[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
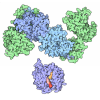
Yorodumi- PDB-8i7o: In situ structure of axonemal doublet microtubules in mouse sperm... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8i7o | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | In situ structure of axonemal doublet microtubules in mouse sperm with 16-nm repeat | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / microtubules / axoneme / sperm / filament | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmale germ-line stem cell population maintenance / axonemal microtubule doublet inner sheath / outer acrosomal membrane / regulation of brood size / establishment of left/right asymmetry / 9+0 motile cilium / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / axonemal B tubule inner sheath ...male germ-line stem cell population maintenance / axonemal microtubule doublet inner sheath / outer acrosomal membrane / regulation of brood size / establishment of left/right asymmetry / 9+0 motile cilium / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / axonemal B tubule inner sheath / axonemal A tubule inner sheath / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Intraflagellar transport / protein polyglutamylation / positive regulation of feeding behavior / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity / inner dynein arm assembly / sperm principal piece / regulation of cilium beat frequency involved in ciliary motility / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / 9+2 motile cilium / Kinesins / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / protein localization to organelle / cilium movement involved in cell motility / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / PKR-mediated signaling / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / acrosomal membrane / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Recycling pathway of L1 / axoneme assembly / microtubule sliding / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / axonemal microtubule / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Hedgehog 'off' state / cilium organization / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / manchette / MHC class II antigen presentation / flagellated sperm motility / cell projection organization / protein targeting to membrane / extrinsic component of membrane / positive regulation of cell motility / : / tubulin complex / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / ciliary base / protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / phosphatase activity / microtubule organizing center / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / mitotic cytokinesis / regulation of cell division / cilium assembly / glial cell projection / axoneme / cellular response to unfolded protein / spermatid development / single fertilization / alpha-tubulin binding / sperm flagellum / beta-tubulin binding / microtubule-based process / intercellular bridge / cytoplasmic microtubule / sperm midpiece / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-tyrosine-phosphatase / centriole / Hsp70 protein binding / acrosomal vesicle / protein tyrosine phosphatase activity / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / mitotic spindle organization / Hsp90 protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor binding / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / mitochondrial intermembrane space / SH3 domain binding / intracellular calcium ion homeostasis / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding / mitotic spindle / intracellular protein localization / myelin sheath / double-stranded RNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhu, Y. / Yin, G.L. / Tai, L.H. / Sun, F. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2023Title: In-cell structural insight into the stability of sperm microtubule doublet. Authors: Linhua Tai / Guoliang Yin / Xiaojun Huang / Fei Sun / Yun Zhu /  Abstract: The propulsion for mammalian sperm swimming is generated by flagella beating. Microtubule doublets (DMTs) along with microtubule inner proteins (MIPs) are essential structural blocks of flagella. ...The propulsion for mammalian sperm swimming is generated by flagella beating. Microtubule doublets (DMTs) along with microtubule inner proteins (MIPs) are essential structural blocks of flagella. However, the intricate molecular architecture of intact sperm DMT remains elusive. Here, by in situ cryo-electron tomography, we solved the in-cell structure of mouse sperm DMT at 4.5-7.5 Å resolutions, and built its model with 36 kinds of MIPs in 48 nm periodicity. We identified multiple copies of Tektin5 that reinforce Tektin bundle, and multiple MIPs with different periodicities that anchor the Tektin bundle to tubulin wall. This architecture contributes to a superior stability of A-tubule than B-tubule of DMT, which was revealed by structural comparison of DMTs from the intact and deformed axonemes. Our work provides an overall molecular picture of intact sperm DMT in 48 nm periodicity that is essential to understand the molecular mechanism of sperm motility as well as the related ciliopathies. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8i7o.cif.gz 8i7o.cif.gz | 11.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8i7o.ent.gz pdb8i7o.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8i7o.json.gz 8i7o.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i7/8i7o https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i7/8i7o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i7/8i7o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i7/8i7o | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  35229MC  8i7rC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 19 types, 179 molecules A2A3AEAGAIBEBGBICGCIDEDGEEEGFEFGGEGGGIHEHGHIIEIGIIJEJGKEKGKI...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48713.035 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 48689.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 61 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 47897.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 62 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | Mass: 50385.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 56754.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | Mass: 52121.449 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 23987.262 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | Mass: 62817.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | Mass: 36659.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | Mass: 23097.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | Mass: 21527.574 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: Q9D9D8, protein-serine/threonine phosphatase, protein-tyrosine-phosphatase #14: Protein | Mass: 57406.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #15: Protein | Mass: 29587.521 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #16: Protein | Mass: 16305.608 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #18: Protein | Mass: 20575.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #20: Protein | Mass: 176028.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #21: Protein | | Mass: 32786.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #23: Protein | Mass: 27763.268 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #24: Protein | Mass: 19512.373 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-EF-hand domain-containing ... , 2 types, 3 molecules G1G2G5
| #9: Protein | Mass: 75235.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | | Mass: 87758.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Cilia- and flagella-associated protein ... , 3 types, 7 molecules N2N3P1P2XCXDXE
| #17: Protein | Mass: 18960.092 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #19: Protein | Mass: 68322.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #22: Protein | Mass: 22781.389 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 123 molecules 
| #25: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: CELL / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: mouse sperm / Type: CELL / Entity ID: #1-#24 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 3 e/Å2 / Avg electron dose per subtomogram: 117 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: UCSF ChimeraX / Version: 1.6/v9 / Classification: model building / URL: https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ / Os: Windows / Type: package |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 37018 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| EM volume selection | Num. of tomograms: 689 / Num. of volumes extracted: 37018 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj