[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-30015: The membrane-embedded Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30015 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
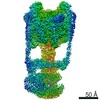
| Title | The membrane-embedded Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | The membrane-embedded Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | rotary ATPase / V/A-ATPase / molecular motor / MOTOR PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATPase binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
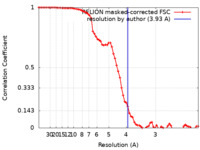
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.93 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kishikawa J / Nakanishi A / Furuta A / Kato T / Namba K / Tamakoshi M / Mitsuoka K / Yokoyama K | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 3 items Japan, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2020 Journal: Elife / Year: 2020Title: Mechanical inhibition of isolated V from V/A-ATPase for proton conductance. Authors: Jun-Ichi Kishikawa / Atsuko Nakanishi / Aya Furuta / Takayuki Kato / Keiichi Namba / Masatada Tamakoshi / Kaoru Mitsuoka / Ken Yokoyama /  Abstract: V-ATPase is an energy converting enzyme, coupling ATP hydrolysis/synthesis in the hydrophilic V domain, with proton flow through the V membrane domain, via rotation of the central rotor complex ...V-ATPase is an energy converting enzyme, coupling ATP hydrolysis/synthesis in the hydrophilic V domain, with proton flow through the V membrane domain, via rotation of the central rotor complex relative to the surrounding stator apparatus. Upon dissociation from the V domain, the V domain of the eukaryotic V-ATPase can adopt a physiologically relevant auto-inhibited form in which proton conductance through the V domain is prevented, however the molecular mechanism of this inhibition is not fully understood. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we determined the structure of both the V/A-ATPase and isolated V at near-atomic resolution, respectively. These structures clarify how the isolated V domain adopts the auto-inhibited form and how the complex prevents formation of the inhibited V form. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30015.map.gz emd_30015.map.gz | 3.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30015-v30.xml emd-30015-v30.xml emd-30015.xml emd-30015.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30015_fsc.xml emd_30015_fsc.xml | 7.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30015.png emd_30015.png | 76.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30015.cif.gz emd-30015.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30015 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30015 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30015 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30015 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ly9MC  6ly8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30015.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30015.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The membrane-embedded Vo domain of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Membrane-embedded Vo domain
| Entire | Name: Membrane-embedded Vo domain |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Membrane-embedded Vo domain
| Supramolecule | Name: Membrane-embedded Vo domain / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / Details: V/A-type ATPase from Thermus thermophilus |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 260 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: V-type ATP synthase subunit I
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 72.204289 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MIAPMEKLVL AGPKGRAKEL LQSLQQAGVV HLETLRPEAL SAYQLSPEER AELRRWEAVS AGAEHTLSLL GLEAEPARPF PEGLEAAEK ALSPIQAHAE GLTRQKQELE EELALAQAYL EPLERLAALA HGLDKSPFLR VIPFLLTEKE LPLVEEALRK A LEDRYLLA ...String: MIAPMEKLVL AGPKGRAKEL LQSLQQAGVV HLETLRPEAL SAYQLSPEER AELRRWEAVS AGAEHTLSLL GLEAEPARPF PEGLEAAEK ALSPIQAHAE GLTRQKQELE EELALAQAYL EPLERLAALA HGLDKSPFLR VIPFLLTEKE LPLVEEALRK A LEDRYLLA HEAYAGGVAA LVVVHRKEVD QAKAALSRAG VAELRLPGAL GELPLSEAAR RLKERAEAAP RELSEVRQHL AK LARESAS TLQSLWTRAQ DEVARLKALE ELASGRFGFA LLGYVPVKAK PKVEEALARH KESVVYAFEP VDEHHEADRI PVV LDNPPW AKPFELLVSF LNTPKYGTFD PTPVVPVFFP FWFGMIVGDI GYALLFYLVG RWLSGYVKRN EPLVIDLFAL KLKP QVIGK LVHILNWMVF WTVVWGVIYG EFFGTFLEHL GVFGTPEHPG LIPILIHRID TAKTANLLIL LSVAFGVVLV FFGLA LRAY LGLKHRHMAH FWEGVGYLGG LVGVLALAAS YLGNLQAGWL QGLMYLGFGV FLLAVLMSRI WLMIPEIFTQ AGHILS HIR IYAVGAAGGI LAGLLTDVGF ALAERLGLLG VLLGLLVAGV LHLLILLLTT LGHMLQPIRL LWVEFFTKFG FYEENGR PY RPFKSVREAQ UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit I |
-Macromolecule #2: V-type ATP synthase, subunit K
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase, subunit K / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.841714 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MKKLLVTVLL AVFGALAFAA EEAAASGGLD RGLIAVGMGL AVGLAALGTG VAQARIGAAG VGAIAEDRSN FGTALIFLLL PETLVIFGL LIAFILNGRL UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase, subunit K |
-Macromolecule #3: V-type ATP synthase subunit C
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.96857 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MADDFAYLNA RVRVRRGTLL KESFFQEALD LSFADFLRLL SETVYGGELA GQGLPDVDRA VLRTQAKLVG DLPRLVTGEA REAVRLLLL RNDLHNLQAL LRAKATGRPF EEVLLLPGTL REEVWRQAYE AQDPAGMAQV LAVPGHPLAR ALRAVLRETQ D LARVEALL ...String: MADDFAYLNA RVRVRRGTLL KESFFQEALD LSFADFLRLL SETVYGGELA GQGLPDVDRA VLRTQAKLVG DLPRLVTGEA REAVRLLLL RNDLHNLQAL LRAKATGRPF EEVLLLPGTL REEVWRQAYE AQDPAGMAQV LAVPGHPLAR ALRAVLRETQ D LARVEALL AKRFFEDVAK AAKGLDQPAL RDYLALEVDA ENLRTAFKLQ GSGLAPDAFF LKGGRFVDRV RFARLMEGDY AV LDELSGT PFSGLSGVRD LKALERGLRC VLLKEAKKGV QDPLGVGLVL AYVKEREWEA VRLRLLARRA YFGLPRAQVE EEV VCP UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit C |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM)
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.166218 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MTGGLVLNAI SRAGGAMGGL GLIKSLAEKE KQLLERLEAA KKEAEERVKR AEAEAKALLE EAEAKAKALE AQYRERERAE TEALLARYR ERAEAEAKAV REKAMARLDE AVALVLKEVL P UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM) |
-Macromolecule #5: V-type ATP synthase subunit E
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.645582 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSKLEAILSQ EVEAEIQALL QEAEAKAEAV KREAEEKAKA LLQARERALE AQYRAALRRA ESAGELLVAT ARTQARGEVL EEVRRRVRE ALEALPQKPE WPEVVRKLAL EALEALPGAK ALVANPEDLP HLEALARERG VELQAEPALR LGVRAVGAEG K TQVENSLL ARLDRAWDAL SSKVAQALWG UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit E |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3.0 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: MOLYBDENUM / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | |||||||||
| Details | The sample was purified from cell membrane of Thermus thermophilus and incorporated into nanodisc. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL CRYO ARM 200 |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: In-column Omega Filter |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-60 / Number real images: 5988 / Average exposure time: 12.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 79.2 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 2.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 1.4 mm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)