+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Three-dimensional structure of vertebrate cardiac muscle myosin filaments. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 105, Issue 7, Page 2386-2390, Year 2008 |
| Publish date | Feb 19, 2008 |
 Authors Authors | Maria E Zoghbi / John L Woodhead / Richard L Moss / Roger Craig /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Contraction of the heart results from interaction of the myosin and actin filaments. Cardiac myosin filaments consist of the molecular motor myosin II, the sarcomeric template protein, titin, and the ...Contraction of the heart results from interaction of the myosin and actin filaments. Cardiac myosin filaments consist of the molecular motor myosin II, the sarcomeric template protein, titin, and the cardiac modulatory protein, myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C). Inherited hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a disease caused mainly by mutations in these proteins. The structure of cardiac myosin filaments and the alterations caused by HCM mutations are unknown. We have used electron microscopy and image analysis to determine the three-dimensional structure of myosin filaments from wild-type mouse cardiac muscle and from a MyBP-C knockout model for HCM. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the wild-type filament reveals the conformation of the myosin heads and the organization of titin and MyBP-C at 4 nm resolution. Myosin heads appear to interact with each other intramolecularly, as in off-state smooth muscle myosin [Wendt T, Taylor D, Trybus KM, Taylor K (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4361-4366], suggesting that all relaxed muscle myosin IIs may adopt this conformation. Titin domains run in an elongated strand along the filament surface, where they appear to interact with part of MyBP-C and with the myosin backbone. In the knockout filament, some of the myosin head interactions are disrupted, suggesting that MyBP-C is important for normal relaxation of the filament. These observations provide key insights into the role of the myosin filament in cardiac contraction, assembly, and disease. The techniques we have developed should be useful in studying the structural basis of other myosin-related HCM diseases. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:18252826 / PubMed:18252826 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 32.0 Å |
| Structure data | 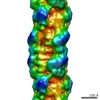 EMDB-1465: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




