+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6f8p | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
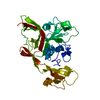
| Title | Crystal structure of Gn from Rift Valley fever virus | |||||||||
 Components Components | Glycoprotein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / phlebovirus / glycoprotein / bunyavirus / host cell entry | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell mitochondrial outer membrane / symbiont-mediated perturbation of host apoptosis / symbiont-mediated suppression of host apoptosis / host cell Golgi membrane / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Rift valley fever virus Rift valley fever virus | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  SAD / Resolution: 1.6 Å SAD / Resolution: 1.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Halldorsson, S. / Bowden, T.A. / Harlos, K. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: Shielding and activation of a viral membrane fusion protein. Authors: Steinar Halldorsson / Sai Li / Mengqiu Li / Karl Harlos / Thomas A Bowden / Juha T Huiskonen /   Abstract: Entry of enveloped viruses relies on insertion of hydrophobic residues of the viral fusion protein into the host cell membrane. However, the intermediate conformations during fusion remain unknown. ...Entry of enveloped viruses relies on insertion of hydrophobic residues of the viral fusion protein into the host cell membrane. However, the intermediate conformations during fusion remain unknown. Here, we address the fusion mechanism of Rift Valley fever virus. We determine the crystal structure of the Gn glycoprotein and fit it with the Gc fusion protein into cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of the virion. Our analysis reveals how the Gn shields the hydrophobic fusion loops of the Gc, preventing premature fusion. Electron cryotomography of virions interacting with membranes under acidic conditions reveals how the fusogenic Gc is activated upon removal of the Gn shield. Repositioning of the Gn allows extension of Gc and insertion of fusion loops in the outer leaflet of the target membrane. These data show early structural transitions that enveloped viruses undergo during host cell entry and indicate that analogous shielding mechanisms are utilized across diverse virus families. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6f8p.cif.gz 6f8p.cif.gz | 140.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6f8p.ent.gz pdb6f8p.ent.gz | 108.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6f8p.json.gz 6f8p.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/6f8p https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/6f8p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/6f8p ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/6f8p | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4197C  4198C  4199C  4200C  4201C  4202C  4203C  4204C  4205C  4206C  4207C  4208C  4209C  4210C  4211C  6f9bC  6f9cC  6f9dC  6f9eC  6f9fC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 34958.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rift valley fever virus / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Rift valley fever virus / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B6S219, UniProt: P21401*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B6S219, UniProt: P21401*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #2: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.47 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 50.15 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 7 / Details: 20% w/v PEG 6000, 0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source |
| |||||||||||||||
| Detector |
| |||||||||||||||
| Radiation |
| |||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength |
| |||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.6→48.995 Å / Num. obs: 46607 / % possible obs: 99.9 % / Redundancy: 9.7 % / CC1/2: 0.998 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.086 / Net I/σ(I): 12.35 | |||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.6→1.64 Å / Redundancy: 9.47 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.044 / Num. unique obs: 3369 / CC1/2: 0.818 / % possible all: 99.6 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  SAD / Resolution: 1.6→48.99 Å / SU ML: 0.18 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 21.67 SAD / Resolution: 1.6→48.99 Å / SU ML: 0.18 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 21.67
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 117.43 Å2 / Biso mean: 35.0946 Å2 / Biso min: 15.18 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.6→48.99 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 16 / % reflection obs: 100 %
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj
