+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1679 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
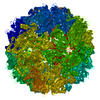
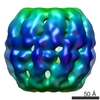
| Title | Characterization of the extremophilic, archaeal virus STIV2 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | This is a 20 A resolution cryo-EM reconstruction of the archaeal virus STIV2 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Archaeal / virus / icosahedral / extremophilic | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 2 Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 2 | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / negative staining / Resolution: 20.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Happonen LJ / Redder P / Peng X / Reigstad LJ / Prangishvili D / Butcher SJ | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2010 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2010Title: Familial relationships in hyperthermo- and acidophilic archaeal viruses. Authors: Lotta Johanna Happonen / Peter Redder / Xu Peng / Laila Johanne Reigstad / David Prangishvili / Sarah Jane Butcher /  Abstract: Archaea often live in extreme, harsh environments such as acidic hot springs and hypersaline waters. To date, only two icosahedrally symmetric, membrane-containing archaeal viruses, SH1 and ...Archaea often live in extreme, harsh environments such as acidic hot springs and hypersaline waters. To date, only two icosahedrally symmetric, membrane-containing archaeal viruses, SH1 and Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus (STIV), have been described in detail. We report the sequence and three-dimensional structure of a third such virus isolated from a hyperthermoacidophilic crenarchaeon, Sulfolobus strain G4ST-2. Characterization of this new isolate revealed it to be similar to STIV on the levels of genome and structural organization. The genome organization indicates that these two viruses have diverged from a common ancestor. Interestingly, the prominent surface turrets of the two viruses are strikingly different. By sequencing and mass spectrometry, we mapped several large insertions and deletions in the known structural proteins that could account for these differences and showed that both viruses can infect the same host. A combination of genomic and proteomic analyses revealed important new insights into the structural organization of these viruses and added to our limited knowledge of archaeal virus life cycles and host-cell interactions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1679.map.gz emd_1679.map.gz | 50.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1679-v30.xml emd-1679-v30.xml emd-1679.xml emd-1679.xml | 9.2 KB 9.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1679.tif 1679.tif | 739.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1679 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1679 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1679 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1679 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_1679_validation.pdf.gz emd_1679_validation.pdf.gz | 268.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_1679_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1679_full_validation.pdf.gz | 267.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_1679_validation.xml.gz emd_1679_validation.xml.gz | 7.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1679 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1679 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1679 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1679 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1679.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 130.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1679.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 130.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | This is a 20 A resolution cryo-EM reconstruction of the archaeal virus STIV2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.42 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : STIV2 virus
| Entire | Name: STIV2 virus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: STIV2 virus
| Supramolecule | Name: STIV2 virus / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 2 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: STIV2 / NCBI-ID: 754004 / Sci species name: Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 2 / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No / Syn species name: STIV2 |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:   Sulfolobus islandicus (archaea) / synonym: ARCHAEA Sulfolobus islandicus (archaea) / synonym: ARCHAEA |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Diameter: 710 Å / T number (triangulation number): 31 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining, cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 3.5 / Details: 50 mM sodium citrate, pH 3.5 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: Vitrified. Grids were blotted for roughly one second before being plunged into liquid ethane. |
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil-grids |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Guillotine Method: A small vial of ethane is placed inside a larger liquid nitrogen reservoir. The grid holding 3 microliters of the sample is held in place at the bottom of a plunger by the means of fine ...Method: A small vial of ethane is placed inside a larger liquid nitrogen reservoir. The grid holding 3 microliters of the sample is held in place at the bottom of a plunger by the means of fine tweezers. When the liquid ethane is ready, a piece of filter paper is then pressed against the sample to blot off excess buffer, sufficient to leave a thin layer on the grid. The filter paper is removed, and the plunger is allowed to drop into the liquid ethane. Once the grid enters the liquid ethane, the sample is rapidly frozen, and the grid is transferred under liquid nitrogen to a storage box immersed in liquid nitrogen for later use in the microscope. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Details | Low dose conditions |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Digitization - Sampling interval: 4.42 µm / Number real images: 358 / Average electron dose: 18 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 66400 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 5.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 68000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Side entry liquid nitrogen-cooled side entry holder Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: Each micrograph |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: I (icosahedral) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 20.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: PFT, POR, EM3DR2, P3DR / Number images used: 713 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















