+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6qvj | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | HsCKK (human CAMSAP1) decorated 14pf taxol-GDP microtubule | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Microtubule CAMSAP Calmodulin-regulated spectrum-associated proteins CKK Cryo-EM Cryo-Electron Microscopy | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule minus-end binding / odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Intraflagellar transport / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC ...microtubule minus-end binding / odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Intraflagellar transport / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly / Kinesins / regulation of cell morphogenesis / GTPase activating protein binding / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / spectrin binding / regulation of synapse organization / nuclear envelope lumen / Recycling pathway of L1 / MHC class I protein binding / regulation of microtubule polymerization / RHOH GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / microtubule-based process / Hedgehog 'off' state / intercellular bridge / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / spindle assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoskeleton organization / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / cellular response to interleukin-4 / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / PKR-mediated signaling / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / neuron projection development / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / azurophil granule lumen / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell body / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Potential therapeutics for SARS / microtubule / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / cilium / membrane raft / protein domain specific binding / cell division / GTPase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / protein-containing complex / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Atherton, J.M. / Luo, Y. / Xiang, S. / Yang, C. / Jiang, K. / Stangier, M. / Vemu, A. / Cook, A. / Wang, S. / Roll-Mecak, A. ...Atherton, J.M. / Luo, Y. / Xiang, S. / Yang, C. / Jiang, K. / Stangier, M. / Vemu, A. / Cook, A. / Wang, S. / Roll-Mecak, A. / Steinmetz, M.O. / Akhmanova, A. / Baldus, M. / Moores, C.A. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Netherlands, Netherlands,  Switzerland, 6items Switzerland, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Structural determinants of microtubule minus end preference in CAMSAP CKK domains. Authors: Joseph Atherton / Yanzhang Luo / Shengqi Xiang / Chao Yang / Ankit Rai / Kai Jiang / Marcel Stangier / Annapurna Vemu / Alexander D Cook / Su Wang / Antonina Roll-Mecak / Michel O Steinmetz ...Authors: Joseph Atherton / Yanzhang Luo / Shengqi Xiang / Chao Yang / Ankit Rai / Kai Jiang / Marcel Stangier / Annapurna Vemu / Alexander D Cook / Su Wang / Antonina Roll-Mecak / Michel O Steinmetz / Anna Akhmanova / Marc Baldus / Carolyn A Moores /      Abstract: CAMSAP/Patronins regulate microtubule minus-end dynamics. Their end specificity is mediated by their CKK domains, which we proposed recognise specific tubulin conformations found at minus ends. To ...CAMSAP/Patronins regulate microtubule minus-end dynamics. Their end specificity is mediated by their CKK domains, which we proposed recognise specific tubulin conformations found at minus ends. To critically test this idea, we compared the human CAMSAP1 CKK domain (HsCKK) with a CKK domain from Naegleria gruberi (NgCKK), which lacks minus-end specificity. Here we report near-atomic cryo-electron microscopy structures of HsCKK- and NgCKK-microtubule complexes, which show that these CKK domains share the same protein fold, bind at the intradimer interprotofilament tubulin junction, but exhibit different footprints on microtubules. NMR experiments show that both HsCKK and NgCKK are remarkably rigid. However, whereas NgCKK binding does not alter the microtubule architecture, HsCKK remodels its microtubule interaction site and changes the underlying polymer structure because the tubulin lattice conformation is not optimal for its binding. Thus, in contrast to many MAPs, the HsCKK domain can differentiate subtly specific tubulin conformations to enable microtubule minus-end recognition. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6qvj.cif.gz 6qvj.cif.gz | 332.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6qvj.ent.gz pdb6qvj.ent.gz | 268 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6qvj.json.gz 6qvj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6qvj_validation.pdf.gz 6qvj_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6qvj_full_validation.pdf.gz 6qvj_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6qvj_validation.xml.gz 6qvj_validation.xml.gz | 51.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6qvj_validation.cif.gz 6qvj_validation.cif.gz | 77.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/6qvj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/6qvj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/6qvj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qv/6qvj | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4654MC  4643C  4644C  4650C  6qusC  6quyC  6qveC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 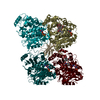
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 5 molecules IOXSU
| #1: Protein | Mass: 19628.666 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAMSAP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAMSAP1 / Production host:  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 50204.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: GTP / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: tsa201 cells / Tissue: Embryonic Kidney / References: UniProt: P68363 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: tsa201 cells / Tissue: Embryonic Kidney / References: UniProt: P68363#3: Protein | Mass: 49717.629 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Details: GDP Taxol / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: tsa201 / Tissue: embryonic kidney / References: UniProt: P07437 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: tsa201 / Tissue: embryonic kidney / References: UniProt: P07437 |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 8 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.8 / Details: BRB20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Details: dose weighted images used in final reconstructions |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.11.1_2575: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 33419 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj
































