[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7t4n: Structure of dimeric unphosphorylated Pediculus humanus (Ph) PINK... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7t4n | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
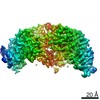
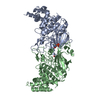
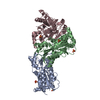
| Title | Structure of dimeric unphosphorylated Pediculus humanus (Ph) PINK1 D357A mutant | |||||||||
 Components Components | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1, putative | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / PINK1 / Kinase / Mitophagy / Parkinson's Disease / Ubiquitin / Phosphorylation / Phospho-ubiquitin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationautophagy of mitochondrion / positive regulation of mitochondrial fission / regulation of apoptotic process / mitochondrial outer membrane / protein kinase activity / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / mitochondrial inner membrane / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse) Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.35 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gan, Z.Y. / Leis, A. / Dewson, G. / Glukhova, A. / Komander, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, Australia,  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Activation mechanism of PINK1. Authors: Zhong Yan Gan / Sylvie Callegari / Simon A Cobbold / Thomas R Cotton / Michael J Mlodzianoski / Alexander F Schubert / Niall D Geoghegan / Kelly L Rogers / Andrew Leis / Grant Dewson / Alisa ...Authors: Zhong Yan Gan / Sylvie Callegari / Simon A Cobbold / Thomas R Cotton / Michael J Mlodzianoski / Alexander F Schubert / Niall D Geoghegan / Kelly L Rogers / Andrew Leis / Grant Dewson / Alisa Glukhova / David Komander /   Abstract: Mutations in the protein kinase PINK1 lead to defects in mitophagy and cause autosomal recessive early onset Parkinson's disease. PINK1 has many unique features that enable it to phosphorylate ...Mutations in the protein kinase PINK1 lead to defects in mitophagy and cause autosomal recessive early onset Parkinson's disease. PINK1 has many unique features that enable it to phosphorylate ubiquitin and the ubiquitin-like domain of Parkin. Structural analysis of PINK1 from diverse insect species with and without ubiquitin provided snapshots of distinct structural states yet did not explain how PINK1 is activated. Here we elucidate the activation mechanism of PINK1 using crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). A crystal structure of unphosphorylated Pediculus humanus corporis (Ph; human body louse) PINK1 resolves an N-terminal helix, revealing the orientation of unphosphorylated yet active PINK1 on the mitochondria. We further provide a cryo-EM structure of a symmetric PhPINK1 dimer trapped during the process of trans-autophosphorylation, as well as a cryo-EM structure of phosphorylated PhPINK1 undergoing a conformational change to an active ubiquitin kinase state. Structures and phosphorylation studies further identify a role for regulatory PINK1 oxidation. Together, our research delineates the complete activation mechanism of PINK1, illuminates how PINK1 interacts with the mitochondrial outer membrane and reveals how PINK1 activity may be modulated by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7t4n.cif.gz 7t4n.cif.gz | 154.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7t4n.ent.gz pdb7t4n.ent.gz | 118 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7t4n.json.gz 7t4n.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t4/7t4n https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t4/7t4n ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t4/7t4n ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t4/7t4n | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25681MC  7t3xC  7t4kC  7t4lC  7t4mC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52929.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: D357A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse) Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse)Gene: 8239562, Phum_PHUM577390 / Plasmid: pOPINK / Production host:  References: UniProt: E0W1I1, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dodecameric unphosphorylated Pediculus humanus (Ph) PINK1 D357A mutant Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.604 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse) Pediculus humanus corporis (human body louse) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 400 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.25 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 10 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1295406 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6EQI Pdb chain-ID: C / Accession code: 6EQI / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 54.59 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj

