+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25800 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
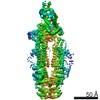
| Title | The structure of ATP-bound ABCA1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HDL / cholesterol / Tangier Disease / ABC transporter / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationorganic hydroxy compound transport / phospholipid transporter activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / ABC-type transporter activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
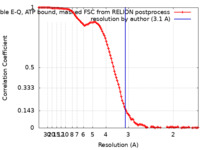
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun Y / Li X | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Cardiovasc Res / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Cardiovasc Res / Year: 2022Title: Cholesterol efflux mechanism revealed by structural analysis of human ABCA1 conformational states. Authors: Yingyuan Sun / Xiaochun Li /  Abstract: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) utilizes energy derived from ATP hydrolysis to export cholesterol and phospholipids from macrophages. ABCA1 plays a central role in the biosynthesis of ...ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) utilizes energy derived from ATP hydrolysis to export cholesterol and phospholipids from macrophages. ABCA1 plays a central role in the biosynthesis of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), which mediates reverse cholesterol transport and prevents detrimental lipid deposition. Mutations in ABCA1 cause Tangier disease characterized by a remarkable reduction in the amount of HDL in blood. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human ABCA1 in ATP-bound and nucleotide-free states. Structural comparison reveals that ATP molecules pull the nucleotide-binding domains together, inducing movements of transmembrane helices 1, 2, 7 and 8 through a series of salt-bridge interactions. Subsequently, extracellular domains (ECDs) undergo a rotation and introduce conformational changes in the ECD-transmembrane interface. In addition, while we observe a sterol-like molecule in ECDs, no such density was observed in the structure of an HDL-deficiency mutant ABCA1, demonstrating the physiological importance of ECDs and a putative interaction mode between ABCA1 and its lipid acceptors. Thus, these structures, along with cholesterol efflux assays, advance the understanding ABCA1-mediated reverse cholesterol transport. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25800.map.gz emd_25800.map.gz | 17.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25800-v30.xml emd-25800-v30.xml emd-25800.xml emd-25800.xml | 23.2 KB 23.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_25800_fsc.xml emd_25800_fsc.xml | 11.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_25800.png emd_25800.png | 80.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25800.cif.gz emd-25800.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_25800_additional_1.map.gz emd_25800_additional_1.map.gz emd_25800_half_map_1.map.gz emd_25800_half_map_1.map.gz emd_25800_half_map_2.map.gz emd_25800_half_map_2.map.gz | 7.2 MB 98.7 MB 98.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25800 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25800 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_25800_validation.pdf.gz emd_25800_validation.pdf.gz | 815 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_25800_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25800_full_validation.pdf.gz | 814.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_25800_validation.xml.gz emd_25800_validation.xml.gz | 18.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_25800_validation.cif.gz emd_25800_validation.cif.gz | 24 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25800 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25800 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25800 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7tbwMC  7tbyC  7tbzC  7tc0C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25800.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25800.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
