[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4198: Localized reconstruction of the Rift Valley fever virus glycoprot... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4198 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
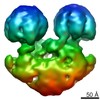
| Title | Localized reconstruction of the Rift Valley fever virus glycoprotein hexamer type 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Localized Reconstruction of Rift Valley fever virus type 1 hexamer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | enveloped virus / RVFV / glycoprotein / fusion protein / VIRUS | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell mitochondrial outer membrane / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host apoptosis / symbiont-mediated suppression of host apoptosis / host cell Golgi membrane / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Rift valley fever virus / Rift valley fever virus /   Rift Valley fever virus Rift Valley fever virus | |||||||||
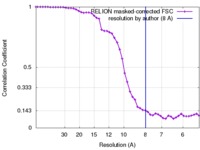
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Halldorsson S / Huiskonen JT | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: Shielding and activation of a viral membrane fusion protein. Authors: Steinar Halldorsson / Sai Li / Mengqiu Li / Karl Harlos / Thomas A Bowden / Juha T Huiskonen /   Abstract: Entry of enveloped viruses relies on insertion of hydrophobic residues of the viral fusion protein into the host cell membrane. However, the intermediate conformations during fusion remain unknown. ...Entry of enveloped viruses relies on insertion of hydrophobic residues of the viral fusion protein into the host cell membrane. However, the intermediate conformations during fusion remain unknown. Here, we address the fusion mechanism of Rift Valley fever virus. We determine the crystal structure of the Gn glycoprotein and fit it with the Gc fusion protein into cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of the virion. Our analysis reveals how the Gn shields the hydrophobic fusion loops of the Gc, preventing premature fusion. Electron cryotomography of virions interacting with membranes under acidic conditions reveals how the fusogenic Gc is activated upon removal of the Gn shield. Repositioning of the Gn allows extension of Gc and insertion of fusion loops in the outer leaflet of the target membrane. These data show early structural transitions that enveloped viruses undergo during host cell entry and indicate that analogous shielding mechanisms are utilized across diverse virus families. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4198.map.gz emd_4198.map.gz | 7.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4198-v30.xml emd-4198-v30.xml emd-4198.xml emd-4198.xml | 12.7 KB 12.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_4198_fsc.xml emd_4198_fsc.xml | 4.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_4198.png emd_4198.png | 131.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4198.cif.gz emd-4198.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4198 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4198 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4198 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4198 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6f9cMC  4197C  4199C  4200C  4201C  4202C 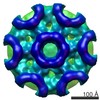 4203C  4204C  4205C  4206C  4207C  4208C 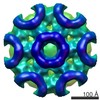 4209C  4210C  4211C  6f8pC  6f9bC  6f9dC  6f9eC  6f9fC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4198.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4198.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Localized Reconstruction of Rift Valley fever virus type 1 hexamer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
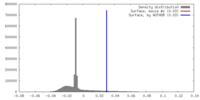
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Rift Valley fever virus
| Entire | Name:   Rift Valley fever virus Rift Valley fever virus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Rift Valley fever virus
| Supramolecule | Name: Rift Valley fever virus / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / Details: Cultured in Vero cells / NCBI-ID: 11588 / Sci species name: Rift Valley fever virus / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: OTHER / Virus enveloped: Yes / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Name: Glycoprotein shell / Diameter: 1100.0 Å / T number (triangulation number): 12 |
-Macromolecule #1: Glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rift valley fever virus Rift valley fever virus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.968902 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: EDPHLRNRPG KGHNYIDGMT QEDATCKPVT YAGACSSFDV LLEKGKFPLF QSYAHHRTLL EAVHDTIIAK ADPPSCDLQS AHGNPCMKE KLVMKTHCPN DYQSAHYLNN DGKMASVKCP PKYELTEDCN FCRQMTGASL KKGSYPLQDL FCQSSEDDGS K LKTKMKGV ...String: EDPHLRNRPG KGHNYIDGMT QEDATCKPVT YAGACSSFDV LLEKGKFPLF QSYAHHRTLL EAVHDTIIAK ADPPSCDLQS AHGNPCMKE KLVMKTHCPN DYQSAHYLNN DGKMASVKCP PKYELTEDCN FCRQMTGASL KKGSYPLQDL FCQSSEDDGS K LKTKMKGV CEVGVQALKK CDGQLSTAHE VVPFAVFKNS KKVYLDKLDL KTEENLLPDS FVCFEHKGQY KGKLDSGQTK RE LKSFDIS QCPKIGGHGS KKCTGDAAFC SAYECTAQYA NAYCSHANGS GIVQIQVSGV WKKPLCVGYE RVVVKRELS UniProtKB: Envelopment polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: Glycoprotein
| Macromolecule | Name: Glycoprotein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Rift valley fever virus Rift valley fever virus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.85557 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DPGCSELIQA SSRITTCSTE GVNTKCRLSG TALIRAGSVG AEACLMLKGV KEDQTKFLKI KTVSSELSCR EGQSYWTGSF SPKCLSSRR CHLVGECHVN RCLSWRDNET SAEFSFVGES TTMRENKCFE QCGGWGCGCF NVNPSCLFVH TYLQSVRKEA L RVFNCIDW ...String: DPGCSELIQA SSRITTCSTE GVNTKCRLSG TALIRAGSVG AEACLMLKGV KEDQTKFLKI KTVSSELSCR EGQSYWTGSF SPKCLSSRR CHLVGECHVN RCLSWRDNET SAEFSFVGES TTMRENKCFE QCGGWGCGCF NVNPSCLFVH TYLQSVRKEA L RVFNCIDW VHKLTLEITD FDGSVSTIDL GASSSRFTNW GSVSLSLDAE GISGSNSFSF IESPGKGYAI VDEPFSEIPR QG FLGEIRC NSESSVLSAH ESCLRAPNLI SYKPMIDQLE CTTNLIDPFV VFERGSLPQT RNDKTFAASK GNRGVQAFSK GSV QADLTL MFDNFEVDFV GAAVSCDAAF LNLTGCYSCN AGARVCLSIT STGTGSLSAH NKDGSLHIVL PSENGTKDQC QILH FTVPE VEEEFMYSCD GDERPLLVKG TLIAID UniProtKB: Envelopment polyprotein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: PBS |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
| Details | Fixed with 0.2% v/v formaldehyde in PBS |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F30 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 22.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6f9c: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)