+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7yi1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Eaf3 CHD bound to H3K36me3 nucleosome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / Dynamic Histone Modifications / Histone Deacetylase Complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationTINTIN complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Rpd3S complex / regulation of RNA stability / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / nucleosome disassembly / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / : / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / histone reader activity ...TINTIN complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Rpd3S complex / regulation of RNA stability / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / nucleosome disassembly / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / : / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / histone reader activity / histone acetyltransferase complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / structural constituent of chromatin / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others)  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, H.T. / Yan, C.Y. / Guan, H.P. / Wang, P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4items China, 4items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Diverse modes of H3K36me3-guided nucleosomal deacetylation by Rpd3S. Authors: Haipeng Guan / Pei Wang / Pei Zhang / Chun Ruan / Yutian Ou / Bo Peng / Xiangdong Zheng / Jianlin Lei / Bing Li / Chuangye Yan / Haitao Li /  Abstract: Context-dependent dynamic histone modifications constitute a key epigenetic mechanism in gene regulation. The Rpd3 small (Rpd3S) complex recognizes histone H3 trimethylation on lysine 36 (H3K36me3) ...Context-dependent dynamic histone modifications constitute a key epigenetic mechanism in gene regulation. The Rpd3 small (Rpd3S) complex recognizes histone H3 trimethylation on lysine 36 (H3K36me3) and deacetylates histones H3 and H4 at multiple sites across transcribed regions. Here we solved the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpd3S in its free and H3K36me3 nucleosome-bound states. We demonstrated a unique architecture of Rpd3S, in which two copies of Eaf3-Rco1 heterodimers are asymmetrically assembled with Rpd3 and Sin3 to form a catalytic core complex. Multivalent recognition of two H3K36me3 marks, nucleosomal DNA and linker DNAs by Eaf3, Sin3 and Rco1 positions the catalytic centre of Rpd3 next to the histone H4 N-terminal tail for deacetylation. In an alternative catalytic mode, combinatorial readout of unmethylated histone H3 lysine 4 and H3K36me3 by Rco1 and Eaf3 directs histone H3-specific deacetylation except for the registered histone H3 acetylated lysine 9. Collectively, our work illustrates dynamic and diverse modes of multivalent nucleosomal engagement and methylation-guided deacetylation by Rpd3S, highlighting the exquisite complexity of epigenetic regulation with delicately designed multi-subunit enzymatic machineries in transcription and beyond. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7yi1.cif.gz 7yi1.cif.gz | 374.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7yi1.ent.gz pdb7yi1.ent.gz | 280 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7yi1.json.gz 7yi1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yi/7yi1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yi/7yi1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yi/7yi1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yi/7yi1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33848MC  7yi0C  7yi2C  7yi3C  7yi4C  7yi5C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 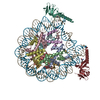
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules BFCGDHKLAE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 11263.231 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #2: Protein | Mass: 13978.241 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #3: Protein | Mass: 13524.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S29T Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #6: Protein | Mass: 45266.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #7: Protein | Mass: 15346.010 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Gene: LOC108703785, LOC121398065, LOC121398067, XELAEV_18002543mg Production host: synthetic construct (others) / References: UniProt: A0A310TTQ1 |
|---|
-Wisdom 601 DNA (167- ... , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 51308.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host: synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 51798.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host: synthetic construct (others) |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 723 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.7 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 1800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 427166 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj






































