[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
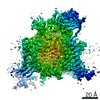
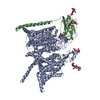
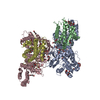
Yorodumi- PDB-6xiw: Cryo-EM structure of the sodium leak channel NALCN-FAM155A complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6xiw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the sodium leak channel NALCN-FAM155A complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ion channel / complex / cysteine rich domain | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium channel activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / monoatomic cation channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sodium ion transmembrane transport ...positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium channel activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / monoatomic cation channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sodium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / calcium ion transmembrane transport / Stimuli-sensing channels / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kschonsak, M. / Chua, H.C. / Noland, C.L. / Weidling, C. / Clairfeuille, T. / Bahlke, O.O. / Ameen, A.O. / Li, Z.R. / Arthur, C.P. / Ciferri, C. ...Kschonsak, M. / Chua, H.C. / Noland, C.L. / Weidling, C. / Clairfeuille, T. / Bahlke, O.O. / Ameen, A.O. / Li, Z.R. / Arthur, C.P. / Ciferri, C. / Pless, S.A. / Payandeh, J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the human sodium leak channel NALCN. Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Cameron L Noland / Claudia Weidling / Thomas Clairfeuille / Oskar Ørts Bahlke / Aishat Oluwanifemi Ameen / Zhong Rong Li / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio ...Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Cameron L Noland / Claudia Weidling / Thomas Clairfeuille / Oskar Ørts Bahlke / Aishat Oluwanifemi Ameen / Zhong Rong Li / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio Ciferri / Stephan Alexander Pless / Jian Payandeh /   Abstract: Persistently depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents enhance electrical excitability. The ion channel responsible for the major background Na conductance in neurons is the Na leak channel, non- ...Persistently depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents enhance electrical excitability. The ion channel responsible for the major background Na conductance in neurons is the Na leak channel, non-selective (NALCN). NALCN-mediated currents regulate neuronal excitability linked to respiration, locomotion and circadian rhythm. NALCN activity is under tight regulation and mutations in NALCN cause severe neurological disorders and early death. NALCN is an orphan channel in humans, and fundamental aspects of channel assembly, gating, ion selectivity and pharmacology remain obscure. Here we investigate this essential leak channel and determined the structure of NALCN in complex with a distinct auxiliary subunit, family with sequence similarity 155 member A (FAM155A). FAM155A forms an extracellular dome that shields the ion-selectivity filter from neurotoxin attack. The pharmacology of NALCN is further delineated by a walled-off central cavity with occluded lateral pore fenestrations. Unusual voltage-sensor domains with asymmetric linkages to the pore suggest mechanisms by which NALCN activity is modulated. We found a tightly closed pore gate in NALCN where the majority of missense patient mutations cause gain-of-function phenotypes that cluster around the S6 gate and distinctive π-bulges. Our findings provide a framework to further study the physiology of NALCN and a foundation for discovery of treatments for NALCN channelopathies and other electrical disorders. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6xiw.cif.gz 6xiw.cif.gz | 292.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6xiw.ent.gz pdb6xiw.ent.gz | 220.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6xiw.json.gz 6xiw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xi/6xiw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xi/6xiw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xi/6xiw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xi/6xiw | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22203MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 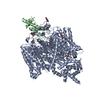
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 206341.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: TYR287 modeled with sulfonation (TYS) as the EM density indicates a post-translational modification of this residue. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NALCN, VGCNL1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NALCN, VGCNL1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8IZF0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8IZF0 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 54205.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FAM155A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FAM155A / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B1AL88 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: B1AL88 |
-Sugars , 1 types, 2 molecules 
| #3: Sugar |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 15 molecules 
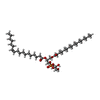





| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-PEV / ( #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: NALCN in complex with FAM155A / Type: COMPLEX Details: NALCN, FAM155A, UNC80 and UNC79 co-expressed and NALCN-FAM155A co-purified Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: sample was gently cross-linked with 0.05% EM-grade glutaraldehyde for 10 min at room temperature and quenched with 0.09 M TRIS pH 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 49.967 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 15080 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 50 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1778009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 365512 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj