[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-16905: 60S ribosomal subunit bound to the E3-UFM1 complex - state 3 (in-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 60S ribosomal subunit bound to the E3-UFM1 complex - state 3 (in-vitro reconstitution) | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ER / UFMylation / recycling / RIBOSOME | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of I-kappaB phosphorylation / UFM1 ligase activity / UFM1-modified protein reader activity / positive regulation of reticulophagy / regulation of phosphatase activity / apoptotic nuclear changes / definitive erythrocyte differentiation / UFM1 transferase activity / negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum ...positive regulation of I-kappaB phosphorylation / UFM1 ligase activity / UFM1-modified protein reader activity / positive regulation of reticulophagy / regulation of phosphatase activity / apoptotic nuclear changes / definitive erythrocyte differentiation / UFM1 transferase activity / negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / protein K69-linked ufmylation / protein ufmylation / negative regulation of protein kinase activity by regulation of protein phosphorylation / : / positive regulation of plasma cell differentiation / negative regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response / regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition / negative regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / negative regulation of T cell activation / regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / translation at presynapse / positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / exit from mitosis / optic nerve development / response to insecticide / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / cartilage development / negative regulation of protein neddylation / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Aminoacyltransferases / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / axial mesoderm development / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / ribosomal protein import into nucleus / regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / response to L-glutamate / ribosome disassembly / protein-DNA complex disassembly / mitogen-activated protein kinase binding / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome assembly / regulation of neuron differentiation / reticulophagy / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / GAIT complex / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / TORC2 complex binding / G1 to G0 transition / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / middle ear morphogenesis / : / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / homeostatic process / negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / negative regulation of MAP kinase activity / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / macrophage chemotaxis / lung morphogenesis / cellular response to actinomycin D / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation / male meiosis I / Protein hydroxylation / Peptide chain elongation / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / positive regulation of protein binding / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / RHOA GTPase cycle / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / blastocyst development / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / NF-kappaB binding / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / Viral mRNA Translation / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / protein localization to nucleus / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / protein targeting / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / protein-RNA complex assembly / : / maturation of LSU-rRNA / rough endoplasmic reticulum / Maturation of protein E Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Penchev I / DaRosa PA / Peter JJ / Kulathu Y / Becker T / Beckmann R / Kopito R | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Germany, Germany,  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: UFM1 E3 ligase promotes recycling of 60S ribosomal subunits from the ER. Authors: Paul A DaRosa / Ivan Penchev / Samantha C Gumbin / Francesco Scavone / Magda Wąchalska / Joao A Paulo / Alban Ordureau / Joshua J Peter / Yogesh Kulathu / J Wade Harper / Thomas Becker / ...Authors: Paul A DaRosa / Ivan Penchev / Samantha C Gumbin / Francesco Scavone / Magda Wąchalska / Joao A Paulo / Alban Ordureau / Joshua J Peter / Yogesh Kulathu / J Wade Harper / Thomas Becker / Roland Beckmann / Ron R Kopito /    Abstract: Reversible modification of target proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs) is widely used by eukaryotic cells to control protein fate and cell behaviour. UFM1 is a UBL that ...Reversible modification of target proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs) is widely used by eukaryotic cells to control protein fate and cell behaviour. UFM1 is a UBL that predominantly modifies a single lysine residue on a single ribosomal protein, uL24 (also called RPL26), on ribosomes at the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). UFM1 conjugation (UFMylation) facilitates the rescue of 60S ribosomal subunits (60S) that are released after