[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1465: Three-dimensional structure of vertebrate cardiac muscle myosin f... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1465 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
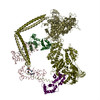
| Title | Three-dimensional structure of vertebrate cardiac muscle myosin filaments. | |||||||||
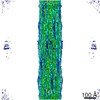
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of cardiac myosin filaments (C-zone) under relaxing conditions. The reconstruction (filtered to 4.0 nm resolution) shows two 42.9 nm repeats. The main globular features are myosin heads, which are arranged in three crowns within each 42.9 nm repeat, following a perturbed helical path. Each crown has 3-fold rotational symmetry. Smaller features with a periodicity of about 4 nm can also be observed. Those features represent the accessory proteins titin and myosin-binding protein-C. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 32.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zoghbi ME / Woodhead JL / Moss RL / Craig R | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2008 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2008Title: Three-dimensional structure of vertebrate cardiac muscle myosin filaments. Authors: Maria E Zoghbi / John L Woodhead / Richard L Moss / Roger Craig /  Abstract: Contraction of the heart results from interaction of the myosin and actin filaments. Cardiac myosin filaments consist of the molecular motor myosin II, the sarcomeric template protein, titin, and the ...Contraction of the heart results from interaction of the myosin and actin filaments. Cardiac myosin filaments consist of the molecular motor myosin II, the sarcomeric template protein, titin, and the cardiac modulatory protein, myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C). Inherited hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a disease caused mainly by mutations in these proteins. The structure of cardiac myosin filaments and the alterations caused by HCM mutations are unknown. We have used electron microscopy and image analysis to determine the three-dimensional structure of myosin filaments from wild-type mouse cardiac muscle and from a MyBP-C knockout model for HCM. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the wild-type filament reveals the conformation of the myosin heads and the organization of titin and MyBP-C at 4 nm resolution. Myosin heads appear to interact with each other intramolecularly, as in off-state smooth muscle myosin [Wendt T, Taylor D, Trybus KM, Taylor K (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4361-4366], suggesting that all relaxed muscle myosin IIs may adopt this conformation. Titin domains run in an elongated strand along the filament surface, where they appear to interact with part of MyBP-C and with the myosin backbone. In the knockout filament, some of the myosin head interactions are disrupted, suggesting that MyBP-C is important for normal relaxation of the filament. These observations provide key insights into the role of the myosin filament in cardiac contraction, assembly, and disease. The techniques we have developed should be useful in studying the structural basis of other myosin-related HCM diseases. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1465.map.gz emd_1465.map.gz | 2.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1465-v30.xml emd-1465-v30.xml emd-1465.xml emd-1465.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  1465.gif 1465.gif emd_1465.tif emd_1465.tif emd_1465_1.tif emd_1465_1.tif | 62.7 KB 3.2 MB 13.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1465 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1465 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1465 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1465 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1465.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1465.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 2.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of cardiac myosin filaments (C-zone) under relaxing conditions. The reconstruction (filtered to 4.0 nm resolution) shows two 42.9 nm repeats. The main globular features are myosin heads, which are arranged in three crowns within each 42.9 nm repeat, following a perturbed helical path. Each crown has 3-fold rotational symmetry. Smaller features with a periodicity of about 4 nm can also be observed. Those features represent the accessory proteins titin and myosin-binding protein-C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 5.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cardiac myosin filaments from mouse ventricle muscle
| Entire | Name: Cardiac myosin filaments from mouse ventricle muscle |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Cardiac myosin filaments from mouse ventricle muscle
| Supramolecule | Name: Cardiac myosin filaments from mouse ventricle muscle / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Myosin
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Myosin / Details: Filament is a polymer of myosin / Oligomeric state: polymer / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 520 KDa / Theoretical: 520 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 Details: 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM EGTA, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM Imidazole, 5 mM MgATP, 0.1 mM blebbistatin,pH 7.2 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: A drop of filament suspension was placed on an electron microscope grid coated with a thin layer of carbon supported by a thicker holey carbon film. The grid was rinsed sequentially with 6 ...Details: A drop of filament suspension was placed on an electron microscope grid coated with a thin layer of carbon supported by a thicker holey carbon film. The grid was rinsed sequentially with 6 drops of relaxing rinse (in mM: 140 NaAc, 1 MgAc2, 1 EGTA, 5 Imidazole, 1 sodium azide, 1 MgATP, pH 7.0 ) and 5 drops of 2% uranyl acetate. Staining was carried out at room temperature with solutions pre-warmed to 37o C. |
| Grid | Details: carbon holey grids (400 mesh copper) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM120T |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: corrected at 240,000 x |
| Details | Grids were observed in a Philips CM120 electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) under low dose conditions. Only filaments on thin carbon over holes were photographed . |
| Date | May 30, 2006 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F224 (2k x 2k) / Number real images: 300 Details: Images were acquired on a CDD camera at 5.7 A/pixel Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 80 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 42000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm / Nominal magnification: 42000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: OTHER |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The filament shows perturbations from a perfect helical structure. |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C3 (3 fold cyclic) Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 32.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER Details: Since these filaments are not perfectly helical, we used single particle analysis for their reconstruction. Filaments were oriented vertically and the region between the 3rd and 10th 42.9 nm ...Details: Since these filaments are not perfectly helical, we used single particle analysis for their reconstruction. Filaments were oriented vertically and the region between the 3rd and 10th 42.9 nm repeats from the bare zone (where MyBP-C is present) was computationally cut. Those selected filament regions were converted to SPIDER format (EM2EM; Image Science and Imperial College, London), and cut into segments 3x42.9 nm long in SPIDER (v11.2, Wadsworth Center, Albany, NY). Relative rotations of different filament segments were determined before back-projection by matching filament images against 2D projections of 3D models rotated around their long axis at known angles. C3 symmetry was imposed during reconstruction. A total of 2564 segments (2600 particles) were used for the reconstruction. |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Details | Atomic structure of the myosin heads (pdb 1i84; with the modifications introduced by Woodhead et al., 2005. Nature. 436:1195)was fitted manually to the globular features of the reconstruction using UCSF Chimera. |
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera

 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)