[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-31959: Human N-type voltage gated calcium channel CaV2.2-alpha2/delta1-b... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-31959 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human N-type voltage gated calcium channel CaV2.2-alpha2/delta1-beta1 complex, bound to ziconotide | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Voltage gated calcium channel / N-type / complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPresynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitter / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / Phase 2 - plateau phase / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / positive regulation of muscle contraction / NCAM1 interactions ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis of neurotransmitter / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / Phase 2 - plateau phase / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / positive regulation of muscle contraction / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / host cell presynaptic membrane / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / ion channel inhibitor activity / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / response to amyloid-beta / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / regulation of calcium ion transport / neuronal dense core vesicle / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / T-tubule / sarcoplasmic reticulum / calcium channel regulator activity / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / calcium ion transmembrane transport / GABA-ergic synapse / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / amyloid-beta binding / toxin activity / chemical synaptic transmission / neuronal cell body / calcium ion binding / synapse / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Conus magus (magus cone) Conus magus (magus cone) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dong Y / Gao Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2021Title: Closed-state inactivation and pore-blocker modulation mechanisms of human Ca2.2. Authors: Yanli Dong / Yiwei Gao / Shuai Xu / Yuhang Wang / Zhuoya Yu / Yue Li / Bin Li / Tian Yuan / Bei Yang / Xuejun Cai Zhang / Daohua Jiang / Zhuo Huang / Yan Zhao /  Abstract: N-type voltage-gated calcium (Ca) channels mediate Ca influx at presynaptic terminals in response to action potentials and play vital roles in synaptogenesis, release of neurotransmitters, and ...N-type voltage-gated calcium (Ca) channels mediate Ca influx at presynaptic terminals in response to action potentials and play vital roles in synaptogenesis, release of neurotransmitters, and nociceptive transmission. Here, we elucidate a cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the human Ca2.2 complex in apo, ziconotide-bound, and two Ca2.2-specific pore blockers-bound states. The second voltage-sensing domain (VSD) is captured in a resting-state conformation, trapped by a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP) molecule, which is distinct from the other three VSDs of Ca2.2, as well as activated VSDs observed in previous structures of Ca channels. This structure reveals the molecular basis for the unique inactivation process of Ca2.2 channels, in which the intracellular gate formed by S6 helices is closed and a W-helix from the domain II-III linker stabilizes closed-state inactivation. The structures of this inactivated, drug-bound complex lay a solid foundation for developing new state-dependent blockers for treatment of chronic pain. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_31959.map.gz emd_31959.map.gz | 118.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-31959-v30.xml emd-31959-v30.xml emd-31959.xml emd-31959.xml | 21.2 KB 21.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_31959.png emd_31959.png | 113.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-31959.cif.gz emd-31959.cif.gz | 9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31959 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31959 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31959 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vfuMC  7vfsC  7vfvC  7vfwC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_31959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_31959.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : CaV2.2-alpha2delta1-beta1 complex
+Supramolecule #1: CaV2.2-alpha2delta1-beta1 complex
+Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent N-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1B
+Macromolecule #2: Omega-conotoxin MVIIA
+Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1
+Macromolecule #4: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
+Macromolecule #7: HEXADECANE
+Macromolecule #8: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #9: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
+Macromolecule #10: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #11: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 9.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






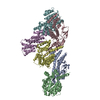
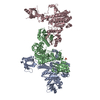
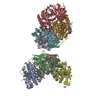











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)