[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-21862: Cryo-EM structure of recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2 ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-21862 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
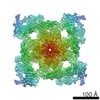
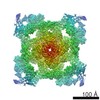
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2 wild type in complex with FKBP12.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ryanodine receptor / Calcium channel / RyR2 / CICR / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-ISOMERASE complex / excitation-contraction coupling | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationestablishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / suramin binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential / regulation of SA node cell action potential / Stimuli-sensing channels / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential ...establishment of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / type B pancreatic cell apoptotic process / Purkinje myocyte to ventricular cardiac muscle cell signaling / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / suramin binding / regulation of AV node cell action potential / regulation of SA node cell action potential / Stimuli-sensing channels / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / embryonic heart tube morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / Ion homeostasis / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / calcium ion transport into cytosol / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / response to caffeine / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / response to redox state / negative regulation of heart rate / cellular response to caffeine / 'de novo' protein folding / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / FK506 binding / response to muscle activity / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / positive regulation of the force of heart contraction / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / smooth muscle contraction / detection of calcium ion / T cell proliferation / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / positive regulation of heart rate / calcium channel inhibitor activity / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Ion homeostasis / response to muscle stretch / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / calcium channel complex / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / regulation of heart rate / sarcomere / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein maturation / peptidylprolyl isomerase / calcium channel regulator activity / establishment of localization in cell / peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity / calcium-mediated signaling / calcium ion transmembrane transport / Stimuli-sensing channels / Z disc / calcium channel activity / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / calcium ion transport / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / protein refolding / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / calmodulin binding / signaling receptor binding / calcium ion binding / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Iyer KA / Hu Y / Nayak AR / Kurebayashi N / Murayama T / Samso M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7 items United States, 7 items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020Title: Structural mechanism of two gain-of-function cardiac and skeletal RyR mutations at an equivalent site by cryo-EM. Authors: Kavita A Iyer / Yifan Hu / Ashok R Nayak / Nagomi Kurebayashi / Takashi Murayama / Montserrat Samsó /   Abstract: Mutations in ryanodine receptors (RyRs), intracellular Ca channels, are associated with deadly disorders. Despite abundant functional studies, the molecular mechanism of RyR malfunction remains ...Mutations in ryanodine receptors (RyRs), intracellular Ca channels, are associated with deadly disorders. Despite abundant functional studies, the molecular mechanism of RyR malfunction remains elusive. We studied two single-point mutations at an equivalent site in the skeletal (RyR1 R164C) and cardiac (RyR2 R176Q) isoforms using ryanodine binding, Ca imaging, and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) of the full-length protein. Loss of the positive charge had greater effect on the skeletal isoform, mediated via distortion of a salt bridge network, a molecular latch inducing rotation of a cytoplasmic domain, and partial progression to open-state traits of the large cytoplasmic assembly accompanied by alteration of the Ca binding site, which concur with the major "hyperactive" feature of the mutated channel. Our cryo-EM studies demonstrated the allosteric effect of a mutation situated ~85 Å away from the pore and identified an isoform-specific structural effect. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_21862.map.gz emd_21862.map.gz | 139.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-21862-v30.xml emd-21862-v30.xml emd-21862.xml emd-21862.xml | 27.3 KB 27.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_21862.png emd_21862.png | 149.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-21862.cif.gz emd-21862.cif.gz | 9.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_21862_half_map_1.map.gz emd_21862_half_map_1.map.gz emd_21862_half_map_2.map.gz emd_21862_half_map_2.map.gz | 74.5 MB 74.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21862 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21862 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21862 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-21862 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6wovMC  6wotC  6wouC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_21862.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_21862.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.377 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
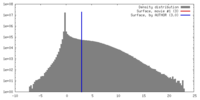
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_21862_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
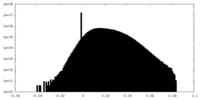
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_21862_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type in c...
| Entire | Name: recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type in complex with FKBP12.6 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type in c...
