+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Tip60 complex locally refined on ARP domain | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human Tip60 complex refined locally on the ARP domain | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Eukaryotic transcription / Histone acetyltransferase / chromatin remodeling / Complex / TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpiccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / sperm DNA condensation / histone chaperone activity / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / cellular response to cytochalasin B ...piccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / sperm DNA condensation / histone chaperone activity / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / cellular response to cytochalasin B / R2TP complex / bBAF complex / npBAF complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / nBAF complex / brahma complex / dynein axonemal particle / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / neural retina development / protein localization to adherens junction / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Swr1 complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein antigen binding / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / GBAF complex / Formation of annular gap junctions / Tat protein binding / Gap junction degradation / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / dense body / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / Ino80 complex / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / regulation of double-strand break repair / blastocyst formation / box C/D snoRNP assembly / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / protein folding chaperone complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / transporter regulator activity / apical junction complex / nitric-oxide synthase binding / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / spinal cord development / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of chromosome organization / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / spermatid development / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of DNA replication / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / brush border / regulation of embryonic development / kinesin binding / MLL1 complex / somatic stem cell population maintenance / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of DNA repair / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA helicase activity / cytoskeleton organization / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / TBP-class protein binding / substantia nigra development / calyx of Held Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
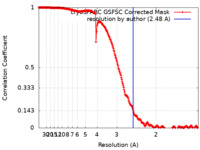
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.48 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li C / Smirnova E / Schnitzler C / Crucifix C / Concordet JP / Brion A / Poterszman A / Schultz P / Papai G / Ben-Shem A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1 items France, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the human TIP60-C histone exchange and acetyltransferase complex. Authors: Changqing Li / Ekaterina Smirnova / Charlotte Schnitzler / Corinne Crucifix / Jean Paul Concordet / Alice Brion / Arnaud Poterszman / Patrick Schultz / Gabor Papai / Adam Ben-Shem /  Abstract: Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two ...Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two enzymatic activities: ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A-H2B for H2A.Z-H2B, and histone acetylation. In yeast, however, these activities are performed by two independent complexes-SWR1 and NuA4, respectively. How the activities of the two complexes are merged into one supercomplex in humans, and what this association entails for the structure and mechanism of the proteins and their recruitment to chromatin, are unknown. Here we describe the structure of the endogenous human TIP60-C. We find a three-lobed architecture composed of SWR1-like (SWR1L) and NuA4-like (NuA4L) parts, which associate with a TRRAP activator-binding module. The huge EP400 subunit contains the ATPase motor, traverses the junction between SWR1L and NuA4L twice and constitutes the scaffold of the three-lobed architecture. NuA4L is completely rearranged compared with its yeast counterpart. TRRAP is flexibly tethered to NuA4L-in stark contrast to its robust connection to the completely opposite side of NuA4 in yeast. A modelled nucleosome bound to SWR1L, supported by tests of TIP60-C activity, suggests that some aspects of the histone exchange mechanism diverge from what is seen in yeast. Furthermore, a fixed actin module (as opposed to the mobile actin subcomplex in SWR1; ref. ), the flexibility of TRRAP and the weak effect of extranucleosomal DNA on exchange activity lead to a different, activator-based mode of enlisting TIP60-C to chromatin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18598.map.gz emd_18598.map.gz | 616.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18598-v30.xml emd-18598-v30.xml emd-18598.xml emd-18598.xml | 26.9 KB 26.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18598_fsc.xml emd_18598_fsc.xml | 22.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18598.png emd_18598.png | 81.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_18598_msk_1.map emd_18598_msk_1.map | 1.2 GB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18598.cif.gz emd-18598.cif.gz | 8.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18598_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18598_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18598_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18598_half_map_2.map.gz | 1.1 GB 1.1 GB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18598 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18598 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18598 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18598 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 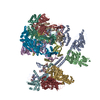 8qr1C  8qriC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18598.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.2 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18598.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.2 GB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human Tip60 complex refined locally on the ARP domain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.73 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_18598_msk_1.map emd_18598_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
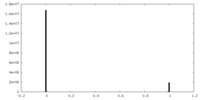
