[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1018: The first step: activation of the Semliki Forest virus spike prot... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The first step: activation of the Semliki Forest virus spike protein precursor causes a localized conformational change in the trimeric spike. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Semliki forest virus | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  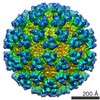 Semliki forest virus Semliki forest virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fuller SD | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 1998 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 1998Title: The first step: activation of the Semliki Forest virus spike protein precursor causes a localized conformational change in the trimeric spike. Authors: I Ferlenghi / B Gowen / F de Haas / E J Mancini / H Garoff / M Sjöberg / S D Fuller /  Abstract: The structure of the particle formed by the SFVmSQL mutant of Semliki Forest virus (SFV) has been defined by cryo-electron microscopy and image reconstruction to a resolution of 21 A. The SQL ...The structure of the particle formed by the SFVmSQL mutant of Semliki Forest virus (SFV) has been defined by cryo-electron microscopy and image reconstruction to a resolution of 21 A. The SQL mutation blocks the cleavage of p62, the precursor of the spike proteins E2 and E3, which normally occurs in the trans-Golgi. The uncleaved spike protein is insensitive to the low pH treatment that triggers membrane fusion during entry of the wild-type virus. The conformation of the spike in the SFVmSQL particle should correspond to that of the inactive precursor found in the early stages of the secretory pathway. Comparison of this "precursor" structure with that of the mature, wild-type, virus allows visualization of the changes that lead to activation, the first step in the pathway toward fusion. We find that the conformational change in the spike is dramatic but localized. The projecting domains of the spikes are completely separated in the precursor and close to generate a cavity in the mature spike. E1, the fusion peptide-bearing protein, interacts only with the p62 in its own third of the trimer before cleavage and then collapses to form a trimer of heterotrimers (E1E2E3)3 surrounding the cavity, poised for the pH-induced conformational change that leads to fusion. The capsid, transmembrane regions and the spike skirts (thin layers of protein that link spikes above the membrane) remain unchanged by cleavage. Similarly, the interactions of the spikes with the nucleocapsid through the transmembrane domains remain constant. Hence, the interactions that lead to virus assembly are unaffected by the SFVmSQL mutation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1018.map.gz emd_1018.map.gz | 21.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1018-v30.xml emd-1018-v30.xml emd-1018.xml emd-1018.xml | 8.8 KB 8.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1018.gif 1018.gif | 45.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1018 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1018 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1018 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1018 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1018.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 31.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED INTEGER (2 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1018.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 31.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS SIGNED INTEGER (2 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Semliki forest virus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Semliki forest mSQL
| Entire | Name: Semliki forest mSQL |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Semliki forest mSQL
| Supramolecule | Name: Semliki forest mSQL / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #1: Semliki forest virus
| Supramolecule | Name: Semliki forest virus / type: virus / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: semliki forest m SQL / Details: mSQL mutation. / NCBI-ID: 11033 / Sci species name: Semliki forest virus / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: STRAIN / Virus enveloped: Yes / Virus empty: No / Syn species name: semliki forest m SQL |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism: baby hamster kidney 21 cells (unknown) / synonym: VERTEBRATES |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Name: envelope / T number (triangulation number): 4 |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 2 / Name: nucleo capsid / T number (triangulation number): 4 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: tris(10mM) NaCL (100mM) ph 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 37 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: Vitrification instrument: EMBL plunger with warm humid air spray Method: blot for 2 sec Graticule grids were used to maintain |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM200FEG/ST |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 105 K |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: PERKIN ELMER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 20 µm / Average electron dose: 8 e/Å2 / Camera length: 44 / Od range: 1 / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 7.628 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.975 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: eucentric / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: ctf multiplication and summation of normalized reconstructions |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: I (icosahedral) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 9.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: EMBL / Number images used: 62 |
| Final angle assignment | Details: sufficient to give maximum inverse eigen value of 0.1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)