+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
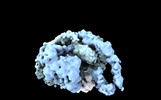
| Title | PAPP-A dimer in complex with endogenous STC2 inhibitor. | |||||||||
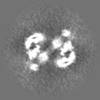
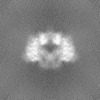
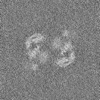
 Map data Map data | Primary, sharpened map of the PAPP-A dimer in complex with STC2 dimer. Refinement focused on the dimerization region | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Metzincin metalloprotease Inhibitor complex / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
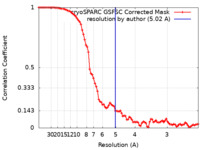
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.02 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kobbero SD / Oxvig C / Gajhede M / Boesen T | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 1 items Denmark, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structure of the proteolytic enzyme PAPP-A with the endogenous inhibitor stanniocalcin-2 reveals its inhibitory mechanism. Authors: Sara Dam Kobberø / Michael Gajhede / Osman Asghar Mirza / Søren Kløverpris / Troels Rønn Kjær / Jakob Hauge Mikkelsen / Thomas Boesen / Claus Oxvig /  Abstract: The metzincin metalloproteinase PAPP-A plays a key role in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling by specific cleavage of inhibitory IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs). Using single- ...The metzincin metalloproteinase PAPP-A plays a key role in the regulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling by specific cleavage of inhibitory IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs). Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we here report the structure of PAPP-A in complex with its endogenous inhibitor, stanniocalcin-2 (STC2), neither of which have been reported before. The highest resolution (3.1 Å) was obtained for the STC2 subunit and the N-terminal approximately 1000 residues of the PAPP-A subunit. The 500 kDa 2:2 PAPP-A·STC2 complex is a flexible multidomain ensemble with numerous interdomain contacts. In particular, a specific disulfide bond between the subunits of STC2 and PAPP-A prevents dissociation, and interactions between STC2 and a module located in the very C-terminal end of the PAPP-A subunit prevent binding of its main substrate, IGFBP-4. While devoid of activity towards IGFBP-4, the active site cleft of the catalytic domain is accessible in the inhibited PAPP-A·STC2 complex, as shown by its ability to hydrolyze a synthetic peptide derived from IGFBP-4. Relevant to multiple human pathologies, this unusual mechanism of proteolytic inhibition may support the development of specific pharmaceutical agents, by which IGF signaling can be indirectly modulated. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15219.map.gz emd_15219.map.gz | 59.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15219-v30.xml emd-15219-v30.xml emd-15219.xml emd-15219.xml | 23.4 KB 23.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_15219_fsc.xml emd_15219_fsc.xml | 8.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_15219.png emd_15219.png | 54 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-15219.cif.gz emd-15219.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_15219_additional_1.map.gz emd_15219_additional_1.map.gz emd_15219_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15219_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15219_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15219_half_map_2.map.gz | 31.7 MB 59.2 MB 59.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15219 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15219 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15219 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15219.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15219.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Primary, sharpened map of the PAPP-A dimer in complex with STC2 dimer. Refinement focused on the dimerization region | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
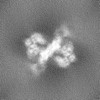
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.18594 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
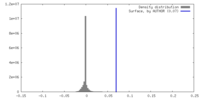
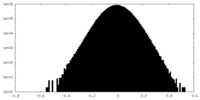
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Raw, unsharpened map of the PAPP-A dimer in...
| File | emd_15219_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
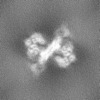
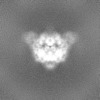
| Annotation | Raw, unsharpened map of the PAPP-A dimer in complex with STC2 dimer. Refinement focused on the dimerization region | ||||||||||||
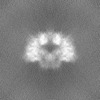
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
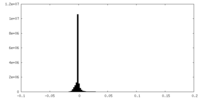
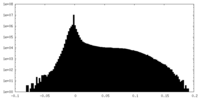
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A of the PAPP-A dimer in...
| File | emd_15219_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
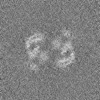
| Annotation | Half map A of the PAPP-A dimer in complex with STC2 dimer. Refinement focused on the dimerization region | ||||||||||||
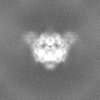
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B of the PAPP-A dimer in...
| File | emd_15219_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B of the PAPP-A dimer in complex with STC2 dimer. Refinement focused on the dimerization region | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PAPP-A dimer in complex with its endogenous inhibitor STC2 dimer
| Entire | Name: PAPP-A dimer in complex with its endogenous inhibitor STC2 dimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: PAPP-A dimer in complex with its endogenous inhibitor STC2 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: PAPP-A dimer in complex with its endogenous inhibitor STC2 dimer type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Inhibited proteolytic complex generated by harvest of serum media, purifying on a nickel column followed by negative affinity purification and size-exclusion chromatography. |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 100 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A
| Supramolecule | Name: Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: Homodimer |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: ubiquitous / Location in cell: extracellular Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: ubiquitous / Location in cell: extracellular |
-Supramolecule #3: Stanniocalcin-2
| Supramolecule | Name: Stanniocalcin-2 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 / Details: Homodimer |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: ubiquitous / Location in cell: extracellular Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: ubiquitous / Location in cell: extracellular |
-Macromolecule #1: PAPP-A
| Macromolecule | Name: PAPP-A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: Pre-pro-peptide / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: pappalysin-1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MRLWSWVLHL GLLSAALGCG LAERPRRARR DPRAGRPPRP AAGPATCATR AARGRRASPP PPPPPGGAW EAVRVPRRRQ QREARGATEE PSPPSRALYF SGRGEQLRLR ADLELPRDAF T LQVWLRAE GGQRSPAVIT GLYDKCSYIS RDRGWVVGIH TISDQDNKDP ...String: MRLWSWVLHL GLLSAALGCG LAERPRRARR DPRAGRPPRP AAGPATCATR AARGRRASPP PPPPPGGAW EAVRVPRRRQ QREARGATEE PSPPSRALYF SGRGEQLRLR ADLELPRDAF T LQVWLRAE GGQRSPAVIT GLYDKCSYIS RDRGWVVGIH TISDQDNKDP RYFFSLKTDR AR QVTTINA HRSYLPGQWV YLAATYDGQF MKLYVNGAQV ATSGEQVGGI FSPLTQKCKV LML GGSALN HNYRGYIEHF SLWKVARTQR EILSDMETHG AHTALPQLLL QENWDNVKHA WSPM KDGSS PKVEFSNAHG FLLDTSLEPP LCGQTLCDNT EVIASYNQLS SFRQPKVVRY RVVNL YEDD HKNPTVTREQ VDFQHHQLAE AFKQYNISWE LDVLEVSNSS LRRRLILANC DISKIG DEN CDPECNHTLT GHDGGDCRHL RHPAFVKKQH