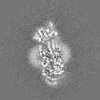
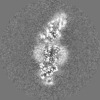
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.844 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
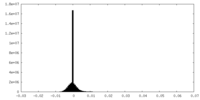
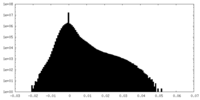
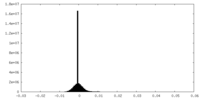
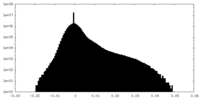
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: focused refinement of the extracellular domain
| File | emd_25800_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | focused refinement of the extracellular domain | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_25800_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_25800_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ABCA1 in complex with ATP
| Entire | Name: ABCA1 in complex with ATP |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ABCA1 in complex with ATP
| Supramolecule | Name: ABCA1 in complex with ATP / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 250 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 255.653016 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MACWPQLRLL LWKNLTFRRR QTCQLLLEVA WPLFIFLILI SVRLSYPPYE QHECHFPNKA MPSAGTLPWV QGIICNANNP CFRYPTPGE APGVVGNFNK SIVARLFSDA RRLLLYSQKD TSMKDMRKVL RTLQQIKKSS SNLKLQDFLV DNETFSGFLY H NLSLPKST ...String: MACWPQLRLL LWKNLTFRRR QTCQLLLEVA WPLFIFLILI SVRLSYPPYE QHECHFPNKA MPSAGTLPWV QGIICNANNP CFRYPTPGE APGVVGNFNK SIVARLFSDA RRLLLYSQKD TSMKDMRKVL RTLQQIKKSS SNLKLQDFLV DNETFSGFLY H NLSLPKST VDKMLRADVI LHKVFLQGYQ LHLTSLCNGS KSEEMIQLGD QEVSELCGLP REKLAAAERV LRSNMDILKP IL RTLNSTS PFPSKELAEA TKTLLHSLGT LAQELFSMRS WSDMRQEVMF LTNVNSSSSS TQIYQAVSRI VCGHPEGGGL KIK SLNWYE DNNYKALFGG NGTEEDAETF YDNSTTPYCN DLMKNLESSP LSRIIWKALK PLLVGKILYT PDTPATRQVM AEVN KTFQE LAVFHDLEGM WEELSPKIWT FMENSQEMDL VRMLLDSRDN DHFWEQQLDG LDWTAQDIVA FLAKHPEDVQ SSNGS VYTW REAFNETNQA IRTISRFMEC VNLNKLEPIA TEVWLINKSM ELLDERKFWA GIVFTGITPG SIELPHHVKY KIRMDI DNV ERTNKIKDGY WDPGPRADPF EDMRYVWGGF AYLQDVVEQA IIRVLTGTEK KTGVYMQQMP YPCYVDDIFL RVMSRSM PL FMTLAWIYSV AVIIKGIVYE KEARLKETMR IMGLDNSILW FSWFISSLIP LLVSAGLLVV ILKLGNLLPY SDPSVVFV F LSVFAVVTIL QCFLISTLFS RANLAAACGG IIYFTLYLPY VLCVAWRDYV GFTLKIFASL LSPVAFGFGC EYFALFEEQ GIGVQWDNLF ESPVEEDGFN LTTSVSMMLF DTFLYGVMTW YIEAVFPGQY GIPRPWYFPC TKSYWFGEES DEKSHPGSNQ KRISEICME EEPTHLKLGV SIQNLVKVYR DGMKVAVDGL ALNFYEGQIT SFLGHNGAGK TTTMSILTGL FPPTSGTAYI L GKDIRSEM STIRQNLGVC PQHNVLFDML TVEEHIWFYA RLKGLSEKHV KAEMEQMALD VGLPSSKLKS KTSQLSGGMQ RK LSVALAF VGGSKVVILD QPTAGVDPYS RRGIWELLLK YRQGRTIILS THHMDEADVL GDRIAIISHG KLCCVGSSLF LKN QLGTGY YLTLVKKDVE SSLSSCRNSS STVSYLKKED SVSQSSSDAG LGSDHESDTL TIDVSAISNL IRKHVSEARL VEDI GHELT YVLPYEAAKE GAFVELFHEI DDRLSDLGIS SYGISETTLE EIFLKVAEES GVDAETSDGT LPARRNRRAF GDKQS CLRP FTEDDAADPN DSDIDPESRE TDLLSGMDGK GSYQVKGWKL TQQQFVALLW KRLLIARRSR KGFFAQIVLP AVFVCI ALV FSLIVPPFGK YPSLELQPWM YNEQYTFVSN DAPEDTGTLE LLNALTKDPG FGTRCMEGNP IPDTPCQAGE EEWTTAP VP QTIMDLFQNG NWTMQNPSPA CQCSSDKIKK MLPVCPPGAG GLPPPQRKQN TADILQDLTG RNISDYLVKT YVQIIAKS L KNKIWVNEFR YGGFSLGVSN TQALPPSQEV NDAIKQMKKH LKLAKDSSAD RFLNSLGRFM TGLDTKNNVK VWFNNKGWH AISSFLNVIN NAILRANLQK GENPSHYGIT AFNHPLNLTK QQLSEVALMT TSVDVLVSIC VIFAMSFVPA SFVVFLIQER VSKAKHLQF ISGVKPVIYW LSNFVWDMCN YVVPATLVII IFICFQQKSY VSSTNLPVLA LLLLLYGWSI TPLMYPASFV F KIPSTAYV VLTSVNLFIG INGSVATFVL ELFTDNKLNN INDILKSVFL IFPHFCLGRG LIDMVKNQAM ADALERFGEN RF VSPLSWD LVGRNLFAMA VEGVVFFLIT VLIQYRFFIR PRPVNAKLSP LNDEDEDVRR ERQRILDGGG QNDILEIKEL TKI YRRKRK PAVDRICVGI PPGECFGLLG VNGAGKSSTF KMLTGDTTVT RGDAFLNKNS ILSNIHEVHQ NMGYCPQFDA ITEL LTGRE HVEFFALLRG VPEKEVGKVG EWAIRKLGLV KYGEKYAGNY SGGNKRKLST AMALIGGPPV VFLDQPTTGM DPKAR RFLW NCALSVVKEG RSVVLTSHSM EECEALCTRM AIMVNGRFRC LGSVQHLKNR FGDGYTIVVR IAGSNPDLKP VQDFFG LAF PGSVLKEKHR NMLQYQLPSS LSSLARIFSI LSQSKKRLHI EDYSVSQTTL DQVFVNFAKD QSDDDHLKDL SLHKNQT VV DVAVLTSFLQ DEKVKESYVG DYKDDDDK UniProtKB: P-type phospholipid transporter |
-Macromolecule #4: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








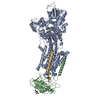

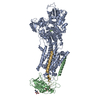
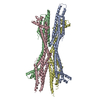
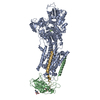


 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)