[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-10333: Structure of active GID E3 ubiquitin ligase complex minus Gid2 an... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10333 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
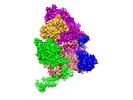
| Title | Structure of active GID E3 ubiquitin ligase complex minus Gid2 and delta Gid9 RING domain | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Suppressed / Suppreseed / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein catabolic process in the vacuole / GID complex / : / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the N-end rule pathway / ascospore formation / traversing start control point of mitotic cell cycle / protein targeting to vacuole / regulation of nitrogen utilization / vacuole / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis ...protein catabolic process in the vacuole / GID complex / : / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the N-end rule pathway / ascospore formation / traversing start control point of mitotic cell cycle / protein targeting to vacuole / regulation of nitrogen utilization / vacuole / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / Neutrophil degranulation / cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / cytoplasmic vesicle / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of apoptotic process / zinc ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
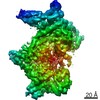
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Qiao S / Prabu JR / Schulman BA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1 items Germany, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Interconversion between Anticipatory and Active GID E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Conformations via Metabolically Driven Substrate Receptor Assembly. Authors: Shuai Qiao / Christine R Langlois / Jakub Chrustowicz / Dawafuti Sherpa / Ozge Karayel / Fynn M Hansen / Viola Beier / Susanne von Gronau / Daniel Bollschweiler / Tillman Schäfer / Arno F ...Authors: Shuai Qiao / Christine R Langlois / Jakub Chrustowicz / Dawafuti Sherpa / Ozge Karayel / Fynn M Hansen / Viola Beier / Susanne von Gronau / Daniel Bollschweiler / Tillman Schäfer / Arno F Alpi / Matthias Mann / J Rajan Prabu / Brenda A Schulman /  Abstract: Cells respond to environmental changes by toggling metabolic pathways, preparing for homeostasis, and anticipating future stresses. For example, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, carbon stress-induced ...Cells respond to environmental changes by toggling metabolic pathways, preparing for homeostasis, and anticipating future stresses. For example, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, carbon stress-induced gluconeogenesis is terminated upon glucose availability, a process that involves the multiprotein E3 ligase GID recruiting N termini and catalyzing ubiquitylation of gluconeogenic enzymes. Here, genetics, biochemistry, and cryoelectron microscopy define molecular underpinnings of glucose-induced degradation. Unexpectedly, carbon stress induces an inactive anticipatory complex (GID), which awaits a glucose-induced substrate receptor to form the active GID. Meanwhile, other environmental perturbations elicit production of an alternative substrate receptor assembling into a related E3 ligase complex. The intricate structure of GID enables anticipating and ultimately binding various N-degron-targeting (i.e., "N-end rule") substrate receptors, while the GID E3 forms a clamp-like structure juxtaposing substrate lysines with the ubiquitylation active site. The data reveal evolutionarily conserved GID complexes as a family of multisubunit E3 ubiquitin ligases responsive to extracellular stimuli. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10333.map.gz emd_10333.map.gz | 8.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10333-v30.xml emd-10333-v30.xml emd-10333.xml emd-10333.xml | 26.5 KB 26.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
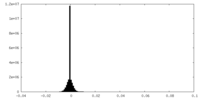
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_10333_fsc.xml emd_10333_fsc.xml | 10 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
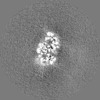
