[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4344: Filament of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT domains of BRCA1 (ACC... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4344 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
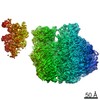
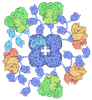
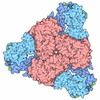
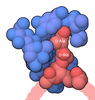
| Title | Filament of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT domains of BRCA1 (ACC-BRCT) at 5.9 A resolution | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Filament / Helical / Multienzyme / Ligase / Biotin-dependent carboxylase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H2AK127 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone H2AK129 ubiquitin ligase activity / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BARD1 loss of function / BRCA1-BARD1 complex / acetyl-CoA carboxylase / BRCA1-B complex / BRCA1-A complex / BRCA1-C complex / negative regulation of centriole replication ...histone H2AK127 ubiquitin ligase activity / histone H2AK129 ubiquitin ligase activity / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective DNA double strand break response due to BARD1 loss of function / BRCA1-BARD1 complex / acetyl-CoA carboxylase / BRCA1-B complex / BRCA1-A complex / BRCA1-C complex / negative regulation of centriole replication / sex-chromosome dosage compensation / fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Defective HLCS causes multiple carboxylase deficiency / random inactivation of X chromosome / Biotin transport and metabolism / malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process / Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis / ubiquitin-modified histone reader activity / chordate embryonic development / cellular response to indole-3-methanol / gamma-tubulin ring complex / negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression / DNA strand resection involved in replication fork processing / homologous recombination / negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process / acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity / acetyl-CoA metabolic process / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA replication, damage repair and senescence / tissue homeostasis / protein K6-linked ubiquitination / Carnitine shuttle / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint / XY body / RNA polymerase binding / DNA repair complex / DNA damage tolerance / centrosome cycle / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / intracellular membraneless organelle / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / negative regulation of gene expression via chromosomal CpG island methylation / response to ionizing radiation / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / lipid homeostasis / negative regulation of cell cycle / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production / ubiquitin ligase complex / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / regulation of DNA repair / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / protein autoubiquitination / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / tubulin binding / Meiotic synapsis / positive regulation of DNA repair / cellular response to ionizing radiation / male germ cell nucleus / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / chromosome segregation / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / negative regulation of cell growth / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / Metalloprotease DUBs / fibrillar center / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of angiogenesis / fatty acid biosynthetic process / p53 binding / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / double-strand break repair / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / actin cytoskeleton / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / chromosome / Neddylation / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / protein homotetramerization / damaged DNA binding / transcription coactivator activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.9 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hunkeler M / Hagmann A | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3 items Switzerland, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Structural basis for regulation of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Authors: Moritz Hunkeler / Anna Hagmann / Edward Stuttfeld / Mohamed Chami / Yakir Guri / Henning Stahlberg / Timm Maier /   Abstract: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, a rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis. Eukaryotic acetyl-CoA carboxylases are large, homodimeric multienzymes. ...Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA, a rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis. Eukaryotic acetyl-CoA carboxylases are large, homodimeric multienzymes. Human acetyl-CoA carboxylase occurs in two isoforms: the metabolic, cytosolic ACC1, and ACC2, which is anchored to the outer mitochondrial membrane and controls fatty acid β-oxidation. ACC1 is regulated by a complex interplay of phosphorylation, binding of allosteric regulators and protein-protein interactions, which is further linked to filament formation. These filaments were discovered in vitro and in vivo 50 years ago, but the structural basis of ACC1 polymerization and regulation remains unknown. Here, we identify distinct activated and inhibited ACC1 filament forms. We obtained cryo-electron microscopy structures of an activated filament that is allosterically induced by citrate (ACC-citrate), and an inactivated filament form that results from binding of the BRCT domains of the breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1). While non-polymeric ACC1 is highly dynamic, filament formation locks ACC1 into different catalytically competent or incompetent conformational states. This unique mechanism of enzyme regulation via large-scale conformational changes observed in ACC1 has potential uses in engineering of switchable biosynthetic systems. Dissecting the regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase opens new paths towards counteracting upregulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in disease. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4344.map.gz emd_4344.map.gz | 31.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4344-v30.xml emd-4344-v30.xml emd-4344.xml emd-4344.xml | 14.7 KB 14.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4344.png emd_4344.png | 48.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4344.cif.gz emd-4344.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4344 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4344 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4344 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4344 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6g2iMC  4342C  4343C  6g2dC  6g2hC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4344.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 202.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4344.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 202.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.058 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT
| Entire | Name: acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT
| Supramolecule | Name: acetyl-CoA carboxylase and BRCT / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1
| Supramolecule | Name: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein
| Supramolecule | Name: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 10 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 265.949344 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDEPSPLAQP LELNQHSRFI IGSVSEDNSE DEISNLVKLD LLEEKEGSLS PASVGSDTLS DLGISSLQDG LALHIRSSMS GLHLVKQGR DRKKIDSQRD FTVASPAEFV TRFGGNKVIE KVLIANNGIA AVKCMRSIRR WSYEMFRNER AIRFVVMVTP E DLKANAEY ...String: MDEPSPLAQP LELNQHSRFI IGSVSEDNSE DEISNLVKLD LLEEKEGSLS PASVGSDTLS DLGISSLQDG LALHIRSSMS GLHLVKQGR DRKKIDSQRD FTVASPAEFV TRFGGNKVIE KVLIANNGIA AVKCMRSIRR WSYEMFRNER AIRFVVMVTP E DLKANAEY IKMADHYVPV PGGPNNNNYA NVELILDIAK RIPVQAVWAG WGHASENPKL PELLLKNGIA FMGPPSQAMW AL GDKIASS IVAQTAGIPT LPWSGSGLRV DWQENDFSKR ILNVPQELYE KGYVKDVDDG LQAAEEVGYP VMIKASEGGG GKG IRKVNN ADDFPNLFRQ VQAEVPGSPI FVMRLAKQSR HLEVQILADQ YGNAISLFGR DCSVQRRHQK IIEEAPATIA TPAV FEHME QCAVKLAKMV GYVSAGTVEY LYSQDGSFYF LELNPRLQVE HPCTEMVADV NLPAAQLQIA MGIPLYRIKD IRMMY GVSP WGDSPIDFED SAHVPCPRGH VIAARITSEN PDEGFKPSSG TVQELNFRSN KNVWGYFSVA AAGGLHEFAD SQFGHC FSW GENREEAISN MVVALKELSI RGDFRTTVEY LIKLLETESF QMNRIDTGWL DRLIAEKVQA ERPDTMLGVV CGALHVA DV SLRNSVSNFL HSLERGQVLP AHTLLNTVDV ELIYEGVKYV LKVTRQSPNS YVVIMNGSCV EVDVHRLSDG GLLLSYDG S SYTTYMKEEV DRYRITIGNK TCVFEKENDP SVMRSPSAGK LIQYIVEDGG HVFAGQCYAE IEVMKMVMTL TAVESGCIH YVKRPGAALD PGCVLAKMQL DNPSKVQQAE LHTGSLPRIQ STALRGEKLH RVFHYVLDNL VNVMNGYCLP DPFFSSKVKD WVERLMKTL RDPSLPLLEL QDIMTSVSGR IPPNVEKSIK KEMAQYASNI TSVLCQFPSQ QIANILDSHA ATLNRKSERE V FFMNTQSI VQLVQRYRSG IRGHMKAVVM DLLRQYLRVE TQFQNGHYDK CVFALREENK SDMNTVLNYI FSHAQVTKKN LL VTMLIDQ LCGRDPTLTD ELLNILTELT QLSKTTNAKV ALRARQVLIA SHLPSYELRH NQVESIFLSA IDMYGHQFCI ENL QKLILS ETSIFDVLPN FFYHSNQVVR MAALEVYVRR AYIAYELNSV QHRQLKDNTC VVEFQFMLPT SHPNRGNIPT LNRM SFSSN LNHYGMTHVA SVSDVLLDNS FTPPCQRMGG MVSFRTFEDF VRIFDEVMGC FSDSPPQ(SEP)PT FPEAGHTSLY D EDKVPRDE PIHILNVAIK TDCDIEDDRL AAMFREFTQQ NKATLVDHGI RRLTFLVAQK DFRKQVNYEV DRRFHREFPK FF TFRARDK FEEDRIYRHL EPALAFQLEL NRMRNFDLTA IPCANHKMHL YLGAAKVEVG TEVTDYRFFV RAIIRHSDLV TKE ASFEYL QNEGERLLLE AMDELEVAFN NTNVRTDCNH IFLNFVPTVI MDPSKIEESV RSMVMRYGSR LWKLRVLQAE LKIN IRLTP TGKAIPIRLF LTNESGYYLD ISLYKEVTDS RTAQIMFQAY GDKQGPLHGM LINTPYVTKD LLQSKRFQAQ SLGTT YIYD IPEMFRQSLI KLWESMSTQA FLPSPPLPSD MLTYTELVLD DQGQLVHMNR LPGGNEIGMV AWKMTFKSPE YPEGRD IIV IGNDITYRIG SFGPQEDLLF LRASELARAE GIPRIYVSAN SGARIGLAEE IRHMFHVAWV DPEDPYKGYR YLYLTPQ DY KRVSALNSVH CEHVEDEGES RYKITDIIGK EEGIGPENLR GSGMIAGESS LAYNEIITIS LVTCRAIGIG AYLVRLGQ R TIQVENSHLI LTGAGALNKV LGREVYTSNN QLGGIQIMHN NGVTHCTVCD DFEGVFTVLH WLSYMPKSVH SSVPLLNSK DPIDRIIEFV PTKTPYDPRW MLAGRPHPTQ KGQWLSGFFD YGSFSEIMQP WAQTVVVGRA RLGGIPVGVV AVETRTVELS IPADPANLD SEAKIIQQAG QVWFPDSAFK TYQAIKDFNR EGLPLMVFAN WRGFSGGMKD MYDQVLKFGA YIVDGLRECC Q PVLVYIPP QAELRGGSWV VIDSSINPRH MEMYADRESR GSVLEPEGTV EIKFRRKDLV KTMRRVDPVY IHLAERLGTP EL STAERKE LENKLKEREE FLIPIYHQVA VQFADLHDTP GRMQEKGVIS DILDWKTSRT FFYWRLRRLL LEDLVKKKIH NAN PELTDG QIQAMLRRWF VEVEGTVKAY VWDNNKDLAE WLEKQLTEED GVHSVIEENI KCISRDYVLK QIRSLVQANP EVAM DSIIH MTQHISPTQR AEVIRILSTM DSPST UniProtKB: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 27.664869 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKHHHHHHPM TSLYKKAGLE NLYFQGVNKR MSMVVSGLTP EEFMLVYKFA RKHHITLTNL ITEETTHVVM KTDAEFVCER TLKYFLGIA GGKWVVSYFW VTQSIKERKM LNEHDFEVRG DVVNGRNHQG PKRARESQDR KIFRGLEICC YGPFTNMPTD Q LEWMVQLC ...String: MKHHHHHHPM TSLYKKAGLE NLYFQGVNKR MSMVVSGLTP EEFMLVYKFA RKHHITLTNL ITEETTHVVM KTDAEFVCER TLKYFLGIA GGKWVVSYFW VTQSIKERKM LNEHDFEVRG DVVNGRNHQG PKRARESQDR KIFRGLEICC YGPFTNMPTD Q LEWMVQLC GASVVKELSS FTLGTGVHPI VVVQPDAWTE DNGFHAIGQM CEAPVVTREW VLDSVALYQC QELDTYLIPQ IP UniProtKB: Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 Details: Collected in movie-mode with total dose of 80 e-/A2 for a total of 80 frames. Frames 3-22 were used for final reconstruction |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER Details: Initial model was generated form 2D class averages using e2initialmodel.py in EMAN2. PDB IDs: 2yl2; 5i87; 4asi; 4y18 |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 2.01) / Number images used: 48483 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
| Final angle assignment | Type: OTHER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















