[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25447: The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25447 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) with ATP/Mg and Lumacaftor (VX-809) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | E1371QCFTR/lumacaftor/ATP | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ABC transporter / ion channel / folding correction / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP-BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / transepithelial water transport / RHO GTPases regulate CFTR trafficking / amelogenesis / intracellular pH elevation ...positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity / : / Sec61 translocon complex binding / channel-conductance-controlling ATPase / intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity / positive regulation of enamel mineralization / transepithelial water transport / RHO GTPases regulate CFTR trafficking / amelogenesis / intracellular pH elevation / chloride channel inhibitor activity / : / Golgi-associated vesicle membrane / multicellular organismal-level water homeostasis / cholesterol transport / bicarbonate transport / bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity / chloride channel regulator activity / vesicle docking involved in exocytosis / membrane hyperpolarization / chloride transmembrane transporter activity / sperm capacitation / cholesterol biosynthetic process / RHOQ GTPase cycle / chloride channel activity / positive regulation of exocytosis / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / chloride channel complex / positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ABC-type transporter activity / 14-3-3 protein binding / cellular response to forskolin / chloride transmembrane transport / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / cellular response to cAMP / PDZ domain binding / establishment of localization in cell / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / Late endosomal microautophagy / recycling endosome / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / transmembrane transport / recycling endosome membrane / Chaperone Mediated Autophagy / Aggrephagy / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / protein-folding chaperone binding / early endosome membrane / early endosome / endosome membrane / Ub-specific processing proteases / apical plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / enzyme binding / cell surface / protein-containing complex / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / nucleus / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
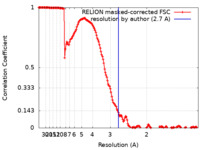
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fiedorczuk K / Chen J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell / Year: 2022Title: Mechanism of CFTR correction by type I folding correctors. Authors: Karol Fiedorczuk / Jue Chen /  Abstract: Small molecule chaperones have been exploited as therapeutics for the hundreds of diseases caused by protein misfolding. The most successful examples are the CFTR correctors, which transformed cystic ...Small molecule chaperones have been exploited as therapeutics for the hundreds of diseases caused by protein misfolding. The most successful examples are the CFTR correctors, which transformed cystic fibrosis therapy. These molecules revert folding defects of the ΔF508 mutant and are widely used to treat patients. To investigate the molecular mechanism of their action, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of CFTR in complex with the FDA-approved correctors lumacaftor or tezacaftor. Both drugs insert into a hydrophobic pocket in the first transmembrane domain (TMD1), linking together four helices that are thermodynamically unstable. Mutating residues at the binding site rendered ΔF508-CFTR insensitive to lumacaftor and tezacaftor, underscoring the functional significance of the structural discovery. These results support a mechanism in which the correctors stabilize TMD1 at an early stage of biogenesis, prevent its premature degradation, and thereby allosterically rescuing many disease-causing mutations. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25447.map.gz emd_25447.map.gz | 304.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25447-v30.xml emd-25447-v30.xml emd-25447.xml emd-25447.xml | 17.2 KB 17.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_25447_fsc.xml emd_25447_fsc.xml | 15.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_25447.png emd_25447.png | 149.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25447.cif.gz emd-25447.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25447 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25447 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25447 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25447 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_25447_validation.pdf.gz emd_25447_validation.pdf.gz | 685.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_25447_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25447_full_validation.pdf.gz | 685.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_25447_validation.xml.gz emd_25447_validation.xml.gz | 14.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_25447_validation.cif.gz emd_25447_validation.cif.gz | 20 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25447 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25447 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25447 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25447 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7svdMC  7sv7C  7svrC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11008 (Title: The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) with ATP/Mg and Lumacaftor (VX-809) EMPIAR-11008 (Title: The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) with ATP/Mg and Lumacaftor (VX-809)Data size: 5.8 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) with ATP/Mg and Lumacaftor (VX-809) [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25447.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25447.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | E1371QCFTR/lumacaftor/ATP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.676 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane...
+Supramolecule #1: The complex of phosphorylated human cystic fibrosis transmembrane...
+Macromolecule #1: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
+Macromolecule #2: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
+Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #5: DODECANE
+Macromolecule #6: DECANE
+Macromolecule #7: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #8: Lumacaftor
+Macromolecule #9: UNKNOWN ATOM OR ION
+Macromolecule #10: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 98.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)