[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-31155: hRAD51 mutation 273-DG-274 postsynaptic complex with dsDNA after ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-31155 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | hRAD51 mutation 273-DG-274 postsynaptic complex with dsDNA after strand exchange process. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpresynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin ...presynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton / response to glucoside / mitotic recombination-dependent replication fork processing / DNA recombinase assembly / cellular response to camptothecin / chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening / double-strand break repair involved in meiotic recombination / nuclear ubiquitin ligase complex / cellular response to cisplatin / DNA strand invasion / cellular response to hydroxyurea / mitotic recombination / DNA strand exchange activity / replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange / lateral element / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / Impaired BRCA2 binding to PALB2 / telomere maintenance via recombination / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / reciprocal meiotic recombination / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nuclear chromosome / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / replication fork processing / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / response to X-ray / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / interstrand cross-link repair / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / condensed nuclear chromosome / cellular response to ionizing radiation / male germ cell nucleus / meiotic cell cycle / cellular response to gamma radiation / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / PML body / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Meiotic recombination / response to toxic substance / single-stranded DNA binding / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / DNA recombination / chromosome, telomeric region / mitochondrial matrix / response to xenobiotic stimulus / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / enzyme binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang HW / Xu JF / Zhao LY | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2021 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2021Title: Mechanisms of distinctive mismatch tolerance between Rad51 and Dmc1 in homologous recombination. Authors: Jingfei Xu / Lingyun Zhao / Sijia Peng / Huiying Chu / Rui Liang / Meng Tian / Philip P Connell / Guohui Li / Chunlai Chen / Hong-Wei Wang /    Abstract: Homologous recombination (HR) is a primary DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair mechanism. The recombinases Rad51 and Dmc1 are highly conserved in the RecA family; Rad51 is mainly responsible for ...Homologous recombination (HR) is a primary DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair mechanism. The recombinases Rad51 and Dmc1 are highly conserved in the RecA family; Rad51 is mainly responsible for DNA repair in somatic cells during mitosis while Dmc1 only works during meiosis in germ cells. This spatiotemporal difference is probably due to their distinctive mismatch tolerance during HR: Rad51 does not permit HR in the presence of mismatches, whereas Dmc1 can tolerate certain mismatches. Here, the cryo-EM structures of Rad51-DNA and Dmc1-DNA complexes revealed that the major conformational differences between these two proteins are located in their Loop2 regions, which contain invading single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) binding residues and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) complementary strand binding residues, stabilizing ssDNA and dsDNA in presynaptic and postsynaptic complexes, respectively. By combining molecular dynamic simulation and single-molecule FRET assays, we identified that V273 and D274 in the Loop2 region of human RAD51 (hRAD51), corresponding to P274 and G275 of human DMC1 (hDMC1), are the key residues regulating mismatch tolerance during strand exchange in HR. This HR accuracy control mechanism provides mechanistic insights into the specific roles of Rad51 and Dmc1 in DNA double-strand break repair and may shed light on the regulatory mechanism of genetic recombination in mitosis and meiosis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_31155.map.gz emd_31155.map.gz | 98.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-31155-v30.xml emd-31155-v30.xml emd-31155.xml emd-31155.xml | 8.3 KB 8.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_31155.png emd_31155.png | 105.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31155 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31155 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31155 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-31155 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_31155.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_31155.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0825 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : hRAD51(mutation 273-DG-274)-dsDNA postsynaptic complex
| Entire | Name: hRAD51(mutation 273-DG-274)-dsDNA postsynaptic complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: hRAD51(mutation 273-DG-274)-dsDNA postsynaptic complex
| Supramolecule | Name: hRAD51(mutation 273-DG-274)-dsDNA postsynaptic complex type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 35 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 96 mM KCl, 2 mM ATP, 5 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM DTT |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 15.8 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 56.18 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 139616 |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








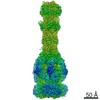














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