| Supramolecule | Name: recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type in complex with FKBP12.6 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.26 MDa |
-Supramolecule #2: recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type
| Supramolecule | Name: recombinant mouse Ryanodine Receptor type 2, RyR2, wild type type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: FKBP12.6
| Supramolecule | Name: FKBP12.6 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Ryanodine receptor 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 565.536 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADAGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ ...String: MADAGEGEDE IQFLRTDDEV VLQCTATIHK EQQKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE STSNSKNVPP DLSICTFVLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEKS EGQVDVEKWK FMMKTAQGGG HRTLLYGHAI LLRHSYSGMY LCCLSTSRSS TDKLAFDVGL QEDTTGEACW W TIHPASKQ RSEGEKVRVG DDLILVSVSS ERYLHLSYGN SSWHVDAAFQ QTLWSVAPIS SGSEAAQGYL IGGDVLRLLH GH MDECLTV PSGEHGEEQR RTVHYEGGAV SVHARSLWRL ETLRVAWSGS HIRWGQPFRL RHVTTGKYLS LMEDKNLLLM DKE KADVKS TAFAFRSSKE KLDVGVRKEV DGMGTSEIKY GDSICYIQHV DTGLWLTYQA VDVKSARMGS IQRKAIMHHE GHMD DGLNL SRSQHEESRT ARVIRSTVFL FNRFIRGLDA LSKKVKLPTI DLPIESVSLS LQDLIGYFHP PDEHLEHEDK QNRLR ALKN RQNLFQEEGM INLVLECIDR LHVYSSAAHF ADVAGREAGE SWKSILNSLY ELLAALIRGN RKNCAQFSGS LDWLIS RLE RLEASSGILE VLHCVLVESP EALNIIKEGH IKSIISLLDK HGRNHKVLDV LCSLCVCHGV AVRSNQHLIC DNLLPGR DL LLQTRLVNHV SSMRPNIFLG VSEGSAQYKK WYYELMVDHT EPFVTAEATH LRVGWASTEG YSPYPGGGEE WGGNGVGD D LFSYGFDGLH LWSGCIARTV SSPNQHLLRT DDVISCCLDL SAPSISFRIN GQPVQGMFEN FNIDGLFFPV VSFSAGIKV RFLLGGRHGE FKFLPPPGYA ACYEAVLPKE KLKVEHSREY KQERTYTRDL LGPTVSLTQA AFTPVPVDTS QIVLPPHLER IRERLAENI HELWVMNKIE LGWQYGPVRD DNKRQHPCLV EFCKLPEQER NYNLQMSLET LKTLLALGCH VGIADEHAEE K VKKMKLPK NYQLTSGYKP APMDLSFIKL TPSQEAMVDK LAENAHNVWA RDRIRQGWTY GIQQDVKNRR NPRLVPYTLL DD RTKKSNK DSLREAVRTL LGYGYHLEAP DQDHASRAEV CSGTGERFRI FRAEKTYAVK AGRWYFEFEA VTAGDMRVGW SRP GCQPDL ELGSDDRAFA FDGFKAQRWH QGNEHYGRSW QAGDVVGCMV DMNEHTMMFT LNGEILLDDS GSELAFKDFD VGDG FIPVC SLGVAQVGRM NFGKDVSTLK YFTICGLQEG YEPFAVNTNR DITMWLSKRL PQFLQVPSNH EHIEVTRIDG TIDSS PCLK VTQKSFGSQN NNTDIMFYRL SMPIECAEVF SKSVAGGLPG AGFYGPKNDL EDFDVDSDFE VLMKTAHGHL VPDRID KDK ETPKPEFNNH KDYAQEKPSR LKQRFLLRRT KPDYSTGHSA