+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23813 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
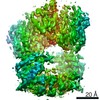
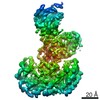
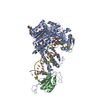
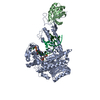
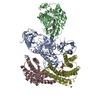
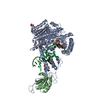
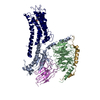
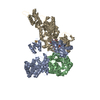
| Title | Autoinhibited B-Raf:(14-3-3)2:MEK complex with resolved RBD | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | B-Raf / MEK / 14-3-3 / B-Raf complex / B-Raf monomer / Inactive B-Raf / Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf / RBD / signaling protein / SIGNALING PROTEIN-TRANSFERASE complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationepithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / synaptic target recognition / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / Golgi reassembly / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / NOTCH4 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus ...epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis / synaptic target recognition / positive regulation of endodermal cell differentiation / negative regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion / Golgi reassembly / negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction / CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axon regeneration / NOTCH4 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / regulation of axon regeneration / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / positive regulation of muscle contraction / Golgi inheritance / establishment of Golgi localization / placenta blood vessel development / MAP-kinase scaffold activity / Signalling to p38 via RIT and RIN / cerebellar cortex formation / labyrinthine layer development / respiratory system process / head morphogenesis / ARMS-mediated activation / melanosome transport / tube formation / endothelial cell apoptotic process / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / type B pancreatic cell proliferation / regulation of synapse maturation / Signaling by MAP2K mutants / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / Rap1 signalling / negative regulation of fibroblast migration / positive regulation of D-glucose transmembrane transport / establishment of protein localization to membrane / vesicle transport along microtubule / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / regulation of Golgi inheritance / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / central nervous system neuron differentiation / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding / regulation of T cell differentiation / positive regulation of axonogenesis / trachea formation / triglyceride homeostasis / Negative feedback regulation of MAPK pathway / KSRP (KHSRP) binds and destabilizes mRNA / regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport / regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / Frs2-mediated activation / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / stress fiber assembly / MAPK3 (ERK1) activation / ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway / regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / face development / endodermal cell differentiation / MAP kinase kinase activity / Bergmann glial cell differentiation / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / thyroid gland development / Regulation of localization of FOXO transcription factors / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / Interleukin-3, Interleukin-5 and GM-CSF signaling / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / somatic stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / Activation of BAD and translocation to mitochondria / phosphoserine residue binding / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / protein kinase activator activity / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / Schwann cell development / response to axon injury / SARS-CoV-2 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / protein targeting / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / cellular response to glucose starvation / keratinocyte differentiation / SARS-CoV-1 targets host intracellular signalling and regulatory pathways / RHO GTPases activate PKNs / Chk1/Chk2(Cds1) mediated inactivation of Cyclin B:Cdk1 complex / neuron projection morphogenesis / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / sperm end piece / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / myelination / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of autophagy / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
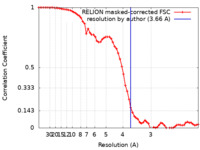
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.66 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Martinez Fiesco JA / Ping Z | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into the BRAF monomer-to-dimer transition mediated by RAS binding. Authors: Juliana A Martinez Fiesco / David E Durrant / Deborah K Morrison / Ping Zhang /  Abstract: RAF kinases are essential effectors of RAS, but how RAS binding initiates the conformational changes needed for autoinhibited RAF monomers to form active dimers has remained unclear. Here, we present ...RAF kinases are essential effectors of RAS, but how RAS binding initiates the conformational changes needed for autoinhibited RAF monomers to form active dimers has remained unclear. