+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2937 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
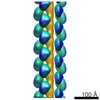
| Title | Electron cryo-microscopy structure of PB1-p62 type T filaments | |||||||||
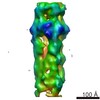
 Map data Map data | 3D reconstruction of PB1(1-122) type T | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Selective autophagy / autophagy receptor / autophagy scaffold / p62/SQSTM1 / single-particle helical reconstruction | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / brown fat cell proliferation / protein binding / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / aggrephagy / response to mitochondrial depolarisation / Lewy body / negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway ...: / brown fat cell proliferation / protein binding / protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein targeting to vacuole involved in autophagy / regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / aggrephagy / response to mitochondrial depolarisation / Lewy body / negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion / amphisome / protein heterooligomerization / regulation of protein complex stability / endosome organization / pexophagy / autophagy of mitochondrion / membraneless organelle assembly / phagophore assembly site / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of mitochondrion organization / regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / aggresome / endosomal transport / intracellular membraneless organelle / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / negative regulation of ferroptosis / cellular response to stress / temperature homeostasis / neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway / response to stress / autolysosome / molecular sequestering activity / positive regulation of macroautophagy / immune system process / mitophagy / energy homeostasis / inclusion body / signaling adaptor activity / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of autophagy / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / protein sequestering activity / autophagosome / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / SH2 domain binding / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Pexophagy / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / protein kinase C binding / ubiquitin binding / sarcomere / response to ischemia / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / macroautophagy / protein catabolic process / apoptotic signaling pathway / P-body / molecular condensate scaffold activity / PML body / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / autophagy / Interleukin-1 signaling / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / protein import into nucleus / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / intracellular protein localization / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / late endosome / sperm midpiece / signaling receptor activity / Neddylation / cytoplasmic vesicle / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / transcription by RNA polymerase II / cell differentiation / protein phosphorylation / lysosome / endosome / intracellular signal transduction / positive regulation of apoptotic process / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / apoptotic process / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / protein kinase binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / protein homodimerization activity / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / extracellular exosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ciuffa R / Lamark T / Tarafder A / Guesdon A / Rybina S / Hagen WJH / Johansen T / Sachse C | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2015 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2015Title: The selective autophagy receptor p62 forms a flexible filamentous helical scaffold. Authors: Rodolfo Ciuffa / Trond Lamark / Abul K Tarafder / Audrey Guesdon / Sofia Rybina / Wim J H Hagen / Terje Johansen / Carsten Sachse /   Abstract: The scaffold protein p62/SQSTM1 is involved in protein turnover and signaling and is commonly found in dense protein bodies in eukaryotic cells. In autophagy, p62 acts as a selective autophagy ...The scaffold protein p62/SQSTM1 is involved in protein turnover and signaling and is commonly found in dense protein bodies in eukaryotic cells. In autophagy, p62 acts as a selective autophagy receptor that recognizes and shuttles ubiquitinated proteins to the autophagosome for degradation. The structural organization of p62 in cellular bodies and the interplay of these assemblies with ubiquitin and the autophagic marker LC3 remain to be elucidated. Here, we present a cryo-EM structural analysis of p62. Together with structures of assemblies from the PB1 domain, we show that p62 is organized in flexible polymers with the PB1 domain constituting a helical scaffold. Filamentous p62 is capable of binding LC3 and addition of long ubiquitin chains induces disassembly and shortening of filaments. These studies explain how p62 assemblies provide a large molecular scaffold for the nascent autophagosome and reveal how they can bind ubiquitinated cargo. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2937.map.gz emd_2937.map.gz | 12.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2937-v30.xml emd-2937-v30.xml emd-2937.xml emd-2937.xml | 23.3 KB 23.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_2937.png emd_2937.png | 443 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2937 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2937 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2937 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
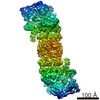
| Related structure data |  4uf9MC 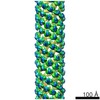 2936C  4uf8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2937.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 18.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2937.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 18.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D reconstruction of PB1(1-122) type T | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.372 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PB1(1-122) domain of p62/Sqstm1
| Entire | Name: PB1(1-122) domain of p62/Sqstm1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: PB1(1-122) domain of p62/Sqstm1
| Supramolecule | Name: PB1(1-122) domain of p62/Sqstm1 / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Details: Helical polymer / Oligomeric state: Helical / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 13.7 KDa / Theoretical: 13.7 KDa / Method: Theoretical weight of construct |
-Macromolecule #1: Sequestosome-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Sequestosome-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: p62/SQSTM1 / Oligomeric state: Helical / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 13.7 KDa / Theoretical: 13.7 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Sequestosome-1 GO: phagophore assembly site, autophagy of mitochondrion, P-body, P-body, positive regulation of protein phosphorylation, immune system process, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, protein ...GO: phagophore assembly site, autophagy of mitochondrion, P-body, P-body, positive regulation of protein phosphorylation, immune system process, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, protein kinase C binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, protein binding, nucleus, nucleus, nucleoplasm, cytoplasm, cytoplasm, cytoplasm, lysosome, lysosome, endosome, late endosome, autophagosome, autophagosome, autophagosome, endoplasmic reticulum, endoplasmic reticulum, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, cytosol, protein phosphorylation, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, autophagy, autophagy, autophagy, apoptotic process, response to stress, intracellular protein localization, zinc ion binding, regulation of mitochondrion organization, endosomal transport, inclusion body, aggresome, aggresome, macroautophagy, positive regulation of macroautophagy, PML body, protein kinase binding, cell differentiation, receptor tyrosine kinase binding, cytoplasmic vesicle, intracellular signal transduction, SH2 domain binding, identical protein binding, identical protein binding, identical protein binding, identical protein binding, identical protein binding, protein homodimerization activity, positive regulation of apoptotic process, negative regulation of apoptotic process, regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction, ubiquitin binding, positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II, regulation of Ras protein signal transduction, metal ion binding, neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway, neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway, protein heterooligomerization, extracellular exosome, K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding, apoptotic signaling pathway, GO: 0098779, regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion InterPro: PB1 domain, UBA-like superfamily, Ubiquitin-associated domain, Zinc finger, ZZ-type |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.25 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, DTT 4 mM |
| Grid | Details: glow-discharged C-flat 1.2/1.3 and 200 mesh Quantifoil multi-A grids |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber temperature: 77 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Method: Backside blotting |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Date | Oct 9, 2012 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 443 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | All of the image processing was carried using the SPRING package. |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 10.09 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 26.71 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 10.3 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: SPRING |
| CTF correction | Details: CTFFIND, convolution images, Wiener filter reconstruction |
| Final angle assignment | Details: SPIDER |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















