+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6usj | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
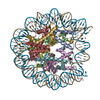
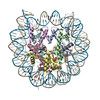
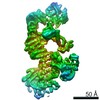
| Title | Structure of two nucleosomes bridged by human PARP2 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / PARP2 / Nucleosome / Complex / Bridging / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to oxygen-glucose deprivation / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / poly-ADP-D-ribose binding / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / NAD+-protein-serine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA ADP-ribosylation / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase ...response to oxygen-glucose deprivation / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / poly-ADP-D-ribose binding / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / NAD+-protein-serine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA ADP-ribosylation / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase / protein auto-ADP-ribosylation / NAD+-protein-aspartate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / protein poly-ADP-ribosylation / NAD+-protein-glutamate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / NAD+-protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / decidualization / Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases / POLB-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / site of DNA damage / NAD+ poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / nucleotidyltransferase activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / base-excision repair / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / double-strand break repair / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Gaullier, G. / Bowerman, S. / Luger, K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2020 Journal: PLoS One / Year: 2020Title: Bridging of nucleosome-proximal DNA double-strand breaks by PARP2 enhances its interaction with HPF1. Authors: Guillaume Gaullier / Genevieve Roberts / Uma M Muthurajan / Samuel Bowerman / Johannes Rudolph / Jyothi Mahadevan / Asmita Jha / Purushka S Rae / Karolin Luger /  Abstract: Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase 2 (PARP2) is one of three DNA-dependent PARPs involved in the detection of DNA damage. Upon binding to DNA double-strand breaks, PARP2 uses nicotinamide adenine ...Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase 2 (PARP2) is one of three DNA-dependent PARPs involved in the detection of DNA damage. Upon binding to DNA double-strand breaks, PARP2 uses nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to synthesize poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) onto itself and other proteins, including histones. PAR chains in turn promote the DNA damage response by recruiting downstream repair factors. These early steps of DNA damage signaling are relevant for understanding how genome integrity is maintained and how their failure leads to genome instability or cancer. There is no structural information on DNA double-strand break detection in the context of chromatin. Here we present a cryo-EM structure of two nucleosomes bridged by human PARP2 and confirm that PARP2 bridges DNA ends in the context of nucleosomes bearing short linker DNA. We demonstrate that the conformation of PARP2 bound to damaged chromatin provides a binding platform for the regulatory protein Histone PARylation Factor 1 (HPF1), and that the resulting HPF1•PARP2•nucleosome complex is enzymatically active. Our results contribute to a structural view of the early steps of the DNA damage response in chromatin. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6usj.cif.gz 6usj.cif.gz | 672.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6usj.ent.gz pdb6usj.ent.gz | 485.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6usj.json.gz 6usj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/us/6usj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/us/6usj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/us/6usj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/us/6usj | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 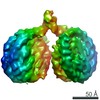 20864MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10336 (Title: Structure of two nucleosomes bridged by human PARP2 / Data size: 677.3 EMPIAR-10336 (Title: Structure of two nucleosomes bridged by human PARP2 / Data size: 677.3 Data #1: Single-particle images of the PARP2-nucleosome complex [picked particles - single frame - unprocessed] Data #2: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs of the PARP2-nucleosome complex [micrographs - multiframe]) |
| Experimental dataset #1 | Data reference:  10.6019/EMPIAR-10336 / Data set type: EMPIAR / Details: EMPIAR-10336 10.6019/EMPIAR-10336 / Data set type: EMPIAR / Details: EMPIAR-10336 |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Widom 601 DNA (160- ... , 2 types, 4 molecules ISJT
| #1: DNA chain | Mass: 51141.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Widom 601 nucleosome positioning sequence with 7 and 11 additional terminal base pairs Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  #2: DNA chain | Mass: 50732.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|
-Protein , 5 types, 18 molecules AEKOBFLPCGMQDHNRUV
| #3: Protein | Mass: 15719.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 11676.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H4C1, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4A, H4C2, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4B, H4C3, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4C, H4C4, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4D, H4C5, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4E, H4C6, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4F, H4C8, H4/H, H4FH, ...Gene: H4C1, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4A, H4C2, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4B, H4C3, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4C, H4C4, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4D, H4C5, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4E, H4C6, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4F, H4C8, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4H, H4C9, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4I, H4C11, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4J, H4C12, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4K, H4C13, H4/K, H4FK, HIST1H4L, H4C14, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4A, H4C15, H4/O, H4FO, HIST2H4B, H4-16, HIST4H4 Production host:  #5: Protein | Mass: 14447.825 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, HIST1H2AE, hCG_1640984, hCG_1787383 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, HIST1H2AE, hCG_1640984, hCG_1787383 / Production host:  #6: Protein | Mass: 14217.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ, H2BFR / Production host:  #7: Protein | Mass: 67069.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: Q112R, F113D Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARP2, ADPRT2, ADPRTL2 / Variant: Isoform 2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARP2, ADPRT2, ADPRTL2 / Variant: Isoform 2 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9UGN5, NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase, Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.554959 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: Buffer was pH-adjusted and filtered through a 0.22 um filter. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Blot time 2s, blot force 0 |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN Specimen holder model: GATAN 626 SINGLE TILT LIQUID NITROGEN CRYO TRANSFER HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4 sec. / Electron dose: 56.1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 632 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 226250 Details: Picked using crYOLO version 1.3.1 with a model trained on the same dataset (with the generic model provided with crYOLO used as pre-trained weights). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 10.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 27889 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Real-space CC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 224.79 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj