+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | TMEM16F 1PBC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | TMEM16F 1PBC | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ca2+-activated ion channels / lipid scramblases / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcalcium activated phospholipid scrambling / calcium activated phosphatidylserine scrambling / calcium activated phosphatidylcholine scrambling / calcium activated galactosylceramide scrambling / positive regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane / purinergic nucleotide receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / phospholipid scramblase activity / bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / intracellularly calcium-gated chloride channel activity ...calcium activated phospholipid scrambling / calcium activated phosphatidylserine scrambling / calcium activated phosphatidylcholine scrambling / calcium activated galactosylceramide scrambling / positive regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane / purinergic nucleotide receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / phospholipid scramblase activity / bone mineralization involved in bone maturation / intracellularly calcium-gated chloride channel activity / negative regulation of cell volume / cholinergic synapse / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / plasma membrane phospholipid scrambling / positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment / bleb assembly / Stimuli-sensing channels / calcium-activated cation channel activity / positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis / dendritic cell chemotaxis / chloride transport / phospholipid translocation / chloride channel activity / chloride channel complex / regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / positive regulation of bone mineralization / chloride transmembrane transport / Neutrophil degranulation / establishment of localization in cell / synaptic membrane / calcium ion transmembrane transport / blood coagulation / positive regulation of apoptotic process / protein homodimerization activity / identical protein binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / Resolution: 3.12 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wu H / Feng S / Cheng Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Identification of a drug binding pocket in TMEM16F calcium-activated ion channel and lipid scramblase. Authors: Shengjie Feng / Cristina Puchades / Juyeon Ko / Hao Wu / Yifei Chen / Eric E Figueroa / Shuo Gu / Tina W Han / Brandon Ho / Tong Cheng / Junrui Li / Brian Shoichet / Yuh Nung Jan / Yifan Cheng / Lily Yeh Jan /  Abstract: The dual functions of TMEM16F as Ca-activated ion channel and lipid scramblase raise intriguing questions regarding their molecular basis. Intrigued by the ability of the FDA-approved drug ...The dual functions of TMEM16F as Ca-activated ion channel and lipid scramblase raise intriguing questions regarding their molecular basis. Intrigued by the ability of the FDA-approved drug niclosamide to inhibit TMEM16F-dependent syncytia formation induced by SARS-CoV-2, we examined cryo-EM structures of TMEM16F with or without bound niclosamide or 1PBC, a known blocker of TMEM16A Ca-activated Cl channel. Here, we report evidence for a lipid scrambling pathway along a groove harboring a lipid trail outside the ion permeation pore. This groove contains the binding pocket for niclosamide and 1PBC. Mutations of two residues in this groove specifically affect lipid scrambling. Whereas mutations of some residues in the binding pocket of niclosamide and 1PBC reduce their inhibition of TMEM16F-mediated Ca influx and PS exposure, other mutations preferentially affect the ability of niclosamide and/or 1PBC to inhibit TMEM16F-mediated PS exposure, providing further support for separate pathways for ion permeation and lipid scrambling. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40768.map.gz emd_40768.map.gz | 59.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40768-v30.xml emd-40768-v30.xml emd-40768.xml emd-40768.xml | 15 KB 15 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_40768.png emd_40768.png | 48.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40768.cif.gz emd-40768.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40768_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40768_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40768_half_map_2.map.gz emd_40768_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40768 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40768 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_40768_validation.pdf.gz emd_40768_validation.pdf.gz | 947.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_40768_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40768_full_validation.pdf.gz | 947.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_40768_validation.xml.gz emd_40768_validation.xml.gz | 12.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_40768_validation.cif.gz emd_40768_validation.cif.gz | 14.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40768 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40768 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40768 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8sunMC  8surC  8tagC  8taiC  8talC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40768.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40768.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMEM16F 1PBC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
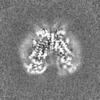
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.839 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: TMEM16F 1PBC half1
| File | emd_40768_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMEM16F 1PBC half1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
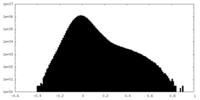
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: TMEM16F 1PBC half2
| File | emd_40768_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMEM16F 1PBC half2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 16F
| Entire | Name: 16F |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 16F
| Supramolecule | Name: 16F / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Anoctamin-6
| Macromolecule | Name: Anoctamin-6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 95.924906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: FEEFNGKPDS LFFTDGQRRI DFILVYEDES KKENNKKGTN EKQKRKRQAY ESNLICHGLQ LEATRSVSDD KLVFVKVHAP WEVLCYYAE IMHIKLPLKP NDLKTRSPFG NLNWFTKVLR VNESVIKPEQ EFFTAPFEKS RMNDFYILDR DSFFNPATRS R IVYFILSR ...String: FEEFNGKPDS LFFTDGQRRI DFILVYEDES KKENNKKGTN EKQKRKRQAY ESNLICHGLQ LEATRSVSDD KLVFVKVHAP WEVLCYYAE IMHIKLPLKP NDLKTRSPFG NLNWFTKVLR VNESVIKPEQ EFFTAPFEKS RMNDFYILDR DSFFNPATRS R IVYFILSR VKYQVMNNVN KFGINRLVSS GIYKAAFPLH DCRFNYESED ISCPSERYLL YREWAHPRSI YKKQPLDLIR KY YGEKIGI YFAWLGYYTQ MLLLAAVVGV ACFLYGYLDQ DNCTWSKEVC DPDIGGQILM CPQCDRLCPF WRLNITCESS KKL CIFDSF GTLIFAVFMG VWVTLFLEFW KRRQAELEYE WDTVELQQEE QARPEYEAQC NHVVINEITQ EEERIPFTTC GKCI RVTLC ASAVFFWILL IIASVIGIIV YRLSVFIVFS TTLPKNPNGT DPIQKYLTPQ MATSITASII SFIIIMILNT IYEKV AIMI TNFELPRTQT DYENSLTMKM FLFQFVNYYS SCFYIAFFKG KFVGYPGDPV YLLGKYRSEE CDPGGCLLEL TTQLTI IMG GKAIWNNIQE VLLPWVMNLI GRYKRVSGSE KITPRWEQDY HLQPMGKLGL FYEYLEMIIQ FGFVTLFVAS FPLAPLL AL VNNILEIRVD AWKLTTQFRR MVPEKAQDIG AWQPIMQGIA ILAVVTNAMI IAFTSDMIPR LVYYWSFSIP PYGDHTYY T MDGYINNTLS VFNITDFKNT DKENPYIGLG NYTLCRYRDF RNPPGHPQEY KHNIYYWHVI AAKLAFIIVM EHIIYSVKF FISYAIPDVS KITKSKIKRE UniProtKB: Anoctamin-6 |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #3: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: 1-Hydroxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrido[1,2-a]benzimidazole-4-carbonitrile
| Macromolecule | Name: 1-Hydroxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrido[1,2-a]benzimidazole-4-carbonitrile type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: JRF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 277.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-JRF: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
|---|---|
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 66.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.12 Å / Number images used: 186223 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






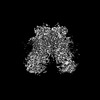









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)