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length BRAF complexes derived from mammalian cells: autoinhibited, monomeric BRAF:14-3-3:MEK and BRAF:14-3-3 complexes, and an inhibitor-bound, dimeric BRAF:14-3-3 complex, at 3.7, 4.1, and 3.9 Å resolution, respectively. In both autoinhibited, monomeric structures, the RAS binding domain (RBD) of BRAF is resolved, revealing that the RBD forms an extensive contact interface with the 14-3-3 protomer bound to the BRAF C-terminal site and that key basic residues required for RBD-RAS binding are exposed. Moreover, through structure-guided mutational studies, our findings indicate that RAS-RAF binding is a dynamic process and that RBD residues at the center of the RBD:14-3-3 interface have a dual function, first contributing to RAF autoinhibition and then to the full spectrum of RAS-RBD interactions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23813.map.gz emd_23813.map.gz | 2.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23813-v30.xml emd-23813-v30.xml emd-23813.xml emd-23813.xml | 18.7 KB 18.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_23813_fsc.xml emd_23813_fsc.xml | 6.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_23813.png emd_23813.png | 52 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23813.cif.gz emd-23813.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23813 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23813 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23813 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23813 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mfdMC  7mfeC  7mffC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23813.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23813.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.058 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Autoinhibited B-Raf:(14-3-3)2:MEK complex with resolved RBD
| Entire | Name: Autoinhibited B-Raf:(14-3-3)2:MEK complex with resolved RBD |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Autoinhibited B-Raf:(14-3-3)2:MEK complex with resolved RBD
| Supramolecule | Name: Autoinhibited B-Raf:(14-3-3)2:MEK complex with resolved RBD type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: B-raf
| Supramolecule | Name: B-raf / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: MEK
| Supramolecule | Name: MEK / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta
| Supramolecule | Name: 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf
| Macromolecule | Name: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 84.697695 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAALSGGGGG GAEPGQALFN GDMEPEAGAG AGAAASSAAD PAIPEEVWNI KQMIKLTQEH IEALLDKFGG EHNPPSIYLE AYEEYTSKL DALQQREQQL LESLGNGTDF SVSSSASMDT VTSSSSSSLS VLPSSLSVFQ NPTDVARSNP KSPQKPIVRV F LPNKQRTV ...String: MAALSGGGGG GAEPGQALFN GDMEPEAGAG AGAAASSAAD PAIPEEVWNI KQMIKLTQEH IEALLDKFGG EHNPPSIYLE AYEEYTSKL DALQQREQQL LESLGNGTDF SVSSSASMDT VTSSSSSSLS VLPSSLSVFQ NPTDVARSNP KSPQKPIVRV F LPNKQRTV VPARCGVTVR DSLKKALMMR GLIPECCAVY RIQDGEKKPI GWDTDISWLT GEELHVEVLE NVPLTTHNFV RK TFFTLAF CDFCRKLLFQ GFRCQTCGYK FHQRCSTEVP LMCVNYDQLD LLFVSKFFEH HPIPQEEASL AETALTSGSS PSA PASDSI GPQILTSPSP SKSIPIPQPF RPADEDHRNQ FGQRDRSS(SEP)A PNVHINTIEP VNIDDLIRDQ GFRGDGGSTT GLSATPPAS LPGSLTNVKA LQKSPGPQRE RKSSSSSEDR NRMKTLGRRD SSDDWEIPDG QITVGQRIGS GSFGTVYKGK W HGDVAVKM LNVTAPTPQQ LQAFKNEVGV LRKTRHVNIL LFMGYSTKPQ LAIVTQWCEG SSLYHHLHII ETKFEMIKLI DI ARQTAQG MDYLHAKSII HRDLKSNNIF LHEDLTVKIG DFGLATVKSR WSGSHQFEQL SGSILWMAPE VIRMQDKNPY SFQ SDVYAF GIVLYELMTG QLPYSNINNR DQIIFMVGRG YLSPDLSKVR SNCPKAMKRL MAECLKKKRD ERPLFPQILA SIEL LARSL PKIHRSA(SEP)EP SLNRAGFQTE DFSLYACASP KTPIQAGGYG AFPVH UniProtKB: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf |
-Macromolecule #2: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 43.493938 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MPKKKPTPIQ LNPAPDGSAV NGTSSAETNL EALQKKLEEL ELDEQQRKRL EAFLTQKQKV GELKDDDFEK ISELGAGNGG VVFKVSHKP SGLVMARKLI HLEIKPAIRN QIIRELQVLH ECNSPYIVGF YGAFYSDGEI SICMEHMDGG SLDQVLKKAG R IPEQILGK ...String: MPKKKPTPIQ LNPAPDGSAV NGTSSAETNL EALQKKLEEL ELDEQQRKRL EAFLTQKQKV GELKDDDFEK ISELGAGNGG VVFKVSHKP SGLVMARKLI HLEIKPAIRN QIIRELQVLH ECNSPYIVGF YGAFYSDGEI SICMEHMDGG SLDQVLKKAG R IPEQILGK VSIAVIKGLT YLREKHKIMH RDVKPSNILV NSRGEIKLCD FGVSGQLIDS MANSFVGTRS YMSPERLQGT HY SVQSDIW SMGLSLVEMA VGRYPIPPPD AKELELMFGC QVEGDAAETP PRPRTPGRPL SSYGMDSRPP MAIFELLDYI VNE PPPKLP SGVFSLEFQD FVNKCLIKNP AERADLKQLM VHAFIKRSDA EEVDFAGWLC STIGLNQPST PTHAAGV UniProtKB: Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta
| Macromolecule | Name: 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 27.777092 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MDKNELVQKA KLAEQAERYD DMAACMKSVT EQGAELSNEE RNLLSVAYKN VVGARRSSWR VVSSIEQKTE GAEKKQQMAR EYREKIETE LRDICNDVLS LLEKFLIPNA SQAESKVFYL KMKGDYYRYL AEVAAGDDKK GIVDQSQQAY QEAFEISKKE M QPTHPIRL ...String: MDKNELVQKA KLAEQAERYD DMAACMKSVT EQGAELSNEE RNLLSVAYKN VVGARRSSWR VVSSIEQKTE GAEKKQQMAR EYREKIETE LRDICNDVLS LLEKFLIPNA SQAESKVFYL KMKGDYYRYL AEVAAGDDKK GIVDQSQQAY QEAFEISKKE M QPTHPIRL GLALNFSVFY YEILNSPEKA CSLAKTAFDE AIAELDTLSE ESYKDSTLIM QLLRDNLTLW TSDTQGDEAE AG EGGEN UniProtKB: 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta |
-Macromolecule #4: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: N-(3-fluoro-4-{[4-methyl-2-oxo-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2H-chromen-3...
| Macromolecule | Name: N-(3-fluoro-4-{[4-methyl-2-oxo-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2H-chromen-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-2-yl)-N'-methylsulfuric diamide type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: CHU |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 471.462 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CHU: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 45 sec. / Details: 20mAmp | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 57.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)