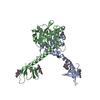
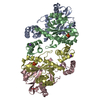
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6rwn | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | SIVrcm intasome in complex with dolutegravir | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RECOMBINATION / retroviral integrase / lentivirus / strand transfer inhibior / protein-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexoribonuclease H activity / DNA integration / viral genome integration into host DNA / establishment of integrated proviral latency / RNA stem-loop binding / viral penetration into host nucleus / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / host cell / viral nucleocapsid ...exoribonuclease H activity / DNA integration / viral genome integration into host DNA / establishment of integrated proviral latency / RNA stem-loop binding / viral penetration into host nucleus / RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / RNA-DNA hybrid ribonuclease activity / host cell / viral nucleocapsid / DNA recombination / aspartic-type endopeptidase activity / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host gene expression / viral translational frameshifting / symbiont entry into host cell / host cell nucleus / host cell plasma membrane / proteolysis / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Simian immunodeficiency virus Simian immunodeficiency virus | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cherepanov, P. / Nans, A. / Cook, N. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Structural basis of second-generation HIV integrase inhibitor action and viral resistance. Authors: Nicola J Cook / Wen Li / Dénes Berta / Magd Badaoui / Allison Ballandras-Colas / Andrea Nans / Abhay Kotecha / Edina Rosta / Alan N Engelman / Peter Cherepanov /    Abstract: Although second-generation HIV integrase strand-transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are prescribed throughout the world, the mechanistic basis for the superiority of these drugs is poorly understood. We ...Although second-generation HIV integrase strand-transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are prescribed throughout the world, the mechanistic basis for the superiority of these drugs is poorly understood. We used single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to visualize the mode of action of the advanced INSTIs dolutegravir and bictegravir at near-atomic resolution. Glutamine-148→histidine (Q148H) and glycine-140→serine (G140S) amino acid substitutions in integrase that result in clinical INSTI failure perturb optimal magnesium ion coordination in the enzyme active site. The expanded chemical scaffolds of second-generation compounds mediate interactions with the protein backbone that are critical for antagonizing viruses containing the Q148H and G140S mutations. Our results reveal that binding to magnesium ions underpins a fundamental weakness of the INSTI pharmacophore that is exploited by the virus to engender resistance and provide a structural framework for the development of this class of anti-HIV/AIDS therapeutics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6rwn.cif.gz 6rwn.cif.gz | 423.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6rwn.ent.gz pdb6rwn.ent.gz | 336.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6rwn.json.gz 6rwn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rw/6rwn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rw/6rwn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rw/6rwn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rw/6rwn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 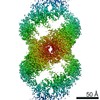 10043MC 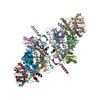 6rwlC  6rwmC  6rwoC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 12 molecules AENLKJIMFDCB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 32732.182 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Mutation: A119D Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: pol / Variant: red capped mangabey isolate from Cameroon / Production host: Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: pol / Variant: red capped mangabey isolate from Cameroon / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 4 molecules QSWT
| #2: DNA chain | Mass: 10134.541 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: U5 LTR vDNA end / Variant: SIVrcmNg409 / Production host: synthetic construct (others) Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: U5 LTR vDNA end / Variant: SIVrcmNg409 / Production host: synthetic construct (others)#3: DNA chain | Mass: 9223.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: U5 LTR vDNA end / Variant: SIVrcmNg409 / Production host: synthetic construct (others) Simian immunodeficiency virus / Gene: U5 LTR vDNA end / Variant: SIVrcmNg409 / Production host: synthetic construct (others) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 24 molecules 

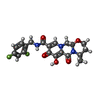






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1600 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.4 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 6838 |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 30 / Used frames/image: 1-30 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 18302 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj