+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Proteasome-ZFAND5 Complex Z-A state | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ZFAND5-proteasome complex Z-A state | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | proteasome / ZFAND5 / Activation / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報host-mediated perturbation of viral transcription / Impaired BRCA2 translocation to the nucleus / Impaired BRCA2 binding to SEM1 (DSS1) / cytosolic proteasome complex / 加水分解酵素; プロテアーゼ; ペプチド結合加水分解酵素; オメガペプチターゼ / proteasome accessory complex / integrator complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / meiosis I / proteasome regulatory particle ...host-mediated perturbation of viral transcription / Impaired BRCA2 translocation to the nucleus / Impaired BRCA2 binding to SEM1 (DSS1) / cytosolic proteasome complex / 加水分解酵素; プロテアーゼ; ペプチド結合加水分解酵素; オメガペプチターゼ / proteasome accessory complex / integrator complex / purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding / meiosis I / proteasome regulatory particle / positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome-activating activity / proteasome regulatory particle, lid subcomplex / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / metal-dependent deubiquitinase activity / protein K63-linked deubiquitination / Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) / Proteasome assembly / Homologous DNA Pairing and Strand Exchange / Defective homologous recombination repair (HRR) due to BRCA1 loss of function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA1 binding function / Defective HDR through Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR) due to PALB2 loss of BRCA2/RAD51/RAD51C binding function / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA) / proteasome core complex / Resolution of D-loop Structures through Holliday Junction Intermediates / Somitogenesis / K63-linked deubiquitinase activity / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / proteasome binding / regulation of protein catabolic process / myofibril / proteasome storage granule / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / blastocyst development / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / immune system process / protein deubiquitination / endopeptidase activator activity / NF-kappaB binding / proteasome endopeptidase complex / proteasome core complex, beta-subunit complex / proteasome assembly / threonine-type endopeptidase activity / proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex / mRNA export from nucleus / enzyme regulator activity / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / proteasome complex / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / sarcomere / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / stem cell differentiation / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / AUF1 (hnRNP D0) binds and destabilizes mRNA / Vpu mediated degradation of CD4 / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Degradation of DVL / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / Dectin-1 mediated noncanonical NF-kB signaling / lipopolysaccharide binding / Degradation of AXIN / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / Activation of NF-kappaB in B cells / P-body / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / G2/M Checkpoints / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 / Negative regulation of NOTCH4 signaling / Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G / Regulation of RUNX3 expression and activity / Hedgehog 'on' state / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / Degradation of GLI2 by the proteasome / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / : / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / response to virus / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.7 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Zhu Y / Lu Y | |||||||||
| 資金援助 | 1件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Mol Cell / 年: 2023 ジャーナル: Mol Cell / 年: 2023タイトル: Molecular mechanism for activation of the 26S proteasome by ZFAND5. 著者: Donghoon Lee / Yanan Zhu / Louis Colson / Xiaorong Wang / Siyi Chen / Emre Tkacik / Lan Huang / Qi Ouyang / Alfred L Goldberg / Ying Lu /   要旨: Various hormones, kinases, and stressors (fasting, heat shock) stimulate 26S proteasome activity. To understand how its capacity to degrade ubiquitylated proteins can increase, we studied mouse ...Various hormones, kinases, and stressors (fasting, heat shock) stimulate 26S proteasome activity. To understand how its capacity to degrade ubiquitylated proteins can increase, we studied mouse ZFAND5, which promotes protein degradation during muscle atrophy. Cryo-electron microscopy showed that ZFAND5 induces large conformational changes in the 19S regulatory particle. ZFAND5's AN1 Zn-finger domain interacts with the Rpt5 ATPase and its C terminus with Rpt1 ATPase and Rpn1, a ubiquitin-binding subunit. Upon proteasome binding, ZFAND5 widens the entrance of the substrate translocation channel, yet it associates only transiently with the proteasome. Dissociation of ZFAND5 then stimulates opening of the 20S proteasome gate. Using single-molecule microscopy, we showed that ZFAND5 binds ubiquitylated substrates, prolongs their association with proteasomes, and increases the likelihood that bound substrates undergo degradation, even though ZFAND5 dissociates before substrate deubiquitylation. These changes in proteasome conformation and reaction cycle can explain the accelerated degradation and suggest how other proteasome activators may stimulate proteolysis. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_14209.map.gz emd_14209.map.gz | 113.7 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-14209-v30.xml emd-14209-v30.xml emd-14209.xml emd-14209.xml | 47.2 KB 47.2 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_14209.png emd_14209.png | 76.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14209.cif.gz emd-14209.cif.gz | 13.2 KB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14209 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14209 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14209 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14209 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  7qy7MC  7qxnC  7qxpC  7qxuC  7qxwC  7qxxC  7qyaC  7qybC M: このマップから作成された原子モデル C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_14209.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_14209.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
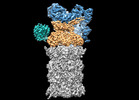
| 注釈 | ZFAND5-proteasome complex Z-A state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.37 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
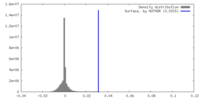
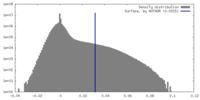
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
+全体 : human proteasome zfand5 complex Z-A state
+超分子 #1: human proteasome zfand5 complex Z-A state
+分子 #1: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 13
+分子 #2: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 4
+分子 #3: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14
+分子 #4: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 8
+分子 #5: 26S proteasome complex subunit SEM1
+分子 #6: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2
+分子 #7: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 1
+分子 #8: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 3
+分子 #9: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 12
+分子 #10: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 11
+分子 #11: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 6
+分子 #12: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 7
+分子 #13: 26S protease regulatory subunit 7
+分子 #14: 26S protease regulatory subunit 4
+分子 #15: PSMC5 isoform 15
+分子 #16: 26S protease regulatory subunit 6B
+分子 #17: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 10B
+分子 #18: 26S protease regulatory subunit 6A
+分子 #19: Proteasome subunit alpha type-6
+分子 #20: Proteasome subunit alpha type-2
+分子 #21: Proteasome subunit alpha type-4
+分子 #22: Proteasome subunit alpha type-7
+分子 #23: Proteasome subunit alpha type-5
+分子 #24: Isoform Long of Proteasome subunit alpha type-1
+分子 #25: Proteasome subunit alpha type-3
+分子 #26: Proteasome subunit beta type-6
+分子 #27: Proteasome subunit beta type-7
+分子 #28: Proteasome subunit beta type-3
+分子 #29: Proteasome subunit beta type-2
+分子 #30: Proteasome subunit beta type-5
+分子 #31: Proteasome subunit beta type-1
+分子 #32: Proteasome subunit beta type-4
+分子 #33: ZINC ION
+分子 #34: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7 |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 46.6 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2.5 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.8 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
- 画像解析
画像解析
| 初期モデル | モデルのタイプ: NONE |
|---|---|
| 最終 再構成 | 解像度のタイプ: BY AUTHOR / 解像度: 4.7 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 使用した粒子像数: 34363 |
| 初期 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| 最終 角度割当 | タイプ: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)