+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10901 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
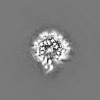
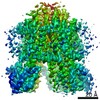
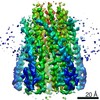
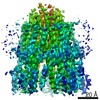
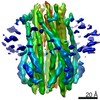
| Title | Vibrio mimicus PomA(5)B(2) complex | |||||||||||||||
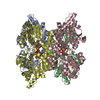
 Map data Map data | Post Processed Vibrio mimicus PomAB complex volume | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum-dependent swarming motility / chemotaxis / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) / Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) /  Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
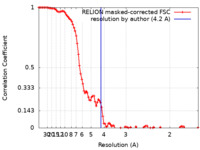
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lea SM / Deme JC / Johnson S | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4 items United Kingdom, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020Title: Structures of the stator complex that drives rotation of the bacterial flagellum. Authors: Justin C Deme / Steven Johnson / Owen Vickery / Amy Aron / Holly Monkhouse / Thomas Griffiths / Rory Hennell James / Ben C Berks / James W Coulton / Phillip J Stansfeld / Susan M Lea /   Abstract: The bacterial flagellum is the prototypical protein nanomachine and comprises a rotating helical propeller attached to a membrane-embedded motor complex. The motor consists of a central rotor ...The bacterial flagellum is the prototypical protein nanomachine and comprises a rotating helical propeller attached to a membrane-embedded motor complex. The motor consists of a central rotor surrounded by stator units that couple ion flow across the cytoplasmic membrane to generate torque. Here, we present the structures of the stator complexes from Clostridium sporogenes, Bacillus subtilis and Vibrio mimicus, allowing interpretation of the extensive body of data on stator mechanism. The structures reveal an unexpected asymmetric AB subunit assembly where the five A subunits enclose the two B subunits. Comparison to structures of other ion-driven motors indicates that this AB architecture is fundamental to bacterial systems that couple energy from ion flow to generate mechanical work at a distance and suggests that such events involve rotation in the motor structures. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10901.map.gz emd_10901.map.gz | 85 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10901-v30.xml emd-10901-v30.xml emd-10901.xml emd-10901.xml | 22.2 KB 22.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10901_fsc.xml emd_10901_fsc.xml | 10.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_10901.png emd_10901.png | 223.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_10901_msk_1.map emd_10901_msk_1.map | 91.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_10901_additional_1.map.gz emd_10901_additional_1.map.gz emd_10901_additional_2.map.gz emd_10901_additional_2.map.gz emd_10901_additional_3.map.gz emd_10901_additional_3.map.gz emd_10901_additional_4.map.gz emd_10901_additional_4.map.gz | 57.5 MB 70.6 MB 71.3 MB 71.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10901 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10901 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10901 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10901 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10901.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10901.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
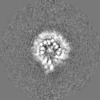
| Annotation | Post Processed Vibrio mimicus PomAB complex volume | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.822 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_10901_msk_1.map emd_10901_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: relion local resolution Vibrio mimicus PomAB complex volume
| File | emd_10901_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | relion local resolution Vibrio mimicus PomAB complex volume | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: refinement volume
| File | emd_10901_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | refinement volume | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: half map 1
| File | emd_10901_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: half map 2
| File | emd_10901_additional_4.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PomA(5)B(2)
| Entire | Name: PomA(5)B(2) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: PomA(5)B(2)
| Supramolecule | Name: PomA(5)B(2) / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: PomA
| Macromolecule | Name: PomA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDLATLIGLI GGLAFVIMAM VLGGSLMMFV DVVSILIVVG GSVFVVLMKF TMGQFFGAGK IASKAFMFK ADEPEDLIAK IVEMADAARK GGFLALEEME IPNPFMQKGI DLLVDGHDAD V VRATLQKD IALTDERHSK GTQVFRAFGD VAPAMGMIST LVGLVAMLSN ...String: MDLATLIGLI GGLAFVIMAM VLGGSLMMFV DVVSILIVVG GSVFVVLMKF TMGQFFGAGK IASKAFMFK ADEPEDLIAK IVEMADAARK GGFLALEEME IPNPFMQKGI DLLVDGHDAD V VRATLQKD IALTDERHSK GTQVFRAFGD VAPAMGMIST LVGLVAMLSN MDDPKSIGPA MA VALLTTL YGAVLSNMIF FPIADKLALR RDQETLNRRL IMDGVLAIQD GQNPRVIDSY LKN YLNASK RALDVDKE |
-Macromolecule #2: PomB
| Macromolecule | Name: PomB / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) Vibrio mimicus (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDDEQQCKCP PPGLPAWLGT FADLMSLLMC FFVLLLSFSE MDVLKFKQIA GSMKFAFGVQ NRLEVKDIP KGTSIIAQEF RPGRPEPTPI DVIMQQTIDI TQQTLDFQEG DSDRAGGNQR D SGKLTGGQ SAESSTQDNQ NTQSEMQQQQ AKAMSEQMET VAESIKKALS ...String: MDDEQQCKCP PPGLPAWLGT FADLMSLLMC FFVLLLSFSE MDVLKFKQIA GSMKFAFGVQ NRLEVKDIP KGTSIIAQEF RPGRPEPTPI DVIMQQTIDI TQQTLDFQEG DSDRAGGNQR D SGKLTGGQ SAESSTQDNQ NTQSEMQQQQ AKAMSEQMET VAESIKKALS REIEQGAIEV EN LGQQIDI RIREKGAFPE GSAFLQPKFR PLVRQIADLV KDIPGKVRVT GHTDNQKLDS ELY RSNWDL SAQRAVSVAQ EMEKVKGFDH QRLQVRGMAD TQPLGPNDTE AQRALNRRVE ISIL QGDPL YSDEVPSLGA PANQ |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 0.0003 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.0001 µm / Nominal magnification: 165000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





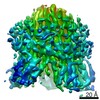

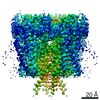



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)