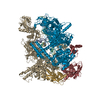
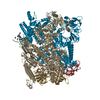
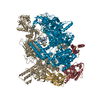
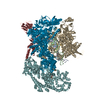
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-40922タイトル Reconstituted E. coli RNA polymerase post-termination complex on negatively-supercoiled DNA: open duplex DNA (rPTCo) Locally Filtered 複合体 : E. coli Post-termination complex with open DNA bubble on negatively supercoiled DNADNA : DNA (27-MER)DNA : DNA (25-MER)タンパク質・ペプチド : DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit alphaタンパク質・ペプチド : DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit betaタンパク質・ペプチド : DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit omegaタンパク質・ペプチド : DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta'リガンド : MAGNESIUM IONリガンド : ZINC ION / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / synthetic construct (人工物) 手法 / / 解像度 : 3.63 Å Brewer JJ / Darst SA / Campbell EA 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH/NIGMS)
ジャーナル : Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年 : 2025タイトル : RapA opens the RNA polymerase clamp to disrupt post-termination complexes and prevent cytotoxic R-loop formation.著者 : Joshua J Brewer / Koe Inlow / Rachel A Mooney / Barbara Bosch / Paul Dominic B Olinares / Leandro Pimentel Marcelino / Brian T Chait / Robert Landick / Jeff Gelles / Elizabeth A Campbell / Seth A Darst / 要旨 : Following transcript release during intrinsic termination, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP) often remains associated with DNA in a post-termination complex (PTC). RNAPs in PTCs are removed from ... Following transcript release during intrinsic termination, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP) often remains associated with DNA in a post-termination complex (PTC). RNAPs in PTCs are removed from the DNA by the SWI2/SNF2 adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) RapA. Here we determined PTC structures on negatively supercoiled DNA and with RapA engaged to dislodge the PTC. We found that core RNAP in the PTC can unwind DNA and initiate RNA synthesis but is prone to producing R-loops. Nucleotide binding to RapA triggers a conformational change that opens the RNAP clamp, allowing DNA in the RNAP cleft to reanneal and dissociate. We show that RapA helps to control cytotoxic R-loop formation in vivo, likely by disrupting PTCs. We suggest that analogous ATPases acting on PTCs to suppress transcriptional noise and R-loop formation may be widespread. These results hold importance for the bacterial transcription cycle and highlight a role for RapA in maintaining genome stability. 履歴 登録 2023年5月30日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2025年4月2日 - マップ公開 2025年4月2日 - 更新 2025年4月30日 - 現状 2025年4月30日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報
 データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2025
ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2025
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_40922.map.gz
emd_40922.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-40922-v30.xml
emd-40922-v30.xml emd-40922.xml
emd-40922.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_40922.png
emd_40922.png emd-40922.cif.gz
emd-40922.cif.gz emd_40922_additional_1.map.gz
emd_40922_additional_1.map.gz emd_40922_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_40922_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40922_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_40922_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40922
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40922 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40922
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40922 emd_40922_validation.pdf.gz
emd_40922_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_40922_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_40922_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40922_validation.xml.gz
emd_40922_validation.xml.gz emd_40922_validation.cif.gz
emd_40922_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40922
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40922 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40922
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40922 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_40922.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_40922.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素








 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)













































