. They are the targets of anti-cancer drugs; however, their mechanisms of activation and catalytic activity have been unclear. Here we demonstrate that the ability of GAC and GLS2 to form filaments is directly coupled to their catalytic activity and present their cryo-EM structures which provide a view of the conformational states essential for catalysis. Filament formation guides an 'activation loop' to assume a specific conformation that works together with a 'lid' to close over the active site and position glutamine for nucleophilic attack by an essential serine. Our findings highlight how ankyrin repeats on GLS2 regulate enzymatic activity, while allosteric activators stabilize, and clinically relevant inhibitors block, filament formation that enables glutaminases to catalyze glutaminolysis and support cancer progression. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_43533.map.gz emd_43533.map.gz | 95.8 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-43533-v30.xml emd-43533-v30.xml emd-43533.xml emd-43533.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_43533.png emd_43533.png | 69.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43533.cif.gz emd-43533.cif.gz | 5 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_43533_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43533_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43533_half_map_2.map.gz emd_43533_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.7 MB 95.7 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43533 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43533 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43533 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43533 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_43533.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_43533.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 0.615 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_43533_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
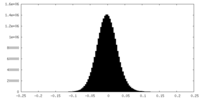
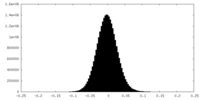
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_43533_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
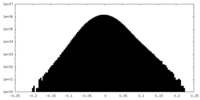
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Tetrameric form of Glutaminase liver isoform, bound with Compound 968
| 全体 | 名称: Tetrameric form of Glutaminase liver isoform, bound with Compound 968 |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Tetrameric form of Glutaminase liver isoform, bound with Compound 968
| 超分子 | 名称: Tetrameric form of Glutaminase liver isoform, bound with Compound 968 タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
-分子 #1: Glutaminase liver isoform, mitochondrial
| 分子 | 名称: Glutaminase liver isoform, mitochondrial / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: glutaminase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MRSMKALQKA LSRAGSHCGR GGWGHPSRSP LLGGGVRHHL SEAAAQGRET PHSHQPQHQD HDSSESGMLS RLGDLLFYTI AEGQERIPI HKFTTALKAT GLQTSDPRLR DCMSEMHRVV QESSSGGLLD RDLFRKCVSS NIVLLTQAFR KKFVIPDFEE F TGHVDRIF ...文字列: MRSMKALQKA LSRAGSHCGR GGWGHPSRSP LLGGGVRHHL SEAAAQGRET PHSHQPQHQD HDSSESGMLS RLGDLLFYTI AEGQERIPI HKFTTALKAT GLQTSDPRLR DCMSEMHRVV QESSSGGLLD RDLFRKCVSS NIVLLTQAFR KKFVIPDFEE F TGHVDRIF EDVKELTGGK VAAYIPQLAK SNPDLWGVSL CTVDGQRHSV GHTKIPFCLQ SCVKPLTYAI SISTLGTDYV HK FVGKEPS GLRYNKLSLN EEGIPHNPMV NAGAIVVSSL IKMDCNKAEK FDFVLQYLNK MAGNEYMGFS NATFQSEKET GDR NYAIGY YLKEKKCFPK GVDMMAALDL YFQLCSVEVT CESGSVMAAT LANGGICPIT GESVLSAEAV RNTLSLMHSC GMYD FSGQF AFHVGLPAKS AVSGAILLVV PNVMGMMCLS PPLDKLGNSH RGTSFCQKLV SLFNFHNYDN LRHCARKLDP RREGA EIRN KTVVNLLFAA YSGDVSALRR FALSAMDMEQ KDYDSRTALH VAAAEGHIEV VKFLIEACKV NPFAKDRWGN IPLDDA VQF NHLEVVKLLQ DYQDSYTLSE TQAEAAAEAL SKENLESMV |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | #0 - Image recording ID: 1 #0 - フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) #0 - 平均電子線量: 48.5 e/Å2 / #1 - Image recording ID: 2 #1 - フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) #1 - 平均電子線量: 38.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 200 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.3000000000000003 µm 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1.0 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Talos Arctica / 画像提供: FEI Company |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー










 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)