登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-40419タイトル Type IIIa beta-amyloid 40 Filaments from Down syndrome 組織 : Type IIIa beta amyloid 40タンパク質・ペプチド : Type IIIb beta-amyloid 40 Filament / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.5 Å Hoq MR / Vago FS / Bharath SR / Jiang W 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging (NIH/NIA) 5U01NS110437 and and 1RF1AG071177
ジャーナル : Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年 : 2024タイトル : Cryo-EM structures of amyloid-β and tau filaments in Down syndrome.著者: Anllely Fernandez / Md Rejaul Hoq / Grace I Hallinan / Daoyi Li / Sakshibeedu R Bharath / Frank S Vago / Xiaoqi Zhang / Kadir A Ozcan / Kathy L Newell / Holly J Garringer / Wen Jiang / ... 著者 : Anllely Fernandez / Md Rejaul Hoq / Grace I Hallinan / Daoyi Li / Sakshibeedu R Bharath / Frank S Vago / Xiaoqi Zhang / Kadir A Ozcan / Kathy L Newell / Holly J Garringer / Wen Jiang / Bernardino Ghetti / Ruben Vidal / 要旨 : Adult individuals with Down syndrome (DS) develop Alzheimer disease (AD). Whether there is a difference between AD in DS and AD regarding the structure of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau filaments is ... Adult individuals with Down syndrome (DS) develop Alzheimer disease (AD). Whether there is a difference between AD in DS and AD regarding the structure of amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau filaments is unknown. Here we report the structure of Aβ and tau filaments from two DS brains. We found two Aβ filaments (types IIIa and IIIb) that differ from those previously reported in sporadic AD and two types of Aβ filaments (I and II) identical to those found in sporadic and familial AD. Tau filaments (paired helical filaments and straight filaments) were identical to those in AD, supporting the notion of a common mechanism through which amyloids trigger aggregation of tau. This knowledge is important for understanding AD in DS and assessing whether adults with DS could be included in AD clinical trials. 履歴 登録 2023年4月10日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2024年4月3日 - マップ公開 2024年4月3日 - 更新 2024年6月26日 - 現状 2024年6月26日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024
ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_40419.map.gz
emd_40419.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-40419-v30.xml
emd-40419-v30.xml emd-40419.xml
emd-40419.xml EMDBヘッダ
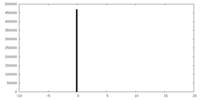
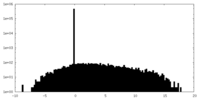
EMDBヘッダ emd_40419_fsc.xml
emd_40419_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_40419.png
emd_40419.png emd-40419.cif.gz
emd-40419.cif.gz emd_40419_additional_1.map.gz
emd_40419_additional_1.map.gz emd_40419_additional_2.map.gz
emd_40419_additional_2.map.gz emd_40419_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_40419_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40419_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_40419_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40419
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40419 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40419
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40419 emd_40419_validation.pdf.gz
emd_40419_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_40419_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_40419_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40419_validation.xml.gz
emd_40419_validation.xml.gz emd_40419_validation.cif.gz
emd_40419_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40419
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40419 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40419
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40419 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
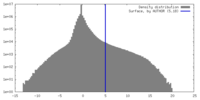
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_40419.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_40419.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー


























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)