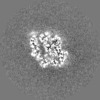
| Images |  emd_10333.png emd_10333.png | 136.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_10333_msk_1.map emd_10333_msk_1.map | 83.7 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10333.cif.gz emd-10333.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_10333_additional.map.gz emd_10333_additional.map.gz emd_10333_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10333_half_map_1.map.gz emd_10333_half_map_2.map.gz emd_10333_half_map_2.map.gz | 4.2 MB 65.5 MB 65.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10333 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10333 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10333 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10333 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 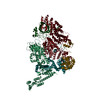 6swyMC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10333.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10333.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
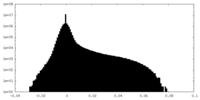
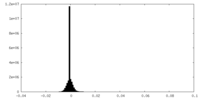
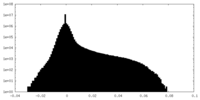
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_10333_msk_1.map emd_10333_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_10333_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_10333_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_10333_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : GIDSR4 minus Gid2/delta Gid9RING
| Entire | Name: GIDSR4 minus Gid2/delta Gid9RING |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: GIDSR4 minus Gid2/delta Gid9RING
| Supramolecule | Name: GIDSR4 minus Gid2/delta Gid9RING / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 28
| Macromolecule | Name: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 28 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 105.658203 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: MTVAYSLENL KKISNSLVGD QLAKVDYFLA PKCQIFQCLL SIEQSDGVEL KNAKLDLLYT LLHLEPQQRD IVGTYYFDIV SAIYKSMSL ASSFTKNNSS TNYKYIKLLN LCAGVYPNCG FPDLQYLQNG FIQLVNHKFL RSKCKIDEVV TIIELLKLFL L VDEKNCSD ...String: MTVAYSLENL KKISNSLVGD QLAKVDYFLA PKCQIFQCLL SIEQSDGVEL KNAKLDLLYT LLHLEPQQRD IVGTYYFDIV SAIYKSMSL ASSFTKNNSS TNYKYIKLLN LCAGVYPNCG FPDLQYLQNG FIQLVNHKFL RSKCKIDEVV TIIELLKLFL L VDEKNCSD FNKSKFMEEE REVTETSHYQ DFKMAESLEH IIVKISSKYL DQISLKYIVR LKVSRPASPS SVKNDPFDNK GV DCTRAIP KKINISNMYD SSLLSLALLL YLRYHYMIPG DRKLRNDATF KMFVLGLLKS NDVNIRCVAL KFLLQPYFTE DKK WEDTRT LEKILPYLVK SFNYDPLPWW FDPFDMLDSL IVLYNEITPM NNPVLTTLAH TNVIFCILSR FAQCLSLPQH NEAT LKTTT KFIKICASFA ASDEKYRLLL LNDTLLLNHL EYGLESHITL IQDFISLKDE IKETTTESHS MCLPPIYDHD FVAAW LLLL KSFSRSVSAL RTTLKRNKIA QLLLQILSKT YTLTKECYFA GQDFMKPEIM IMGITLGSIC NFVVEFSNLQ SFMLRN GII DIIEKMLTDP LFNSKKAWDD NEDERRIALQ GIPVHEVKAN SLWVLRHLMY NCQNEEKFQL LAKIPMNLIL DFINDPC WA VQAQCFQLLR NLTCNSRKIV NILLEKFKDV EYKIDPQTGN KISIGSTYLF EFLAKKMRLL NPLDTQQKKA MEGILYII V NLAAVNENKK QLVIEQDEIL NIMSEILVET TTDSSSYGND SNLKLACLWV LNNLLWNSSV SHYTQYAIEN GLEPGHSPS DSENPQSTVT IGYNESVAGG YSRGKYYDEP DGDDSSSNAN DDEDDDNDEG DDEGDEFVRT PAAKGSTSNV QVTRATVERC RKLVEVGLY DLVRKNITDE SLSVREKART LLYHMDLLLK VK UniProtKB: GID complex subunit 5 |
-Macromolecule #2: Glucose-induced degradation protein 8
| Macromolecule | Name: Glucose-induced degradation protein 8 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.789152 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: MTISTLSNET TKSGSCSGQG KNGGKDFTYG KKCFTKEEWK EQVAKYSAMG ELYANKTIHY PLKIQPNSSG GSQDEGFATI QTTPIEPTL PRLLLNYFVS MAYEDSSIRM AKELGFIRNN KDIAVFNDLY KIKERFHIKH LIKLGRINEA MEEINSIFGL E VLEETFNA ...String: MTISTLSNET TKSGSCSGQG KNGGKDFTYG KKCFTKEEWK EQVAKYSAMG ELYANKTIHY PLKIQPNSSG GSQDEGFATI QTTPIEPTL PRLLLNYFVS MAYEDSSIRM AKELGFIRNN KDIAVFNDLY KIKERFHIKH LIKLGRINEA MEEINSIFGL E VLEETFNA TGSYTGRTDR QQQQQQQQFD IDGDLHFKLL LLNLIEMIRS HHQQENITKD SNDFILNLIQ YSQNKLAIKA SS SVKKMQE LELAMTLLLF PLSDSADSGS IKLPKSLQNL YSISLRSKIA DLVNEKLLKF IHPRIQFEIS NNNSKFPDLL NSD KKIITQ NFTVYNNNLV NGSNGTKITH ISSDQPINEK MSSNEVTAAA NSVWLNQRDG NVGTGSAATT FHNLENKNYW NQTS ELLSS SNGKEKGLEF NNYYSSEFPY EPRLTQIMKL WCWCENQLHH NQIGVPRVEN UniProtKB: GID complex subunit 8 |
-Macromolecule #3: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and de...