RLTEDVLADD RDDYEYLMQT STYYYSVRIF PGQEPAN VW VGWITSDFHQ YDTGFDLDRV RTVTVTLGDE KGKVHESIKR SNCYMVCAGE SMSPGQGRNN SNGLEIGCVV DAASGLLT F IANGKELSTY YQVEPSTKLF PAVFAQATSP NVFQFELGRI KNVMPLSAGL FKSEHKNPVP QCPPRLHVQF LSHVLWSRM PNQFLKVDVS RISERQGWLV QCLDPLQFMS LHIPEENRSV DILELTEQEE LLQFHYHTLR LYSAVCALGN HRVAHALCSH VDEPQLLYA IENKYMPGLL RAGYYDLLID IHLSSYATAR LMMNNEFIVP MTEETKSITL FPDENKKHGL PGIGLSTSLR P RMRFSSPS FVSISNDCYQ YSPEFPLDIL KAKTIQMLTE AVKEGSLHAR DPVGGTTEFL FVPLIKLFYT LLIMGIFHNE DL KHILQLI EPSVFKEAAV PEEEGGTPEK EISIEDAKLE GEEEAKGGKR PKEGLLQMKL PEPVKLQMCL LLQYLCDCQV RHR IEAIVA FSDDFVAKLQ DNQRFRYNEV MQALNMSAAL TARKTREFRS PPQEQINMLL NFKDDKSECP CPEEIRDQLL DFHE DLMTH CGIELDEDGS LDGSNDLTIR GRLLSLVEKV TYLKKKQAEK PVASDSRKCS SLQQLISETM VRWAQESVIE DPELV RAMF VLLHRQYDGI GGLVRALPKT YTINGVSVED TINLLASLGQ IRSLLSVRMG KEEEKLMIRG LGDIMNNKVF YQHPNL MRA LGMHETVMEV MVNVLGGGES KEITFPKMVA NCCRFLCYFC RISRQNQKAM FDHLSYLLEN SSVGLASPAM RGSTPLD VA AASVMDNNEL ALALREPDLE KVVRYLAGCG LQSCQMLVSK GYPDIGWNPV EGERYLDFLR FAVFCNGESV EENANVVV R LLIRRPECFG PALRGEGGNG LLAAMEEAIK IAEDPSRDGP SPTSGSSKTL DIEEEEDDTI HMGNAIMTFY AALIDLLGR CAPEMHLIHA GKGEAIRIRS ILRSLIPLGD LVGVISIAFQ MPTIAKDGKV VEPDMSAGFC PDHKAAMVLF LDRVYGIEVQ DFLLHLLEV GFLPDLRAAA SLDTAALSAT DMALALNRYL CTAVLPLLTR CAPLFAGTEH HASLIDSLLH TVYRLSKGCS L TKAQRDSI EVCLLSICGQ LRPSMMQHLL RRLVFDVPLL NEHAKMPLKL LTNHYERCWK YYCLPGGWGN FGAASEEELH LS RKLFWGI FDALSQKKYE QELFKLALPC LSAVAGALPP DYMESNYVSM MEKQSSMDSE GNFNPQPVDT SNITIPEKLE YFI NKYAEH SHDKWSMDKL ANGWIYGEIY SDSSKIQPLM KPYKLLSEKE KEIYRWPIKE SLKTMLAWGW RIERTREGDS MALY NRTRR ISQTSQVSID AAHGYSPRAI DMSNVTLSRD LHAMAEMMAE NYHNIWAKKK KLELESKGGG NHPLLVPYDT LTAKE KAKD REKAQDIFKF LQISGYVVSR GFKDLDLDTP SIEKRFAYSF LQQLIRYVDE AHQYILEFDG GSRSKGEHFP YEQEIK FFA KVVLPLIDQY FKNHRLYFLS AASRPLCTGG HASNKEKEMV TSLFCKLGVL VRHRISLFGN DATSIVNCLH ILGQTLD AR TVMKTGLDSV KSALRAFLDN AAEDLEKTME NLKQGQFTHT RSQPKGVTQI INYTTVALLP MLSSLFEHIG QHQFGEDL I LEDVQVSCYR ILTSLYALGT SKSIYVERQR SALGECLAAF AGAFPIAFLE THLDKHNVYS IYNTRSSRER AALSLPANV EDVCPNIPSL EKLMTEIIEL AESGIRYTQM PYMMEVVLPM LCSYMSRWWE HGPENHPERA EMCCTALNSE HMNTLLGNIL KIIYNNLGI DEGAWMKRLA VFSQPIINKV KPQLLKTHFL PLMEKLKKKA AMVVSEEDHL KAEARGDMSE AELLILDEFT T LARDLYAF YPLLIRFVDY NRAKWLKEPN PEAEELFRMV AEVFIYWSKS HNFKREEQNF VVQNEINNMS FLITDTKSKM SK AAISDQE RKKMKRKGDR YSMQTSLIVA ALKRLLPIGL NICAPGDQEL