+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23663 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
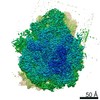
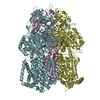
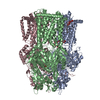
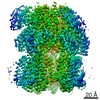
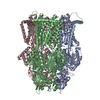
| Title | Multidrug Efflux pump AdeJ with Eravacylcine bound | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Multidrug Efflux pump AdeJ with Eravacylcine bound | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | multidrug efflux pump / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | Hydrophobe/amphiphile efflux-1 HAE1 / Multidrug efflux transporter AcrB TolC docking domain, DN/DC subdomains / Acriflavin resistance protein / AcrB/AcrD/AcrF family / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / response to toxic substance / plasma membrane / Efflux pump membrane transporter Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.86 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang Z | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2021 Journal: mBio / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM Determination of Eravacycline-Bound Structures of the Ribosome and the Multidrug Efflux Pump AdeJ of Acinetobacter baumannii. Authors: Zhemin Zhang / Christopher E Morgan / Robert A Bonomo / Edward W Yu /  Abstract: Antibiotic-resistant strains of the Gram-negative pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii have emerged as a significant global health threat. One successful therapeutic option to treat bacterial infections ...Antibiotic-resistant strains of the Gram-negative pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii have emerged as a significant global health threat. One successful therapeutic option to treat bacterial infections has been to target the bacterial ribosome. However, in many cases, multidrug efflux pumps within the bacterium recognize and extrude these clinically important antibiotics designed to inhibit the protein synthesis function of the bacterial ribosome. Thus, multidrug efflux within A. baumannii and other highly drug-resistant strains is a major cause of failure of drug-based treatments of infectious diseases. We here report the first structures of the cinetobacter rug fflux (Ade)J pump in the presence of the antibiotic eravacycline, using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). We also describe cryo-EM structures of the eravacycline-bound forms of the A. baumannii ribosome, including the 70S, 50S, and 30S forms. Our data indicate that the AdeJ pump primarily uses hydrophobic interactions to bind eravacycline, while the 70S ribosome utilizes electrostatic interactions to bind this drug. Our work here highlights how an antibiotic can bind multiple bacterial targets through different mechanisms and potentially enables drug optimization by taking advantage of these different modes of ligand binding. Acinetobacter baumannii has developed into a highly antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative pathogen. The prevalent AdeJ multidrug efflux pump mediates resistance to different classes of antibiotics known to inhibit the function of the 70S ribosome. Here, we report the first structures of the A. baumannii AdeJ pump, both in the absence and presence of eravacycline. We also describe structures of the A. baumannii ribosome bound by this antibiotic. Our results indicate that AdeJ and the ribosome use very distinct binding modes for drug recognition. Our work will ultimately enable structure-based drug discovery to combat antibiotic-resistant A. baumannii infection. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23663.map.gz emd_23663.map.gz | 9.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23663-v30.xml emd-23663-v30.xml emd-23663.xml emd-23663.xml | 10.2 KB 10.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23663.png emd_23663.png | 183.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23663.cif.gz emd-23663.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23663 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23663 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23663 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23663 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7m4pMC  7m4qC  7m4uC  7m4vC  7m4wC  7m4xC  7m4yC  7m4zC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23663.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 10.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23663.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 10.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Multidrug Efflux pump AdeJ with Eravacylcine bound | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
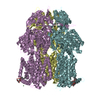
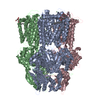
-Entire : multidrug efflux pump AdeJ
| Entire | Name: multidrug efflux pump AdeJ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: multidrug efflux pump AdeJ
| Supramolecule | Name: multidrug efflux pump AdeJ / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Efflux pump membrane transporter
| Macromolecule | Name: Efflux pump membrane transporter / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 114.637781 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAQFFIHRPI FAWVIALVIM LAGILTLTKM PIAQYPTIAP PTVTIAATYP GASAETVENT VTQIIEQQMN GLDGLRYISS NSAGNGQAS IQLNFEQGVD PDIAQVQVQN KLQSATALLP EDVQRQGVTV TKSGASFLQV IAFYSPDNNL SDSDIKDYVN S SIKEPLSR ...String: MAQFFIHRPI FAWVIALVIM LAGILTLTKM PIAQYPTIAP PTVTIAATYP GASAETVENT VTQIIEQQMN GLDGLRYISS NSAGNGQAS IQLNFEQGVD PDIAQVQVQN KLQSATALLP EDVQRQGVTV TKSGASFLQV IAFYSPDNNL SDSDIKDYVN S SIKEPLSR VAGVGEVQVF GGSYAMRIWL DPAKLTSYQL TPSDIATALQ AQNSQVAVGQ LGGAPAVQGQ VLNATVNAQS LL QTPEQFK NIFLKNTASG AEVRLKDVAR VELGSDNYQF DSKFNGKPAA GLAIKIATGA NALDTAEAVE QRLSELRKNY PTG LADKLA YDTTPFIRLS IESVVHTLIE AVILVFIVMF LFLQNWRATI IPTLAVPVVV LGTFAVINIF GFSINTLTMF AMVL AIGLL VDDAIVVVEN VERVMSEDHT DPVTATSRSM QQISGALVGI TSVLTAVFVP MAFFGGTTGV IYRQFSITLV TAMVL SLIV ALTFTPALCA TILKQHDPNK EPSNNIFARF FRSFNNGFDR MSHSYQNGVS RMLKGKIFSG VLYAVVVALL VFLFQK LPS SFLPEEDQGV VMTLVQLPPN ATLDRTGKVI DTMTNFFMNE KDTVESIFTV SGFSFTGVGQ NAGIGFVKLK DWSKRTT PE TQIGSLIQRG MALNMIIKDA SYVMPLQLPA MPELGVTAGF NLQLKDSSGQ GHEKLIAARN TILGLASQDK RLVGVRPN G QEDTPQYQIN VDQAQAGAMG VSIAEINNTM RIAWGGSYIN DFVDRGRVKK VYVQGDAGSR MMPEDLNKWY VRNNKGEMV PFSAFATGEW TYGSPRLERY NGVSSVNIQG TPAPGVSSGD AMKAMEEIIG KLPSMGLQGF DYEWTGLSLE ERESGAQAPF LYALSLLIV FLCLAALYES WSIPFSVLLV VPLGVIGAIV LTYLGMIIKG DPNLSNNIYF QVAIIAVIGL SAKNAILIVE F AKELQEKG EDLLDATLHA AKMRLRPIIM TTLAFGFGVL PLALSTGAGA GSQHSVGFGV LGGVLSATFL GIFFIPVFYV WI RSIFKYK PKTINTQEHK S UniProtKB: Efflux pump membrane transporter |
-Macromolecule #2: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: 3PE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 748.065 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3PE: |
-Macromolecule #3: Eravacycline
| Macromolecule | Name: Eravacycline / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: YQM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 558.555 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-YQM: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 36.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.86 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 95451 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



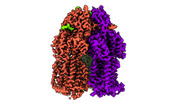




 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)





