| Macromolecule | Name: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and ...Name: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30,Vacuolar import and degradation protein 30 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 117.308906 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: MSEYMDDVDR EFINCLFPSY LLQQPVAYDL WILYLQHRKL FHKLKNTNLI NADENPTGVG MGRTKLTALT RKEIWSKLMN LGVLGTISF EAVNDDYLIQ VYKYFYPDVN DFTLRFGVKD SNKNSVRVMK ASSDMRKNAQ ELLEPVLSER EMALNSNTSL E NDRNDDDD ...String: MSEYMDDVDR EFINCLFPSY LLQQPVAYDL WILYLQHRKL FHKLKNTNLI NADENPTGVG MGRTKLTALT RKEIWSKLMN LGVLGTISF EAVNDDYLIQ VYKYFYPDVN DFTLRFGVKD SNKNSVRVMK ASSDMRKNAQ ELLEPVLSER EMALNSNTSL E NDRNDDDD DDDDDDDDDD DDDDDDDESD LESLEGEVDT DTDDNNEGDG SDNHEEGGEE GSRGADADVS SAQQRAERVA DP WIYQRSR SAINIETESR NLWDTSDKNS GLQYYPPDQS PSSSFSSPRV SSGNDKNDNE ATNVLSNSGS KKKNSMIPDI YKI LGYFLP SRWQAQPNNS LQLSQDGITH LQPNPDYHSY MTYERSSASS ASTRNRLRTS FENSGKVDFA VTWANKSLPD NKLT IFYYE IKVLSVTSTE SAENSNIVIG YKLVENELME ATTKKSVSRS SVAGSSSSLG GSNNMSSNRV PSTSFTMEGT QRRDY IYEG GVSAMSLNVD GSINKCQKYG FDLNVFGYCG FDGLITNSTE QSKEYAKPFG RDDVIGCGIN FIDGSIFFTK NGIHLG NAF TDLNDLEFVP YVALRPGNSI KTNFGLNEDF VFDIIGYQDK WKSLAYEHIC RGRQMDVSIE EFDSDESEED ETENGPE EN KSTNVNEDLM DIDQEDGAAG NKDTKKLNDE KDNNLKFLLG EDNRFIDGKL VRPDVNNINN LSVDDGSLPN TLNVMIND Y LIHEGLVDVA KGFLKDLQKD AVNVNGQHSE SKDVIRHNER QIMKEERMVK IRQELRYLIN KGQISKCINY IDNEIPDLL KNNLELVFEL KLANYLVMIK KSSSKDDDEI ENLILKGQEL SNEFIYDTKI PQSLRDRFSG QLSNVSALLA YSNPLVEAPK EISGYLSDE YLQERLFQVS NNTILTFLHK DSECALENVI SNTRAMLSTL LEYNAFGSTN SSDPRYYKAI NFDEDVLNL (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) UniProtKB: GID complex subunit 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 24
| Macromolecule | Name: Vacuolar import and degradation protein 24 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.291934 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: MINNPKVDSV AEKPKAVTSK QSEQAASPEP TPAPPVSRNQ YPITFNLTST APFHLHDRHR YLQEQDLYKC ASRDSLSSLQ QLAHTPNGS TRKKYIVEDQ SPYSSENPVI VTSSYNHTVC TNYLRPRMQF TGYQISGYKR YQVTVNLKTV DLPKKDCTSL S PHLSGFLS ...String: MINNPKVDSV AEKPKAVTSK QSEQAASPEP TPAPPVSRNQ YPITFNLTST APFHLHDRHR YLQEQDLYKC ASRDSLSSLQ QLAHTPNGS TRKKYIVEDQ SPYSSENPVI VTSSYNHTVC TNYLRPRMQF TGYQISGYKR YQVTVNLKTV DLPKKDCTSL S PHLSGFLS IRGLTNQHPE ISTYFEAYAV NHKELGFLSS SWKDEPVLNE FKATDQTDLE HWINFPSFRQ LFLMSQKNGL NS TDDNGTT NAAKKLPPQQ LPTTPSADAG NISRIFSQEK QFDNYLNERF IFMKWKEKFL VPDALLMEGV DGASYDGFYY IVH DQVTGN IQGFYYHQDA EKFQQLELVP SLKNKVESSD CSFEFA UniProtKB: GID complex substrate-recognition subunit 4 |
-Macromolecule #5: Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein F...
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10,Protein FYV10 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.432879 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) Spodoptera aff. frugiperda 1 BOLD-2017 (butterflies/moths) |
| Sequence | String: MAEKSIFNEP DVDFHLKLNQ QLFHIPYELL SKRIKHTQAV INKETKSLHE HTAALNQIFE HNDVEHDELA LAKITEMIRK VDHIERFLN TQIKSYCQIL NRIKKRLEFF HELKDIKSQN SGTSHNGNNE GTRTKLIQWY QSYTNILIGD YLTRNNPIKY N SETKDHWN ...String: MAEKSIFNEP DVDFHLKLNQ QLFHIPYELL SKRIKHTQAV INKETKSLHE HTAALNQIFE HNDVEHDELA LAKITEMIRK VDHIERFLN TQIKSYCQIL NRIKKRLEFF HELKDIKSQN SGTSHNGNNE GTRTKLIQWY QSYTNILIGD YLTRNNPIKY N SETKDHWN SGVVFLKQSQ LDDLIDYDVL LEANRISTSL LHERNLLPLI SWINENKKTL TKKSSILEFQ ARLQEYIELL KV DNYTDAI VCFQRFLLPF VKSNFTDLKL ASGLLIFIKY CNDQKPTSST SSGFDTEEIK SQSLPMKKDR IFQHFFHKSL PRI TSKPAV NTTDYDKSSL INLQSGDFER YLNLLDDQRW SVLNDLFLSD FYSMYGISQN DPLLIYLSLG ISSLKTRDCL HPSD DENGN QETETATTAE KEVEDLQLFT LHSLKR(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) UniProtKB: GID complex subunit 9 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.25 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.5 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 54.48 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)