IALAKNRFSL KDTEEEVRDI IRSNIHLQGK LED PAIRWQ MALYKDLPNR TEDPSDPERT VERVLGIANV LFHLEQKSKY TGRGYFSLVE HPQRSKKAVW HKLLSKQRKR AVVA CFRMA PLYNLPRHRA VNLFLQGYEK SWIETEEHYF EDKLIEDLAK PGAELPEEDE AMKRVDPLHQ LILLFSRTAL TEKCK LEED FLYMAYADIM AKSCHDEEDD DGEEEVKSFE EKEMEKQKLL YQQARLHDRG AAEMVLQTIS ASKGETGPMV AATLKL GIA ILNGGNSTVQ QKMLDYLKEK KDVGFFQSLA GLMQSCSVLD LNAFERQNKA EGLGMVTEEG SGEKVLQDDE FTCDLFR FL QLLCEGHNSD FQNYLRTQTG NNTTVNIIIS TVDYLLRVQE SISDFYWYYS GKDIIDEQGQ RNFSKAIQVA KQVFNTLT E YIQGPCTGNQ QSLAHSRLWD AVVGFLHVFA HMQMKLSQDS SQIELLKELM DLQKDMVVML LSMLEGNVVN GTIGKQMVD MLVESSNNVE MILKFFDMFL KLKDLTSSDT FKEYDPDGKG VISKRDFHKA MESHKHYTQS ETEFLLSCAE TDENETLDYE EFVKRFHEP AKDIGFNVAV LLTNLSEHMP NDTRLQTFLE LAESVLNYFQ PFLGRIEIMG SAKRIERVYF EISESSRTQW E KPQVKESK RQFIFDVVNE GGEKEKMELF VNFCEDTIFE MQLAAQISES DLNERLANKE ESEKERPEEQ APRMGFFSLL TI QSALFAL RYNVLTLVRM LSLKSLKKQM KRMKKMTVKD MVLAFFSSYW SVFVTLLHFV ASVCRGFFRI VSSLLLGGSL VEG AKKIKV AELLANMPDP TQDEVRGDEE EGERKPLESA LPSEDLTDLK ELTEESDLLS DIFGLDLKRE GGQYKLIPHN PNAG LSDLM TNPVPVPEVQ EKFQEQKAKE EKEEKEETKS EPEKAEGEDG EKEEKAKDEK SKQKLRQLHT HRYGEPEVPE SAFWK KIIA YQQKLLNYFA RNFYNMRMLA LFVAFAINFI LLFYKVSTSS VVEGKELPTR TSSDTAKVTN SLDSSPHRII AVHYVL EES SGYMEPTLRI LAILHTIISF FCIIGYYCLK VPLVIFKREK EVARKLEFDG LYITEQPSED DIKGQWDRLV INTQSFP NN YWDKFVKRKV MDKYGEFYGR DRISELLGMD KAALDFSDAR EKKKPKKDSS LSAVLNSIDV KYQMWKLGVV FTDNSFLY L AWYMTMSVLG HYNNFFFAAH LLDIAMGFKT LRTILSSVTH NGKQLVLTVG LLAVVVYLYT VVAFNFFRKF YNKSEDGDT PDMKCDDMLT CYMFHMYVGV RAGGGIGDEI EDPAGDEYEI YRIIFDITFF FFVIVILLAI IQGLIIDAFG ELRDQQEQVK EDMETKCFI CGIGNDYFDT VPHGFETHTL QEHNLANYLF FLMYLINKDE TEHTGQESYV WKMYQERCWE FFPAGDCFRK Q YEDQLN UniProtKB: Ryanodine receptor 2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.667305 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GVEIETISPG DGRTFPKKGQ TCVVHYTGML QNGKKFDSSR DRNKPFKFRI GKQEVIKGFE EGAAQMSLGQ RAKLTCTPDV AYGATGHPG VIPPNATLIF DVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.10 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil, UltrAuFoil, R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR Details: Grid was coated with Carbon using a Denton Vacuum Evaporator 502B prior to vitrification. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 4470 / Average exposure time: 14.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)