[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-39477: Cryo-EM structure of the LH1 complex from Allochromatium tepidum -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the LH1 complex from Allochromatium tepidum | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LH1 COMPLEX / PHOTOSYNTHESIS | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplasma membrane light-harvesting complex / bacteriochlorophyll binding / photosynthesis, light reaction / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.78 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang G-L / Sun S / Yu L-J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biomolecules / Year: 2025 Journal: Biomolecules / Year: 2025Title: Probing the Dual Role of Ca in the LH1-RC Complex by Constructing and Analyzing Ca-Bound and Ca-Free LH1 Complexes. Authors: Mei-Juan Zou / Shuai Sun / Guang-Lei Wang / Yi-Hao Yan / Wei Ji / Zheng-Yu Wang-Otomo / Michael T Madigan / Long-Jiang Yu /    Abstract: The genome of the mildly thermophilic hot spring purple sulfur bacterium, (.) , contains a multigene family that encodes a series of α- and β-polypeptides, collectively forming a heterogeneous ...The genome of the mildly thermophilic hot spring purple sulfur bacterium, (.) , contains a multigene family that encodes a series of α- and β-polypeptides, collectively forming a heterogeneous light-harvesting 1 (LH1) complex. The LH1, therefore, offers a unique model for studying an intermediate phenotype between phototrophic thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria, particularly regarding their LH1 transition and moderately enhanced thermal stability. Of the 16 α-polypeptides in the LH1, six α1 bind Ca to connect with β1- or β3-polypeptides in specific Ca-binding sites. Here, we use the purple bacterium strain H2 as a host to express Ca-bound and Ca-free LH1-only complexes composed of α- and β-polypeptides that either contain or lack the calcium-binding motif WxxDxI; purified preparations of each complex were then used to test how Ca affects their thermostability and spectral features. The cryo-EM structures of both complexes were closed circular rings consisting of 14 αβ-polypeptides. The absorption maximum of Ca-bound LH1 (α1/β1 and α1/β3) was at 894 nm, while that of Ca-free (α2/β1) was at 888 nm, indicating that Ca imparts a transition of 6 nm. Crucially for the ecological success of , Ca-bound LH1 complexes were more thermostable than Ca-free complexes, indicating that calcium plays at least two major roles in photosynthesis by -improving photocomplex stability and modifying its spectrum. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_39477.map.gz emd_39477.map.gz | 168 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-39477-v30.xml emd-39477-v30.xml emd-39477.xml emd-39477.xml | 14.6 KB 14.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_39477_fsc.xml emd_39477_fsc.xml | 12.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_39477.png emd_39477.png | 73.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-39477.cif.gz emd-39477.cif.gz | 5.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_39477_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39477_half_map_1.map.gz emd_39477_half_map_2.map.gz emd_39477_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39477 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39477 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39477 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-39477 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ypdMC  8ypbC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_39477.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_39477.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_39477_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_39477_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : LH1 COMPLEX
| Entire | Name: LH1 COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: LH1 COMPLEX
| Supramolecule | Name: LH1 COMPLEX / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Beta subunit of light-harvesting 1 complex
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta subunit of light-harvesting 1 complex / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 14 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 5.269103 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Rhodospirillum rubrum ATCC 11170 (bacteria) Rhodospirillum rubrum ATCC 11170 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MANSSMTGLT EQEAQEFHGI FVQSMTAFFG IVVIAHILAW LWRPWL UniProtKB: Beta subunit of light-harvesting 1 complex |
-Macromolecule #2: LH1 alpha subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: LH1 alpha subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 14 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) Allochromatium tepidum (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 5.108121 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Rhodospirillum rubrum ATCC 11170 (bacteria) Rhodospirillum rubrum ATCC 11170 (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: MHKIWQIFDP RRTLVALFGF LFVLGLLIHF ILLSSPAFNW LSGS |
-Macromolecule #3: BACTERIOCHLOROPHYLL A
| Macromolecule | Name: BACTERIOCHLOROPHYLL A / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 28 / Formula: BCL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 911.504 Da |
| Chemical component information | 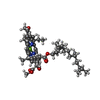 ChemComp-BCL: |
-Macromolecule #4: SPIRILLOXANTHIN
| Macromolecule | Name: SPIRILLOXANTHIN / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 14 / Formula: CRT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 596.925 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CRT: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






































