+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 7kwo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001) | ||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | BLOOD CLOTTING / Complex / Hemophilia / FVIII / VWF | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報Defective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Weibel-Palade body / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor ...Defective F8 accelerates dissociation of the A2 domain / Defective F8 binding to the cell membrane / Defective F8 secretion / Gamma carboxylation, hypusinylation, hydroxylation, and arylsulfatase activation / Defective F8 sulfation at Y1699 / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / Weibel-Palade body / Defective F8 binding to von Willebrand factor / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen / Defective binding of VWF variant to GPIb:IX:V / hemostasis / blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway / platelet alpha granule / Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen / Cargo concentration in the ER / Defective factor IX causes thrombophilia / Defective cofactor function of FVIIIa variant / Defective F9 variant does not activate FX / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / p130Cas linkage to MAPK signaling for integrins / cell-substrate adhesion / COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle / Defective F8 cleavage by thrombin / Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) / immunoglobulin binding / GRB2:SOS provides linkage to MAPK signaling for Integrins / Integrin cell surface interactions / Common Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / collagen binding / Intrinsic Pathway of Fibrin Clot Formation / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / Integrin signaling / extracellular matrix / platelet alpha granule lumen / acute-phase response / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / platelet activation / response to wounding / Golgi lumen / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / blood coagulation / integrin binding / Platelet degranulation / signaling receptor activity / protein-folding chaperone binding / collagen-containing extracellular matrix / protease binding / oxidoreductase activity / cell adhesion / copper ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / endoplasmic reticulum / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding / plasma membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.9 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Fuller, J.R. / Batchelor, J.D. | ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Blood / 年: 2021 ジャーナル: Blood / 年: 2021タイトル: Molecular determinants of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor complex revealed by BIVV001 cryo-electron microscopy. 著者: James R Fuller / Kevin E Knockenhauer / Nina C Leksa / Robert T Peters / Joseph D Batchelor 要旨: Interaction of factor VIII (FVIII) with von Willebrand factor (VWF) is mediated by the VWF D'D3 domains and thrombin-mediated release is essential for hemostasis after vascular injury. VWF-D'D3 ...Interaction of factor VIII (FVIII) with von Willebrand factor (VWF) is mediated by the VWF D'D3 domains and thrombin-mediated release is essential for hemostasis after vascular injury. VWF-D'D3 mutations resulting in loss of FVIII binding are the underlying cause of von Willebrand disease (VWD) type 2N. Furthermore, the FVIII-VWF interaction has significant implications for the development of therapeutics for bleeding disorders, particularly hemophilia A, in which endogenous VWF clearance imposes a half-life ceiling on replacement FVIII therapy. To understand the structural basis of FVIII engagement by VWF, we solved the structure of BIVV001 by cryo-electron microscopy to 2.9 Å resolution. BIVV001 is a bioengineered clinical-stage FVIII molecule for the treatment of hemophilia A. In BIVV001, VWF-D'D3 is covalently linked to an Fc domain of a B domain-deleted recombinant FVIII (rFVIII) Fc fusion protein, resulting in a stabilized rFVIII/VWF-D'D3 complex. Our rFVIII/VWF structure resolves BIVV001 architecture and provides a detailed spatial understanding of previous biochemical and clinical observations related to FVIII-VWF engagement. Notably, the FVIII acidic a3 peptide region (FVIII-a3), established as a critical determinant of FVIII/VWF complex formation, inserts into a basic groove formed at the VWF-D'/rFVIII interface. Our structure shows direct interaction of sulfated Y1680 in FVIII-a3 and VWF-R816 that, when mutated, leads to severe hemophilia A or VWD type 2N, respectively. These results provide insight on this key coagulation complex, explain the structural basis of many hemophilia A and VWD type 2N mutations, and inform studies to further elucidate how VWF dissociates rapidly from FVIII upon activation. #1:  ジャーナル: Comput. Cryst. Newsl. / 年: 2013 ジャーナル: Comput. Cryst. Newsl. / 年: 2013タイトル: New tool: phenix.real_space_refine 著者: Afonine, P.V. / Headd, J.J. / Terwilliger, T.C. / Adams, P.D. #2: ジャーナル: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / 年: 2019 タイトル: Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. 著者: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / ...著者: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert D Oeffner / Billy K Poon / Michael G Prisant / Randy J Read / Jane S Richardson / David C Richardson / Massimo D Sammito / Oleg V Sobolev / Duncan H Stockwell / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre G Urzhumtsev / Lizbeth L Videau / Christopher J Williams / Paul D Adams /    要旨: Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological ...Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological processes and to develop new therapeutics against diseases. The overall structure-solution workflow is similar for these techniques, but nuances exist because the properties of the reduced experimental data are different. Software tools for structure determination should therefore be tailored for each method. Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination that handles data from any of these techniques. Tasks performed with Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle and deposition. Each tool caters to the type of experimental data. The design of Phenix emphasizes the automation of procedures, where possible, to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default parameters are chosen to encourage best practice. A graphical user interface provides access to many command-line features of Phenix and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking and re-running of previous tasks. #3:  ジャーナル: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / 年: 2018 ジャーナル: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / 年: 2018タイトル: ISOLDE: a physically realistic environment for model building into low-resolution electron-density maps. 著者: Tristan Ian Croll /  要旨: This paper introduces ISOLDE, a new software package designed to provide an intuitive environment for high-fidelity interactive remodelling/refinement of macromolecular models into electron-density ...This paper introduces ISOLDE, a new software package designed to provide an intuitive environment for high-fidelity interactive remodelling/refinement of macromolecular models into electron-density maps. ISOLDE combines interactive molecular-dynamics flexible fitting with modern molecular-graphics visualization and established structural biology libraries to provide an immersive interface wherein the model constantly acts to maintain physically realistic conformations as the user interacts with it by directly tugging atoms with a mouse or haptic interface or applying/removing restraints. In addition, common validation tasks are accelerated and visualized in real time. Using the recently described 3.8 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the eukaryotic minichromosome maintenance (MCM) helicase complex as a case study, it is demonstrated how ISOLDE can be used alongside other modern refinement tools to avoid common pitfalls of low-resolution modelling and improve the quality of the final model. A detailed analysis of changes between the initial and final model provides a somewhat sobering insight into the dangers of relying on a small number of validation metrics to judge the quality of a low-resolution model. #4: ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2016 タイトル: Automated structure refinement of macromolecular assemblies from cryo-EM maps using Rosetta. 著者: Ray Yu-Ruei Wang / Yifan Song / Benjamin A Barad / Yifan Cheng / James S Fraser / Frank DiMaio /  要旨: Cryo-EM has revealed the structures of many challenging yet exciting macromolecular assemblies at near-atomic resolution (3-4.5Å), providing biological phenomena with molecular descriptions. ...Cryo-EM has revealed the structures of many challenging yet exciting macromolecular assemblies at near-atomic resolution (3-4.5Å), providing biological phenomena with molecular descriptions. However, at these resolutions, accurately positioning individual atoms remains challenging and error-prone. Manually refining thousands of amino acids - typical in a macromolecular assembly - is tedious and time-consuming. We present an automated method that can improve the atomic details in models that are manually built in near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM maps. Applying the method to three systems recently solved by cryo-EM, we are able to improve model geometry while maintaining the fit-to-density. Backbone placement errors are automatically detected and corrected, and the refinement shows a large radius of convergence. The results demonstrate that the method is amenable to structures with symmetry, of very large size, and containing RNA as well as covalently bound ligands. The method should streamline the cryo-EM structure determination process, providing accurate and unbiased atomic structure interpretation of such maps. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  7kwo.cif.gz 7kwo.cif.gz | 354.9 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb7kwo.ent.gz pdb7kwo.ent.gz | 261.6 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  7kwo.json.gz 7kwo.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  7kwo_validation.pdf.gz 7kwo_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  7kwo_full_validation.pdf.gz 7kwo_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  7kwo_validation.xml.gz 7kwo_validation.xml.gz | 63.9 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  7kwo_validation.cif.gz 7kwo_validation.cif.gz | 95.2 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kw/7kwo https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kw/7kwo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kw/7kwo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kw/7kwo | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 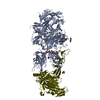
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-タンパク質 , 2種, 2分子 AV
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 218874.969 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P00451*PLUS Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P00451*PLUS |
|---|---|
| #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 179048.953 Da / 分子数: 1 / Mutation: C1099A, C1142A / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P04275*PLUS Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P04275*PLUS |
-糖 , 2種, 4分子 
| #3: 多糖 | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose |
|---|---|
| #4: 糖 |
-非ポリマー , 3種, 4分子 




| #5: 化合物 | | #6: 化合物 | ChemComp-ZN / | #7: 化合物 | ChemComp-CU / | |
|---|
-詳細
| 構成要素の詳細 | Coagulation factor FVIII-Fc-XTEN is fusion protein of human coagulation factor VIII (Uniprot: ...Coagulation factor FVIII-Fc-XTEN is fusion protein of human coagulation factor VIII (Uniprot: P00451), XTEN polypeptide, and Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 (UniProt: P01857). von Willebrand factor-XTEN-Fc is fusion protein of human von Willebrand factor (VWF) (Uniprot: P04275), XTEN polypeptide, and Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 (UniProt: P01857). |
|---|---|
| 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | Y |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: rFVIIIFc-VWF-XTEN (BIVV001) / タイプ: COMPLEX 詳細: An engineered therapeutic complex between coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor D'D3 Entity ID: #1-#2 / 由来: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.31164974 MDa / 実験値: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液成分 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | Experiment-ID: 1 / 濃度: 0.75 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES / 詳細: Prepared by gel filtration chromatography immediately prior to vitrification.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料支持 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 |
|
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 倍率(公称値): 81000 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2600 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 1200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / アライメント法: COMA FREE |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 40 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| 電子光学装置 | エネルギーフィルター名称: GIF Bioquantum / エネルギーフィルタースリット幅: 20 eV |
| 画像スキャン | 横: 11520 / 縦: 8184 |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 画像処理 | 詳細: Micrograph movies were motion-corrected and dose-weighted using Relion 3.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C1 (非対称) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 2.9 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 116200 / クラス平均像の数: 1 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | プロトコル: FLEXIBLE FIT / 空間: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 精密化 | 交差検証法: NONE 立体化学のターゲット値: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子変位パラメータ | Biso mean: 32.14 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー












 PDBj
PDBj