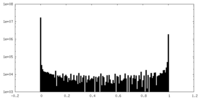
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_18598_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
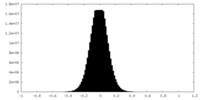
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_18598_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
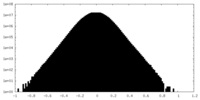
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tip60 complex
| Entire | Name: Tip60 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tip60 complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Tip60 complex / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 |
-Macromolecule #1: EP400
| Macromolecule | Name: EP400 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATGQ NVNITLQSVG PVVGGNQQIT LAPLPLPSPT SPGFQFSAQP RRFEHGSPSY IQVTSPLSQQ VQTQSPTQPS PGPGQALQNV RAGAPGPGLG LCSSSPTGGF ...String: MHHGTGPQNV QHQLQRSRAC PGSEGEEQPA HPNPPPSPAA PFAPSASPSA PQSPSYQIQQ LMNRSPATGQ NVNITLQSVG PVVGGNQQIT LAPLPLPSPT SPGFQFSAQP RRFEHGSPSY IQVTSPLSQQ VQTQSPTQPS PGPGQALQNV RAGAPGPGLG LCSSSPTGGF VDASVLVRQI SLSPSSGGHF VFQDGSGLTQ IAQGAQVQLQ HPGTPITVRE RRPSQPHTQS GGTIHHLGPQ SPAAAGGAGL QPLASPSHIT TANLPPQISS IIQGQLVQQQ QVLQGPPLPR PLGFERTPGV LLPGAGGAAG FGMTSPPPPT SPSRTAVPPG LSSLPLTSVG NTGMKKVPKK LEEIPPASPE MAQMRKQCLD YHYQEMQALK EVFKEYLIEL FFLQHFQGNM MDFLAFKKKH YAPLQAYLRQ NDLDIEEEEE EEEEEEEKSE VINDEVKVVT GKDGQTGTPV AIATQLPPKV SAAFSSQQQP FQQALAGSLV AGAGSTVETD LFKRQQAMPS TGMAEQSKRP RLEVGHQGVV FQHPGADAGV PLQQLMPTAQ GGMPPTPQAA QLAGQRQSQQ QYDPSTGPPV QNAASLHTPL PQLPGRLPPA GVPTAALSSA LQFAQQPQVV EAQTQLQIPV KTQQPNVPIP APPSSQLPIP PSQPAQLALH VPTPGKVQVQ ASQLSSLPQM VASTRLPVDP APPCPRPLPT SSTSSLAPVS GSGPGPSPAR SSPVNRPSSA TNKALSPVTS RTPGVVASAP TKPQSPAQNA TSSQDSSQDT LTEQITLENQ VHQRIAELRK AGLWSQRRLP KLQEAPRPKS HWDYLLEEMQ WMATDFAQER RWKVAAAKKL VRTVVRHHEE KQLREERGKK EEQSRLRRIA ASTAREIECF WSNIEQVVEI KLRVELEEKR KKALNLQKVS RRGKELRPKG FDALQESSLD SGMSGRKRKA SISLTDDEVD DEEETIEEEE ANEGVVDHQT ELSNLAKEAE LPLLDLMKLY EGAFLPSSQW PRPKPDGEDT SGEEDADDCP GDRESRKDLV LIDSLFIMDQ FKAAERMNIG KPNAKDIADV TAVAEAILPK GSARVTTSVK FNAPSLLYGA LRDYQKIGLD WLAKLYRKNL NGILADEAGL GKTVQIIAFF AHLACNEGNW GPHLVVVRSC NILKWELELK RWCPGLKILS YIGSHRELKA KRQEWAEPNS FHVCITSYTQ FFRGLTAFTR VRWKCLVIDE MQRVKGMTER HWEAVFTLQS QQRLLLIDSP LHNTFLELWT MVHFLVPGIS RPYLSSPLRA PSEESQDYYH KVVIRLHRVT QPFILRRTKR DVEKQLTKKY EHVLKCRLSN RQKALYEDVI LQPGTQEALK SGHFVNVLSI LVRLQRICNH PGLVEPRHPG SSYVAGPLEY PSASLILKAL ERDFWKEADL SMFDLIGLEN KITRHEAELL SKKKIPRKLM EEISTSAAPA ARPAAAKLKA SRLFQPVQYG QKPEGRTVAF PSTHPPRTAA PTTASAAPQG PLRGRPPIAT FSANPEAKAA AAPFQTSQAS ASAPRHQPAS ASSTAASPAH PAKLRAQTTA QASTPGQPPP QPQAPSHAAG QSALPQRLVL PSQAQARLPS GEVVKIAQLA SITGPQSRVA QPETPVTLQF QGSKFTLSHS QLRQLTAGQP LQLQGSVLQI VSAPGQPYLR APGPVVMQTV SQAGAVHGAL GSKPPAGGPS PAPLTPQVGV PGRVAVNALA VGEPGTASKP ASPIGGPTQE EKTRLLKERL DQIYLVNERR CSQAPVYGRD LLRICALPSH GRVQWRGSLD GRRGKEAGPA HSYTSSSESP SELMLTLCRC GESLQDVIDR VAFVIPPVVA APPSLRVPRP PPLYSHRMRI LRQGLREHAA PYFQQLRQTT APRLLQFPEL RLVQFDSGKL EALAILLQKL KSEGRRVLIL SQMILMLDIL EMFLNFHYLT YVRIDENASS EQRQELMRSF NRDRRIFCAI LSTHSRTTGI NLVEADTVVF YDNDLNPVMD AKAQEWCDRI GRCKDIHIYR LVSGNSIEEK LLKNGTKDLI REVAAQGNDY SMAFLTQRTI QELFEVYSPM DDAGFPVKAE EFVVLSQEPS VTETIAPKIA RPFIEALKSI EYLEEDAQKS AQEGVLGPHT DALSSDSENM PCDEEPSQLE ELADFMEQLT PIEKYALNYL ELFHTSIEQE KERNSEDAVM TAVRAWEFWN LKTLQEREAR LRLEQEEAEL LTYTREDAYS MEYVYEDVDG QTEVMPLWTP PTPPQDDSDI YLDSVMCLMY EATPIPEAKL