[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
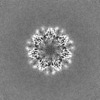
Yorodumi- EMDB-41070: Cryo-EM structure of tetradecameric CaMKII beta holoenzyme T287A ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
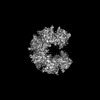
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of tetradecameric CaMKII beta holoenzyme T287A T306A T307A | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | High-order oligomer / Protein Kinase / Signaling / Memory / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / activation of meiosis involved in egg activation / cellular response to homocysteine / HSF1-dependent transactivation / cell projection morphogenesis / RAF activation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of synapse maturation / Interferon gamma signaling ...regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / activation of meiosis involved in egg activation / cellular response to homocysteine / HSF1-dependent transactivation / cell projection morphogenesis / RAF activation / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase complex / positive regulation of synapse maturation / Interferon gamma signaling / Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase / positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / regulation of synapse maturation / regulation of neuron migration / calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / Ion homeostasis / neuromuscular process controlling balance / response to psychosocial stress / spindle midzone / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / response to cadmium ion / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / phospholipase binding / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / bioluminescence / positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / apoptotic signaling pathway / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of neuron projection development / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / calcium ion transport / long-term synaptic potentiation / nervous system development / protein autophosphorylation / perikaryon / cell differentiation / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / dendrite / centrosome / protein kinase binding / glutamatergic synapse / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chien C-T / Chiu W / Khan S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2024Title: Hub stability in the calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Authors: Chih-Ta Chien / Henry Puhl / Steven S Vogel / Justin E Molloy / Wah Chiu / Shahid Khan /   Abstract: The calcium calmodulin protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a multi-subunit ring assembly with a central hub formed by the association domains. There is evidence for hub polymorphism between and within ...The calcium calmodulin protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a multi-subunit ring assembly with a central hub formed by the association domains. There is evidence for hub polymorphism between and within CaMKII isoforms, but the link between polymorphism and subunit exchange has not been resolved. Here, we present near-atomic resolution cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures revealing that hubs from the α and β isoforms, either standalone or within an β holoenzyme, coexist as 12 and 14 subunit assemblies. Single-molecule fluorescence microscopy of Venus-tagged holoenzymes detects intermediate assemblies and progressive dimer loss due to intrinsic holoenzyme lability, and holoenzyme disassembly into dimers upon mutagenesis of a conserved inter-domain contact. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations show the flexibility of 4-subunit precursors, extracted in-silico from the β hub polymorphs, encompassing the curvature of both polymorphs. The MD explains how an open hub structure also obtained from the β holoenzyme sample could be created by dimer loss and analysis of its cryo-EM dataset reveals how the gap could open further. An assembly model, considering dimer concentration dependence and strain differences between polymorphs, proposes a mechanism for intrinsic hub lability to fine-tune the stoichiometry of αβ heterooligomers for their dynamic localization within synapses in neurons. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41070.map.gz emd_41070.map.gz | 117.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41070-v30.xml emd-41070-v30.xml emd-41070.xml emd-41070.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_41070.png emd_41070.png | 74.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41070.cif.gz emd-41070.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41070_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41070_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41070_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41070_half_map_2.map.gz | 116 MB 116 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41070 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41070 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41070 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41070 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8t6kMC  8sygC  8t15C  8t17C  8t18C  8t6qC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41070.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41070.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
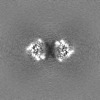
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_41070_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
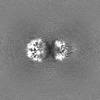
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
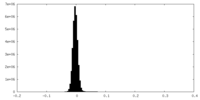
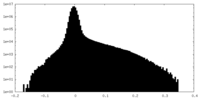
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_41070_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
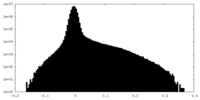
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme T287A T306A T307A
| Entire | Name: Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme T287A T306A T307A |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme T287A T306A T307A
| Supramolecule | Name: Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme T287A T306A T307A / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme mutant
| Macromolecule | Name: Venus-tagged CaMKII Beta Holoenzyme mutant / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 14 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 90.846859 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH VSKGEELFTG VVPILVELDG DVNGHKFSVS GEGEGDATYG KLTLKLICTT GKLPVPWPTL VTTLGYGLQ CFARYPDHMK QHDFFKSAMP EGYVQERTIF FKDDGNYKTR AEVKFEGDTL VNRIELKGID FKEDGNILGH K LEYNYNSH ...String: MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH VSKGEELFTG VVPILVELDG DVNGHKFSVS GEGEGDATYG KLTLKLICTT GKLPVPWPTL VTTLGYGLQ CFARYPDHMK QHDFFKSAMP EGYVQERTIF FKDDGNYKTR AEVKFEGDTL VNRIELKGID FKEDGNILGH K LEYNYNSH NVYITADKQK NGIKANFKIR HNIEDGGVQL ADHYQQNTPI GDGPVLLPDN HYLSYQSKLS KDPNEKRDHM VL LEFVTAA GITLGMDELY KSGLRSRAQA SNSAVDMATT VTCTRFTDEY QLYEDIGKGA FSVVRRCVKL CTGHEYAAKI INT KKLSAR DHQKLEREAR ICRLLKHSNI VRLHDSISEE GFHYLVFDLV TGGELFEDIV AREYYSEADA SHCIQQILEA VLHC HQMGV VHRDLKPENL LLASKCKGAA VKLADFGLAI EVQGDQQAWF GFAGTPGYLS PEVLRKEAYG KPVDIWACGV ILYIL LVGY PPFWDEDQHK LYQQIKAGAY DFPSPEWDTV TPEAKNLINQ MLTINPAKRI TAHEALKHPW VCQRSTVASM MHRQEA VEC LKKFNARRKL KGAILAAMLA TRNFSVGRQT TAPATMSTAA SGTTMGLVEQ AKSLLNKKAD GVKPQTNSTK NSSAITS PK GSLPPAALEP QTTVIHNPVD GIKESSDSTN TTIEDEDAKA RKQEIIKTTE QLIEAVNNGD FEAYAKICDP GLTSFEPE A LGNLVEGMDF HRFYFENLLA KNSKPIHTTI LNPHVHVIGE DAACIAYIRL TQYIDGQGRP RTSQSEETRV WHRPDGKWQ NVHFHCSGAP VAPLQ UniProtKB: Green fluorescent protein, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit beta |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 20 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: D7 (2x7 fold dihedral) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 138904 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)