+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Inhibited EP-complete | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | membrane protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationenteropeptidase / brush border / serine-type endopeptidase activity / proteolysis / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang XL / Ding ZY / Huang HJ | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structures reveal the activation and substrate recognition mechanism of human enteropeptidase. Authors: Xiaoli Yang / Zhanyu Ding / Lisi Peng / Qiuyue Song / Deyu Zhang / Fang Cui / Chuanchao Xia / Keliang Li / Hua Yin / Shiyu Li / Zhaoshen Li / Haojie Huang /  Abstract: Enteropeptidase (EP) initiates intestinal digestion by proteolytically processing trypsinogen, generating catalytically active trypsin. EP dysfunction causes a series of pancreatic diseases including ...Enteropeptidase (EP) initiates intestinal digestion by proteolytically processing trypsinogen, generating catalytically active trypsin. EP dysfunction causes a series of pancreatic diseases including acute necrotizing pancreatitis. However, the molecular mechanisms of EP activation and substrate recognition remain elusive, due to the lack of structural information on the EP heavy chain. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of human EP in inactive, active, and substrate-bound states at resolutions from 2.7 to 4.9 Å. The EP heavy chain was observed to clamp the light chain with CUB2 domain for substrate recognition. The EP light chain N-terminus induced a rearrangement of surface-loops from inactive to active conformations, resulting in activated EP. The heavy chain then served as a hinge for light-chain conformational changes to recruit and subsequently cleave substrate. Our study provides structural insights into rearrangements of EP surface-loops and heavy chain dynamics in the EP catalytic cycle, advancing our understanding of EP-associated pancreatitis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32828.map.gz emd_32828.map.gz | 46 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32828-v30.xml emd-32828-v30.xml emd-32828.xml emd-32828.xml | 7.9 KB 7.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_32828.png emd_32828.png | 82.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-32828.cif.gz emd-32828.cif.gz | 3.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32828 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32828 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32828 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32828 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8h3uMC  7wqwC  7wqxC  7wqzC  7wr7C 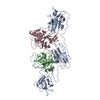 8h3sC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32828.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32828.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.046 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Enteropeptidase
| Entire | Name: Enteropeptidase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Enteropeptidase
| Supramolecule | Name: Enteropeptidase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 119676 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)




