PPVYVRKERK RHKTDPSAAG RKKKQRHGEA VVPPRSLFDR ATPGLLKIRR EGKEQKKNIL LKQQVPFAKP LPTFAKPTAE PGQDNPEWLI SEDWALLQAV KQLLELPLNL TIVSPAHTPN WDLVSDVVNS CSRIYRSSKQ CRNRYENVII PREEGKSKNN RPLRTSQIYA QDENATHTQL YTSHFDLMKM TAGKRSPPIK PLLGMNPFQK NPKHASVLAE SGINYDKPLP PIQVASLRAE RIAKEKKALA DQQKAQQPAV AQPPPPQPQP PPPPQQPPPP LPQPQAAGSQ PPAGPPAVQP QPQPQPQTQP QPVQAPAKAQ PAITTGGSAA VLAGTIKTSV TGTSMPTGAV SGNVIVNTIA GVPAATFQSI NKRLASPVAP GALTTPGGSA PAQVVHTQPP PRAVGSPATA TPDLVSMATT QGVRAVTSVT ASAVVTTNLT PVQTPARSLV PQVSQATGVQ LPGKTITPAH FQLLRQQQQQ QQQQQQQQQQ QQQQQQQQQQ QQQQTTTTSQ VQVPQIQGQA QSPAQIKAVG KLTPEHLIKM QKQKLQMPPQ PPPPQAQSAP PQPTAQVQVQ TSQPPQQQSP QLTTVTAPRP GALLTGTTVA NLQVARLTRV PTSQLQAQGQ MQTQAPQPAQ VALAKPPVVS VPAAVVSSPG VTTLPMNVAG ISVAIGQPQK AAGQTVVAQP VHMQQLLKLK QQAVQQQKAI QPQAAQGPAA VQQKITAQQI TTPGAQQKVA YAAQPALKTQ FLTTPISQAQ KLAGAQQVQT QIQVAKLPQV VQQQTPVASI QQVASASQQA SPQTVALTQA TAAGQQVQMI PAVTATAQVV QQKLIQQQVV TTASAPLQTP GAPNPAQVPA SSDSPSQQPK LQMRVPAVRL KTPTKPPCQ UniProtKB: E1A-binding protein p400 |
-Macromolecule #2: EPC1
| Macromolecule | Name: EPC1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESIY PGEFKMPKQL IHIQPFSLDA EQPDYDLDSE DEVFVNKLKK KMDICPLQFE EMIDRLEKGS GQQPVSLQEA KLLLKEDDEL ...String: MSKLSFRARA LDASKPLPVF RCEDLPDLHE YASINRAVPQ MPTGMEKEEE SEHHLQRAIS AQQVYGEKRD NMVIPVPEAE SNIAYYESIY PGEFKMPKQL IHIQPFSLDA EQPDYDLDSE DEVFVNKLKK KMDICPLQFE EMIDRLEKGS GQQPVSLQEA KLLLKEDDEL IREVYEYWIK KRKNCRGPSL IPSVKQEKRD GSSTNDPYVA FRRRTEKMQT RKNRKNDEAS YEKMLKLRRD LSRAVTILEM IKRREKSKRE LLHLTLEIME KRYNLGDYNG EIMSEVMAQR QPMKPTYAIP IIPITNSSQF KHQEAMDVKE FKVNKQDKAD LIRPKRKYEK KPKVLPSSAA ATPQQTSPAA LPVFNAKDLN QYDFPSSDEE PLSQVLSGSS EAEEDNDPDG PFAFRRKAGC QYYAPHLDQT GNWPWTSPKD GGLGDVRYRY CLTTLTVPQR CIGFARRRVG RGGRVLLDRA HSDYDSVFHH LDLEMLSSPQ HSPVNQFANT SETNTSDKSF SKDLSQILVN IKSCRWRHFR PRTPSLHDSD NDELSCRKLY RSINRTGTAQ PGTQTCSTST QSKSSSGSAH FAFTAEQYQQ HQQQLALMQK QQLAQIQQQQ ANSNSSTNTS QNLASNQQKS GFRLNIQGLE RTLQGFVSKT LDSASAQFAA SALVTSEQLM GFKMKDDVVL GIGVNGVLPA SGVYKGLHLS STTPTALVHT SPSTAGSALL QPSNITQTSS SHSALSHQVT AANSATTQVL IGNNIRLTVP SSVATVNSIA PINARHIPRT LSAVPSSALK LAAAANCQVS KVPSSSSVDS VPRENHESEK PALNNIADNT VAMEVT UniProtKB: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: VPS72
| Macromolecule | Name: VPS72 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSLAGGRAPR KTAGNRLSGL LEAEEEDEFY QTTYGGFTEE SGDDEYQGDQ SDTEDEVDSD FDIDEGDEPS SDGEAEEPRR KRRVVTKAYK EPLKSLRPRK VNTPAGSSQK AREEKALLPL ELQDDGSDSR KSMRQSTAEH TRQTFLRVQE RQGQSRRRKG PHCERPLTQE ...String: MSLAGGRAPR KTAGNRLSGL LEAEEEDEFY QTTYGGFTEE SGDDEYQGDQ SDTEDEVDSD FDIDEGDEPS SDGEAEEPRR KRRVVTKAYK EPLKSLRPRK VNTPAGSSQK AREEKALLPL ELQDDGSDSR KSMRQSTAEH TRQTFLRVQE RQGQSRRRKG PHCERPLTQE ELLREAKITE ELNLRSLETY ERLEADKKKQ VHKKRKCPGP IITYHSVTVP LVGEPGPKEE NVDIEGLDPA PSVSALTPHA GTGPVNPPAR CSRTFITFSD DATFEEWFPQ GRPPKVPVRE VCPVTHRPAL YRDPVTDIPY ATARAFKIIR EAYKKYITAH GLPPTASALG PGPPPPEPLP GSGPRALRQK IVIK UniProtKB: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72 homolog |
-Macromolecule #4: DMAP1