ribosome-associated quality-control-mediated splitting of ribosomes that stall during co-translational translocation of secretory proteins into the ER. Neither the molecular mechanism by which the UFMylation machinery achieves such precise target selection nor how this ribosomal modification promotes 60S rescue is known. Here we show that ribosome UFMylation in vivo occurs on free 60S and we present sequential cryo-electron microscopy snapshots of the heterotrimeric UFM1 E3 ligase (E3(UFM1)) engaging its substrate uL24. E3(UFM1) binds the L1 stalk, empty transfer RNA-binding sites and the peptidyl transferase centre through carboxy-terminal domains of UFL1, which results in uL24 modification more than 150 Å away. After catalysing UFM1 transfer, E3(UFM1) remains stably bound to its product, UFMylated 60S, forming a C-shaped clamp that extends all the way around the 60S from the transfer RNA-binding sites to the polypeptide tunnel exit. Our structural and biochemical analyses suggest a role for E3(UFM1) in post-termination release and recycling of the large ribosomal subunit from the ER membrane. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16905.map.gz emd_16905.map.gz | 277.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16905-v30.xml emd-16905-v30.xml emd-16905.xml emd-16905.xml | 69.9 KB 69.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_16905.png emd_16905.png | 74.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16905.cif.gz emd-16905.cif.gz | 15.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16905_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16905_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16905_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16905_half_map_2.map.gz | 278.4 MB 277.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16905 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16905 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16905 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16905 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8oj5MC  8ohdC  8oj0C  8oj8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16905.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 347.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16905.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 347.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.838 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
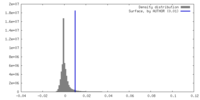
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_16905_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_16905_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : E3-UFM1 complex bound to the 60S ribosome
+Supramolecule #1: E3-UFM1 complex bound to the 60S ribosome
+Macromolecule #1: 28S rRNA
+Macromolecule #2: 5S rRNA
+Macromolecule #3: 5.8S rRNA
+Macromolecule #4: E3 UFM1-protein ligase 1
+Macromolecule #5: CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 3
+Macromolecule #6: DDRGK domain-containing protein 1
+Macromolecule #7: Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1
+Macromolecule #8: 60S ribosomal protein L8
+Macromolecule #9: 60S ribosomal protein L3
+Macromolecule #10: 60S ribosomal protein L4
+Macromolecule #11: 60S ribosomal protein L5
+Macromolecule #12: 60S ribosomal protein L6
+Macromolecule #13: 60S ribosomal protein L7
+Macromolecule #14: 60S ribosomal protein L7a
+Macromolecule #15: 60S ribosomal protein L9
+Macromolecule #16: Ribosomal protein uL16-like
+Macromolecule #17: 60S ribosomal protein L11
+Macromolecule #18: 60S ribosomal protein L13
+Macromolecule #19: 60S ribosomal protein L14
+Macromolecule #20: 60S ribosomal protein L15
+Macromolecule #21: 60S ribosomal protein L13a
+Macromolecule #22: 60S ribosomal protein L17
+Macromolecule #23: 60S ribosomal protein L18
+Macromolecule #24: 60S ribosomal protein L19
+Macromolecule #25: 60S ribosomal protein L18a
+Macromolecule #26: 60S ribosomal protein L21
+Macromolecule #27: 60S ribosomal protein L22
+Macromolecule #28: 60S ribosomal protein L23
+Macromolecule #29: 60S ribosomal protein L24
+Macromolecule #30: 60S ribosomal protein L23a
+Macromolecule #31: 60S ribosomal protein L26
+Macromolecule #32: 60S ribosomal protein L27
+Macromolecule #33: 60S ribosomal protein L27a
+Macromolecule #34: 60S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #35: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #36: 60S ribosomal protein L31
+Macromolecule #37: 60S ribosomal protein L32
+Macromolecule #38: 60S ribosomal protein L35a
+Macromolecule #39: 60S ribosomal protein L34
+Macromolecule #40: 60S ribosomal protein L35
+Macromolecule #41: 60S ribosomal protein L36
+Macromolecule #42: 60S ribosomal protein L37
+Macromolecule #43: 60S ribosomal protein L38
+Macromolecule #44: 60S ribosomal protein L39
+Macromolecule #45: Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40
+Macromolecule #46: 60S ribosomal protein L36a
+Macromolecule #47: 60S ribosomal protein L37a
+Macromolecule #48: 60S ribosomal protein L28
+Macromolecule #49: 60S ribosomal protein L10a
+Macromolecule #50: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #51: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 35935 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8oj5: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)