[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28724: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S, denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Insulin receptor / insulin / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSignaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / Signal attenuation / Insulin receptor recycling / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth ...Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / Signal attenuation / Insulin receptor recycling / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / regulation of female gonad development / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / nuclear lumen / insulin-like growth factor I binding / insulin receptor activity / exocrine pancreas development / insulin binding / adrenal gland development / PTB domain binding / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / regulation of protein secretion / Insulin processing / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / alpha-beta T cell activation / insulin receptor substrate binding / regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / activation of protein kinase B activity / epidermis development / negative regulation of protein secretion / protein kinase activator activity / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / heart morphogenesis / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / transport vesicle / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of cytokine production / animal organ morphogenesis / endosome lumen / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / insulin receptor binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / hormone activity / regulation of synaptic plasticity / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / caveola / receptor internalization / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / vasodilation / male gonad development / cognition / recycling endosome membrane / glucose metabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / nuclear envelope / late endosome / cell-cell signaling / glucose homeostasis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li J / Wu JY / Hall C / Bai XC / Choi E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Molecular basis for the role of disulfide-linked αCTs in the activation of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and insulin receptor. Authors: Jie Li / Jiayi Wu / Catherine Hall / Xiao-Chen Bai / Eunhee Choi /  Abstract: The insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) control metabolic homeostasis and cell growth and proliferation. The IR and IGF1R form similar disulfide bonds linked ...The insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) control metabolic homeostasis and cell growth and proliferation. The IR and IGF1R form similar disulfide bonds linked homodimers in the apo-state; however, their ligand binding properties and the structures in the active state differ substantially. It has been proposed that the disulfide-linked C-terminal segment of α-chain (αCTs) of the IR and IGF1R control the cooperativity of ligand binding and regulate the receptor activation. Nevertheless, the molecular basis for the roles of disulfide-linked αCTs in IR and IGF1R activation are still unclear. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of full-length mouse IGF1R/IGF1 and IR/insulin complexes with modified αCTs that have increased flexibility. Unlike the -shaped asymmetric IGF1R dimer with a single IGF1 bound, the IGF1R with the enhanced flexibility of αCTs can form a -shaped symmetric dimer with two IGF1s bound. Meanwhile, the IR with non-covalently linked αCTs predominantly adopts an asymmetric conformation with four insulins bound, which is distinct from the -shaped symmetric IR. Using cell-based experiments, we further showed that both IGF1R and IR with the modified αCTs cannot activate the downstream signaling potently. Collectively, our studies demonstrate that the certain structural rigidity of disulfide-linked αCTs is critical for optimal IR and IGF1R signaling activation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28724.map.gz emd_28724.map.gz | 61.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28724-v30.xml emd-28724-v30.xml emd-28724.xml emd-28724.xml | 17.6 KB 17.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28724.png emd_28724.png | 20.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28724.cif.gz emd-28724.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28724_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28724_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28724_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28724_half_map_2.map.gz | 80.7 MB 80.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28724 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28724 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28724 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28724 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8eyyMC  8eyrC  8eyxC  8ez0C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28724.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28724.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
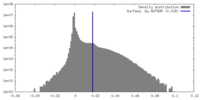
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse...
| File | emd_28724_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse...
| File | emd_28724_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant...
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant...
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 153.184406 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: HLYPGEVCPG MDIRNNLTRL HELENCSVIE GHLQILLMFK TRPEDFRDLS FPKLIMITDY LLLFRVYGLE SLKDLFPNLT VIRGSRLFF NYALVIFEMV HLKELGLYNL MNITRGSVRI EKNNELCYLA TIDWSRILDS VEDNYIVLNK DDNEECGDVC P GTAKGKTN ...String: HLYPGEVCPG MDIRNNLTRL HELENCSVIE GHLQILLMFK TRPEDFRDLS FPKLIMITDY LLLFRVYGLE SLKDLFPNLT VIRGSRLFF NYALVIFEMV HLKELGLYNL MNITRGSVRI EKNNELCYLA TIDWSRILDS VEDNYIVLNK DDNEECGDVC P GTAKGKTN CPATVINGQF VERCWTHSHC QKVCPTICKS HGCTAEGLCC HKECLGNCSE PDDPTKCVAC RNFYLDGQCV ET CPPPYYH FQDWRCVNFS FCQDLHFKCR NSRKPGCHQY VIHNNKCIPE CPSGYTMNSS NLMCTPCLGP CPKVCQILEG EKT IDSVTS AQELRGCTVI NGSLIINIRG GNNLAAELEA NLGLIEEISG FLKIRRSYAL VSLSFFRKLH LIRGETLEIG NYSF YALDN QNLRQLWDWS KHNLTITQGK LFFHYNPKLC LSEIHKMEEV SGTKGRQERN DIALKTNGDQ ASCENELLKF SFIRT SFDK ILLRWEPYWP PDFRDLLGFM LFYKEAPYQN VTEFDGQDAC GSNSWTVVDI DPPQRSNDPK SQTPSHPGWL MRGLKP WTQ YAIFVKTLVT FSDERRTYGA KSDIIYVQTD ATNPSVPLDP ISVSNSSSQI ILKWKPPSDP NGNITHYLVY WERQAED SE LFELDYCLKG LKLPSRTWSP PFESDDSQKH NQSEYDDSAS ESSSSPKTDS QILKELEESS FRKTFEDYLH NVVFVPRP S RKRRSLEEVG NVTATTLTLP DFPNVSSTIV PTSQEEHRPF EKVVNKESLV ISGLRHFTGY RIELQACNQD SPDERCSVA AYVSARTMPE AKADDIVGPV THEIFENNVV HLMWQEPKEP NGLIVLYEVS YRRYGDEELH LCVSRKHFAL ERGCRLRGLS PGNYSVRVR ATSLAGNGSW TEPTYFYVTD YLDVPSNIAK IIIGPLIFVF LFSVVIGSIY LFLRKRQPDG PMGPLYASSN P EYLSASDV FPSSVYVPDE WEVPREKITL LRELGQGSFG MVYEGNAKDI IKGEAETRVA VKTVNESASL RERIEFLNEA SV MKGFTCH HVVRLLGVVS KGQPTLVVME LMAHGDLKSH LRSLRPDAEN NPGRPPPTLQ EMIQMTAEIA DGMAYLNAKK FVH RDLAAR NCMVAHDFTV KIGDFGMTRD IYETDYYRKG GKGLLPVRWM SPESLKDGVF TASSDMWSFG VVLWEITSLA EQPY QGLSN EQVLKFVMDG GYLDPPDNCP ERLTDLMRMC WQFNPKMRPT FLEIVNLLKD DLHPSFPEVS FFYSEENKAP ESEEL EMEF EDMENVPLDR SSHCQREEAG GREGGSSLSI KRTYDEHIPY THMNGGKKNG RVLTLPRSNP S UniProtKB: Insulin receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Insulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.989862 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
| Sequence | String: MALWMRLLPL LALLALWGPD PAAAFVNQHL CGSHLVEALY LVCGERGFFY TPKTRREAED LQVGQVELGG GPGAGSLQPL ALEGSLQKR GIVEQCCTSI CSLYQLENYC N UniProtKB: Insulin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)