[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8oid: Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8oid | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ADP-bound, filamentous beta-actin harboring the N111S mutation | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Actin filament / cytoskeletal protein / ATPase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex ...positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / Regulation of CDH1 Function / Formation of the polybromo-BAF (pBAF) complex / Formation of the non-canonical BAF (ncBAF) complex / Formation of the canonical BAF (cBAF) complex / Formation of the embryonic stem cell BAF (esBAF) complex / Formation of neuronal progenitor and neuronal BAF (npBAF and nBAF) / bBAF complex / cellular response to cytochalasin B / npBAF complex / nBAF complex / brahma complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / protein localization to adherens junction / dense body / Tat protein binding / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / regulation of double-strand break repair / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Adherens junctions interactions / RHOF GTPase cycle / adherens junction assembly / apical protein localization / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / tight junction / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / apical junction complex / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / nitric-oxide synthase binding / transporter regulator activity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / Recycling pathway of L1 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / brush border / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / kinesin binding / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / cytoskeleton organization / substantia nigra development / axonogenesis / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis / actin filament / adherens junction / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell differentiation / cell motility / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / kinetochore / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / VEGFA-VEGFR2 Pathway / platelet aggregation / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / tau protein binding / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / nuclear matrix / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / cell-cell junction / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / UCH proteinases / nucleosome Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert, W. / Blanc, F.E.C. / Roy, A. / Belyy, A. / Hofnagel, O. / Hummer, G. / Bieling, P. / Raunser, S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3items Germany, European Union, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Molecular mechanisms of inorganic-phosphate release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Florian E C Blanc / Ankit Roy / Alexander Belyy / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Oliver Hofnagel / Gerhard Hummer / Peter Bieling / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release ...The release of inorganic phosphate (P) from actin filaments constitutes a key step in their regulated turnover, which is fundamental to many cellular functions. The mechanisms underlying P release from the core and barbed end of actin filaments remain unclear. Here, using human and bovine actin isoforms, we combine cryo-EM with molecular-dynamics simulations and in vitro reconstitution to demonstrate how actin releases P through a 'molecular backdoor'. While constantly open at the barbed end, the backdoor is predominantly closed in filament-core subunits and opens only transiently through concerted amino acid rearrangements. This explains why P escapes rapidly from the filament end but slowly from internal subunits. In a nemaline-myopathy-associated actin variant, the backdoor is predominantly open in filament-core subunits, resulting in accelerated P release and filaments with drastically shortened ADP-P caps. Our results provide the molecular basis for P release from actin and exemplify how a disease-linked mutation distorts the nucleotide-state distribution and atomic structure of the filament. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8oid.cif.gz 8oid.cif.gz | 405.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8oid.ent.gz pdb8oid.ent.gz | 277.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8oid.json.gz 8oid.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/8oid https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/8oid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/8oid ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oi/8oid | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 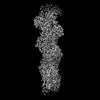 16889MC 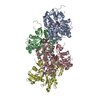 8oi6C 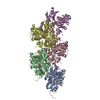 8oi8C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Ens-ID: ens_1
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj















