[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
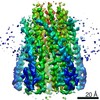
Yorodumi- PDB-6ysf: Structure of the flagellar MotAB stator complex from Clostridium ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ysf | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
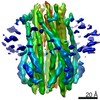
| Title | Structure of the flagellar MotAB stator complex from Clostridium sporogenes | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / Stator Flagellar rotation ion driven motor | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lea, S.M. / Deme, J.C. / Johnson, S.J. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4items United Kingdom, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020Title: Structures of the stator complex that drives rotation of the bacterial flagellum. Authors: Justin C Deme / Steven Johnson / Owen Vickery / Amy Aron / Holly Monkhouse / Thomas Griffiths / Rory Hennell James / Ben C Berks / James W Coulton / Phillip J Stansfeld / Susan M Lea /   Abstract: The bacterial flagellum is the prototypical protein nanomachine and comprises a rotating helical propeller attached to a membrane-embedded motor complex. The motor consists of a central rotor ...The bacterial flagellum is the prototypical protein nanomachine and comprises a rotating helical propeller attached to a membrane-embedded motor complex. The motor consists of a central rotor surrounded by stator units that couple ion flow across the cytoplasmic membrane to generate torque. Here, we present the structures of the stator complexes from Clostridium sporogenes, Bacillus subtilis and Vibrio mimicus, allowing interpretation of the extensive body of data on stator mechanism. The structures reveal an unexpected asymmetric AB subunit assembly where the five A subunits enclose the two B subunits. Comparison to structures of other ion-driven motors indicates that this AB architecture is fundamental to bacterial systems that couple energy from ion flow to generate mechanical work at a distance and suggests that such events involve rotation in the motor structures. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ysf.cif.gz 6ysf.cif.gz | 235.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ysf.ent.gz pdb6ysf.ent.gz | 188.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ysf.json.gz 6ysf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ys/6ysf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ys/6ysf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ys/6ysf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ys/6ysf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 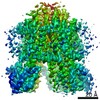 10895MC  6yslC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 27948.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria)Gene: motB, NCTC13020_02207, NCTC534_01101, VT92_0222420, VT96_0225960 Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 29613.506 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) / Gene: motA, NCTC13020_02206 / Production host: Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) / Gene: motA, NCTC13020_02206 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MotAB / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) Clostridium sporogenes (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 0.3 nm / Nominal defocus min: 0.1 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1998900 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 314230 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj