[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4uxt: Conserved mechanisms of microtubule-stimulated ADP release, ATP b... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4uxt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
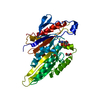
| Title | Conserved mechanisms of microtubule-stimulated ADP release, ATP binding, and force generation in transport kinesins | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed kinesin ATPase / anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex / retrograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde axonal protein transport / ciliary rootlet / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex ...plus-end-directed kinesin ATPase / anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex / retrograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / anterograde axonal protein transport / ciliary rootlet / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / Kinesins / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / positive regulation of axon guidance / kinesin complex / microtubule motor activity / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule-based movement / Insulin processing / synaptic vesicle transport / cytoskeletal motor activity / kinesin binding / postsynaptic cytosol / microtubule-based process / cytoplasmic microtubule / vesicle-mediated transport / axon cytoplasm / MHC class II antigen presentation / dendrite cytoplasm / cellular response to interleukin-4 / axon guidance / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / neuron migration / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / microtubule binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / chemical synaptic transmission / microtubule / perikaryon / cilium / protein heterodimerization activity / GTPase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / GTP binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  HOMO SAPIENS (human) HOMO SAPIENS (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.4 Å | ||||||
| Model type details | CA ATOMS ONLY, CHAIN A, B, C | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Atherton, J. / Farabella, I. / Yu, I.M. / Rosenfeld, S.S. / Houdusse, A. / Topf, M. / Moores, C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2014 Journal: Elife / Year: 2014Title: Conserved mechanisms of microtubule-stimulated ADP release, ATP binding, and force generation in transport kinesins. Authors: Joseph Atherton / Irene Farabella / I-Mei Yu / Steven S Rosenfeld / Anne Houdusse / Maya Topf / Carolyn A Moores /    Abstract: Kinesins are a superfamily of microtubule-based ATP-powered motors, important for multiple, essential cellular functions. How microtubule binding stimulates their ATPase and controls force generation ...Kinesins are a superfamily of microtubule-based ATP-powered motors, important for multiple, essential cellular functions. How microtubule binding stimulates their ATPase and controls force generation is not understood. To address this fundamental question, we visualized microtubule-bound kinesin-1 and kinesin-3 motor domains at multiple steps in their ATPase cycles--including their nucleotide-free states--at ∼ 7 Å resolution using cryo-electron microscopy. In both motors, microtubule binding promotes ordered conformations of conserved loops that stimulate ADP release, enhance microtubule affinity and prime the catalytic site for ATP binding. ATP binding causes only small shifts of these nucleotide-coordinating loops but induces large conformational changes elsewhere that allow force generation and neck linker docking towards the microtubule plus end. Family-specific differences across the kinesin-microtubule interface account for the distinctive properties of each motor. Our data thus provide evidence for a conserved ATP-driven mechanism for kinesins and reveal the critical mechanistic contribution of the microtubule interface. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4uxt.cif.gz 4uxt.cif.gz | 65.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4uxt.ent.gz pdb4uxt.ent.gz | 34.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4uxt.json.gz 4uxt.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/4uxt https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/4uxt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/4uxt ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/4uxt | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2769MC  2765C  2766C  2767C  2768C  2770C  2771C  4uxoC  4uxpC  4uxrC  4uxsC  4uxyC  4uy0C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 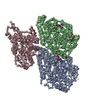
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 50107.238 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 49907.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 38030.184 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: MOTOR DOMAIN, UNP RESIDUES 1-340 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PET151-D-TOPO / Production host: HOMO SAPIENS (human) / Plasmid: PET151-D-TOPO / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 5 molecules 








| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / |
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-TA1 / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 13-PROTOFILAMENT MICROTUBULE-BOUND HUMAN KINESIN-1 MOTOR DOMAIN IN ABSENCE OF NUCLEOTIDES Type: COMPLEX |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20MM PIPES, 2MM MGCL2, 1MM EGTA, 2MM DTT, 10 U/ML APYRASE pH: 6.8 Details: 20MM PIPES, 2MM MGCL2, 1MM EGTA, 2MM DTT, 10 U/ML APYRASE |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: HOLEY CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: LIQUID ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 / Date: Dec 10, 2012 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Calibrated magnification: 100000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 400 nm / Cs: 2.3 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 90 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 497 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: FREALIGN | |||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.4 Å / Num. of particles: 168974 / Actual pixel size: 1.5 Å Details: SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-2769. (DEPOSITION ID: 12602). Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient / Details: METHOD--FLEXIBLE REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--X-RAY | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 1BG2 Accession code: 1BG2 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | |||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 7.4 Å | |||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 7.4 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj