[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24466: Cryo-EM structure of Xenopus Patched-1 in complex with GAS1 and S... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24466 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
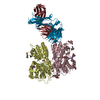
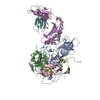
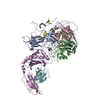
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Xenopus Patched-1 in complex with GAS1 and Sonic Hedgehog | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of nodal signaling pathway / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation ...regulation of nodal signaling pathway / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / negative regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / morphogen activity / regulation of odontogenesis / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development / hedgehog receptor activity / trunk neural crest cell migration / Formation of lateral plate mesoderm / hindgut morphogenesis / polarity specification of anterior/posterior axis / regulation of glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation / regulation of prostatic bud formation / formation of anatomical boundary / smoothened binding / positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation / metanephric mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in metanephros development / ventral midline development / trachea morphogenesis / hedgehog family protein binding / cholesterol-protein transferase activity / HHAT G278V doesn't palmitoylate Hh-Np / telencephalon regionalization / bud outgrowth involved in lung branching / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling / Ligand-receptor interactions / laminin-1 binding / lung epithelium development / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / salivary gland cavitation / spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / negative regulation of mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / cell development / spinal cord motor neuron differentiation / positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / establishment of epithelial cell polarity / intermediate filament organization / prostate gland development / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / limb bud formation / embryonic skeletal system development / skeletal muscle fiber differentiation / lung lobe morphogenesis / Activation of SMO / mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / patched binding / animal organ formation / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / embryonic foregut morphogenesis / hindbrain development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development / epithelial cell proliferation involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / somite development / ectoderm development / neuron fate commitment / negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation / mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / stem cell development / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / self proteolysis / smooth muscle tissue development / artery development / thalamus development / positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment / negative thymic T cell selection / pattern specification process / regulation of stem cell proliferation / oligodendrocyte development / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / male genitalia development / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / embryonic pattern specification / epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / lung-associated mesenchyme development / dopaminergic neuron differentiation / intein-mediated protein splicing / glycosaminoglycan binding / Formation of axial mesoderm / oxysterol binding / Developmental Lineage of Pancreatic Acinar Cells Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) / | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang P / Lian T / Wierbowski B / Garcia-Linares S / Jiang J / Salic A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Dev Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Dev Cell / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for catalyzed assembly of the Sonic hedgehog-Patched1 signaling complex. Authors: Pengxiang Huang / Bradley M Wierbowski / Tengfei Lian / Charlene Chan / Sara García-Linares / Jiansen Jiang / Adrian Salic /  Abstract: The dually lipidated Sonic hedgehog (SHH) morphogen signals through the tumor suppressor membrane protein Patched1 (PTCH1) to activate the Hedgehog pathway, which is fundamental in development and ...The dually lipidated Sonic hedgehog (SHH) morphogen signals through the tumor suppressor membrane protein Patched1 (PTCH1) to activate the Hedgehog pathway, which is fundamental in development and cancer. SHH engagement with PTCH1 requires the GAS1 coreceptor, but the mechanism is unknown. We demonstrate a unique role for GAS1, catalyzing SHH-PTCH1 complex assembly in vertebrate cells by direct SHH transfer from the extracellular SCUBE2 carrier to PTCH1. Structure of the GAS1-SHH-PTCH1 transition state identifies how GAS1 recognizes the SHH palmitate and cholesterol modifications in modular fashion and how it facilitates lipid-dependent SHH handoff to PTCH1. Structure-guided experiments elucidate SHH movement from SCUBE2 to PTCH1, explain disease mutations, and demonstrate that SHH-induced PTCH1 dimerization causes its internalization from the cell surface. These results define how the signaling-competent SHH-PTCH1 complex assembles, the key step triggering the Hedgehog pathway, and provide a paradigm for understanding morphogen reception and its regulation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24466.map.gz emd_24466.map.gz | 33.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24466-v30.xml emd-24466-v30.xml emd-24466.xml emd-24466.xml | 14.5 KB 14.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_24466.png emd_24466.png | 148.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24466.cif.gz emd-24466.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24466 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24466 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24466 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24466 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rhqMC  7rhrC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24466.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24466.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Patched Hedgehog GAS1 complex
+Supramolecule #1: Patched Hedgehog GAS1 complex
+Macromolecule #1: Patched-1
+Macromolecule #2: Sonic hedgehog protein N-product
+Macromolecule #3: Growth arrest-specific protein 1
+Macromolecule #5: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #6: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
+Macromolecule #7: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #9: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #10: PALMITIC ACID
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 71.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.53 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 54175 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















 Insecta environmental sample (insect)
Insecta environmental sample (insect)