+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25196 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of SGLT1 at 3.15 angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Membrane transporter / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.15 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Qu Q / Han L | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structure and mechanism of the SGLT family of glucose transporters. Authors: Lei Han / Qianhui Qu / Deniz Aydin / Ouliana Panova / Michael J Robertson / Yan Xu / Ron O Dror / Georgios Skiniotis / Liang Feng /   Abstract: Glucose is a primary energy source in living cells. The discovery in 1960s that a sodium gradient powers the active uptake of glucose in the intestine heralded the concept of a secondary active ...Glucose is a primary energy source in living cells. The discovery in 1960s that a sodium gradient powers the active uptake of glucose in the intestine heralded the concept of a secondary active transporter that can catalyse the movement of a substrate against an electrochemical gradient by harnessing energy from another coupled substrate. Subsequently, coupled Na/glucose transport was found to be mediated by sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs). SGLTs are responsible for active glucose and galactose absorption in the intestine and for glucose reabsorption in the kidney, and are targeted by multiple drugs to treat diabetes. Several members within the SGLT family transport key metabolites other than glucose. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the prototypic human SGLT1 and a related monocarboxylate transporter SMCT1 from the same family. The structures, together with molecular dynamics simulations and functional studies, define the architecture of SGLTs, uncover the mechanism of substrate binding and selectivity, and shed light on water permeability of SGLT1. These results provide insights into the multifaceted functions of SGLTs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
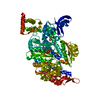
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25196.map.gz emd_25196.map.gz | 101.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25196-v30.xml emd-25196-v30.xml emd-25196.xml emd-25196.xml | 11.1 KB 11.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25196.png emd_25196.png | 61.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25196.cif.gz emd-25196.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25196 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25196 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25196 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25196 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_25196_validation.pdf.gz emd_25196_validation.pdf.gz | 485.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_25196_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25196_full_validation.pdf.gz | 485.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_25196_validation.xml.gz emd_25196_validation.xml.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_25196_validation.cif.gz emd_25196_validation.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25196 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25196 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25196 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25196 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7slaMC  7sl8C  7sl9C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25196.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 107.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25196.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 107.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.85 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SGLT1 and nanobody complex
| Entire | Name: SGLT1 and nanobody complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SGLT1 and nanobody complex
| Supramolecule | Name: SGLT1 and nanobody complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sodium/glucose cotransporter 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 74.622031 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDSSTWSPKT TAVTRPVETH ELIRNAADIS VIVIYFLLVM AVGLWSMFKT NRGTVGGFFL AGRSMVWWPI GASLFASNIG SGHFIGLAG TGAASGLAVG GFEWNALVLL LVLGWVFVPI YIKAGVVTMP EYLRKRFGGQ RIQVYLSVLS LFLYIFTKIS V DIFSGAIF ...String: MDSSTWSPKT TAVTRPVETH ELIRNAADIS VIVIYFLLVM AVGLWSMFKT NRGTVGGFFL AGRSMVWWPI GASLFASNIG SGHFIGLAG TGAASGLAVG GFEWNALVLL LVLGWVFVPI YIKAGVVTMP EYLRKRFGGQ RIQVYLSVLS LFLYIFTKIS V DIFSGAIF INLALGWNLY LSIILLLAIT ALYTITGGLA AVIYTDTLQT LIMLIGALIL MGFAFHEVGG YDAFMEKYMK AI PTIVSDG NTTFQEKCYT PRADSFHIFR DPLTGDLPWP GFIFGLTILA LWYWCTDQVI VQRCLAAKNM SHVKGGCILA GYL KLLPMF IMVMPGMISR ILFPDKVACV VPSECEKYCG TKVGCTNIAY PTLVVELMPN GLRGLMLAVM LAALMSSLTS IFNS ASTLF TMDIYAKVRK RASEKELMIV GRLFVLFLVV VSIAWIPIVQ SAQSGQLFDY IQSVSSYLAP PVAAVFLLAI FWKRV NEQG AFWGLILGLL LGLSRLILEF AYGTGSCMEP SNCPTIICGV HYLYFAIILF AISGIVTVVV SLLTKPIPDV HLYRLC WSL RNSKEERIDL DAEEENIQEG PKETIEIETQ VPEKKKGIFR RAYDLFCGLE QHGAPKMTEE EEKAMKMKMT DTSEKPL WR TVLNINAILL LAVAIFCHAY FASNSLEVLF Q |
-Macromolecule #2: nanobody Nb1
| Macromolecule | Name: nanobody Nb1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.126768 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAQVQLQESG GGLVQAGGSL RLSCAASGTI FVFDKMGWYR QAPGKEREFV ATISRGGSTN YADSVKGRFT ISRDNAKNTV YLQMNSLKP EDTAVYYCAV RYTPWRRYSY WGQGTQVTVS SHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #3: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 67.88 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.15 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 94369 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)