| Macromolecule | Name: DMAP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGSK KVRPWKWMPF TNPARKDGAM FFHWRRAAEE GKDYPFARFN KTVQVPVYSE QEYQLYLHDD AWTKAETDHL FDLSRRFDLR ...String: MATGADVRDI LELGGPEGDA ASGTISKKDI INPDKKKSKK SSETLTFKRP EGMHREVYAL LYSDKKDAPP LLPSDTGQGY RTVKAKLGSK KVRPWKWMPF TNPARKDGAM FFHWRRAAEE GKDYPFARFN KTVQVPVYSE QEYQLYLHDD AWTKAETDHL FDLSRRFDLR FVVIHDRYDH QQFKKRSVED LKERYYHICA KLANVRAVPG TDLKIPVFDA GHERRRKEQL ERLYNRTPEQ VAEEEYLLQE LRKIEARKKE REKRSQDLQK LITAADTTAE QRRTERKAPK KKLPQKKEAE KPAVPETAGI KFPDFKSAGV TLRSQRMKLP SSVGQKKIKA LEQMLLELGV ELSPTPTEEL VHMFNELRSD LVLLYELKQA CANCEYELQM LRHRHEALAR AGVLGGPATP ASGPGPASAE PAVTEPGLGP DPKDTIIDVV GAPLTPNSRK RRESASSSSS VKKAKKP UniProtKB: DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: ACL6A
| Macromolecule | Name: ACL6A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLKN GMVEDWDSFQ AILDHTYKMH VKSEASLHPV LMSEAPWNTR AKREKLTELM FEHYNIPAFF LCKTAVLTAF ANGRSTGLIL ...String: MSGGVYGGDE VGALVFDIGS YTVRAGYAGE DCPKVDFPTA IGMVVERDDG STLMEIDGDK GKQGGPTYYI DTNALRVPRE NMEAISPLKN GMVEDWDSFQ AILDHTYKMH VKSEASLHPV LMSEAPWNTR AKREKLTELM FEHYNIPAFF LCKTAVLTAF ANGRSTGLIL DSGATHTTAI PVHDGYVLQQ GIVKSPLAGD FITMQCRELF QEMNIELVPP YMIASKEAVR EGSPANWKRK EKLPQVTRSW HNYMCNCVIQ DFQASVLQVS DSTYDEQVAA QMPTVHYEFP NGYNCDFGAE RLKIPEGLFD PSNVKGLSGN TMLGVSHVVT TSVGMCDIDI RPGLYGSVIV AGGNTLIQSF TDRLNRELSQ KTPPSMRLKL IANNTTVERR FSSWIGGSIL ASLGTFQQMW ISKQEYEEGG KQCVERKCP UniProtKB: Actin-like protein 6A |
-Macromolecule #6: ACTIN
| Macromolecule | Name: ACTIN / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT HTVPIYEGYA ...String: MDDDIAALVV DNGSGMCKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IEHGIVTNWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGDGVT HTVPIYEGYA LPHAILRLDL AGRDLTDYLM KILTERGYSF TTTAEREIVR DIKEKLCYVA LDFEQEMATA ASSSSLEKSY ELPDGQVITI GNERFRCPEA LFQPSFLGME SCGIHETTFN SIMKCDVDIR KDLYANTVLS GGTTMYPGIA DRMQKEITAL APSTMKIKII APPERKYSVW IGGSILASLS TFQQMWISKQ EYDESGPSIV HRKCF UniProtKB: Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #7: RUVBL1
| Macromolecule | Name: RUVBL1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MKIEEVKSTT KTQRIASHSH VKGLGLDESG LAKQAASGLV GQENAREACG VIVELIKSKK MAGRAVLLAG PPGTGKTALA LAIAQELGSK VPFCPMVGSE VYSTEIKKTE VLMENFRRAI GLRIKETKEV YEGEVTELTP CETENPMGGY GKTISHVIIG LKTAKGTKQL ...String: MKIEEVKSTT KTQRIASHSH VKGLGLDESG LAKQAASGLV GQENAREACG VIVELIKSKK MAGRAVLLAG PPGTGKTALA LAIAQELGSK VPFCPMVGSE VYSTEIKKTE VLMENFRRAI GLRIKETKEV YEGEVTELTP CETENPMGGY GKTISHVIIG LKTAKGTKQL KLDPSIFESL QKERVEAGDV IYIEANSGAV KRQGRCDTYA TEFDLEAEEY VPLPKGDVHK KKEIIQDVTL HDLDVANARP QGGQDILSMM GQLMKPKKTE ITDKLRGEIN KVVNKYIDQG IAELVPGVLF VDEVHMLDIE CFTYLHRALE SSIAPIVIFA SNRGNCVIRG TEDITSPHGI PLDLLDRVMI IRTMLYTPQE MKQIIKIRAQ TEGINISEEA LNHLGEIGTK TTLRYSVQLL TPANLLAKIN GKDSIEKEHV EEISELFYDA KSSAKILADQ QDKYMK UniProtKB: RuvB-like 1 |
-Macromolecule #8: RUVBL2
| Macromolecule | Name: RUVBL2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MATVTATTKV PEIRDVTRIE RIGAHSHIRG LGLDDALEPR QASQGMVGQL AARRAAGVVL EMIREGKIAG RAVLIAGQPG TGKTAIAMGM AQALGPDTPF TAIAGSEIFS LEMSKTEALT QAFRRSIGVR IKEETEIIEG EVVEIQIDRP ATGTGSKVGK LTLKTTEMET ...String: MATVTATTKV PEIRDVTRIE RIGAHSHIRG LGLDDALEPR QASQGMVGQL AARRAAGVVL EMIREGKIAG RAVLIAGQPG TGKTAIAMGM AQALGPDTPF TAIAGSEIFS LEMSKTEALT QAFRRSIGVR IKEETEIIEG EVVEIQIDRP ATGTGSKVGK LTLKTTEMET IYDLGTKMIE SLTKDKVQAG DVITIDKATG KISKLGRSFT RARDYDAMGS QTKFVQCPDG ELQKRKEVVH TVSLHEIDVI NSRTQGFLAL FSGDTGEIKS EVREQINAKV AEWREEGKAE IIPGVLFIDE VHMLDIESFS FLNRALESDM APVLIMATNR GITRIRGTSY QSPHGIPIDL LDRLLIVSTT PYSEKDTKQI LRIRCEEEDV EMSEDAYTVL TRIGLETSLR YAIQLITAAS LVCRKRKGTE VQVDDIKRVY SLFLDESRST QYMKEYQDAF LFNELKGETM DTS UniProtKB: RuvB-like 2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)