NGVCDMDCNY ERFNFDGGEC CDPEITN VT QTCFDPDSPH RAYLDVNELK NILKLDGSTH LNIFFAKSSE EELAGVATWP WDKEALMH L GGIVLNPSFY GMPGHTHTMI HEIGHSLGLY HVFRGISEIQ SCSDPCMETE PSFETGDLC NDTNPAPKHK SCGDPGPGND TCGFHSFFNT PYNNFMSYAD DDCTDSFTPN QVARMHCYLD LVYQGWQPS RKPAPVALAP QVLGHTTDSV TLEWFPPIDG HFFERELGSA CHLCLEGRIL V QYASNASS PMPCSPSGHW SPREAEGHPD VEQPCKSSVR TWSPNSAVNP HTVPPACPEP QG CYLELEF LYPLVPESLT IWVTFVSTDW DSSGAVNDIK LLAVSGKNIS LGPQNVFCDV PLT IRLWDV GEEVYGIQIY TLDEHLEIDA AMLTSTADTP LCLQCKPLKY KVVRDPPLQM DVAS ILHLN RKFVDMDLNL GSVYQYWVIT ISGTEESEPS PAVTYIHGSG YCGDGIIQKD QGEQC DDMN KINGDGCSLF CRQEVSFNCI DEPSRCYFHD GDGVCEEFEQ KTSIKDCGVY TPQGFL DQW ASNASVSHQD QQCPGWVIIG QPAASQVCRT KVIDLSEGIS QHAWYPCTIS YPYSQLA QT TFWLRAYFSQ PMVAAAVIVH LVTDGTYYGD QKQETISVQL LDTKDQSHDL GLHVLSCR N NPLIIPVVHD LSQPFYHSQA VRVSFSSPLV AISGVALRSF DNFDPVTLSS CQRGETYSP AEQSCVHFAC EKTDCPELAV ENASLNCSSS DRYHGAQCTV SCRTGYVLQI RRDDELIKSQ TGPSVTVTC TEGKWNKQVA CEPVDCSIPD HHQVYAASFS CPEGTTFGSQ CSFQCRHPAQ L KGNNSLLT CMEDGLWSFP EALCELMCLA PPPVPNADLQ TARCRENKHK VGSFCKYKCK PG YHVPGSS RKSKKRAFKT QCTQDGSWQE GACVPVTCDP PPPKFHGLYQ CTNGFQFNSE CRI KCEDSD ASQGLGSNVI HCRKDGTWNG SFHVCQEMQG QCSVPNELNS NLKLQCPDGY AIGS ECATS CLDHNSESII LPMNVTVRDI PHWLNPTRVE RVVCTAGLKW YPHPALIHCV KGCEP FMGD NYCDAINNRA FCNYDGGDCC TSTVKTKKVT PFPMSCDLQG DCACRDPQAQ EHSRKD LRG YSHG GENBANK: GENBANK: AL691426 |
-Macromolecule #2: Stanniocalcin 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Stanniocalcin 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: TDATNPPEGP QDRSSQQKGR LSLQNTAEIQ HCLVNAGDVG CGVFECFENN SCEIRGLHGI CMTFLHNAG KFDAQGKSFI KDALKCKAHA LRHRFGCISR KCPAIREMVS QLQRECYLKH D LCAAAQEN TRVIVEMIHF KDLLLHEPYV DLVNLLLTCG EEVKEAITHS ...String: TDATNPPEGP QDRSSQQKGR LSLQNTAEIQ HCLVNAGDVG CGVFECFENN SCEIRGLHGI CMTFLHNAG KFDAQGKSFI KDALKCKAHA LRHRFGCISR KCPAIREMVS QLQRECYLKH D LCAAAQEN TRVIVEMIHF KDLLLHEPYV DLVNLLLTCG EEVKEAITHS VQVQCEQNWG SL CSILSFC TSAIQKPPTA PPERQPQVDR TKLSRAHHGE AGHHLPEPSS RETGRGAKGE RGS KSHPNA HARGRVGGLG AQGPSGSSEW EDEQSEYSDI RR GENBANK: GENBANK: AF031036 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.6 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Component:
Details: HEPES buffer 20 mM Hepes pH 7.5 100 mM NaCl, 1mM CaCl | ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 45 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Details: Blot time 4.5 sec. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | #0 - Image recording ID: 1 / #0 - Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / #0 - Number grids imaged: 1 / #0 - Number real images: 32144 / #0 - Average exposure time: 0.91 sec. / #0 - Average electron dose: 59.0 e/Å2 / #1 - Image recording ID: 2 / #1 - Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / #1 - Number grids imaged: 1 / #1 - Number real images: 10060 / #1 - Average exposure time: 0.8 sec. / #1 - Average electron dose: 58.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)